Abstract
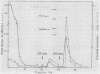
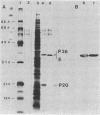
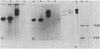
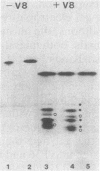
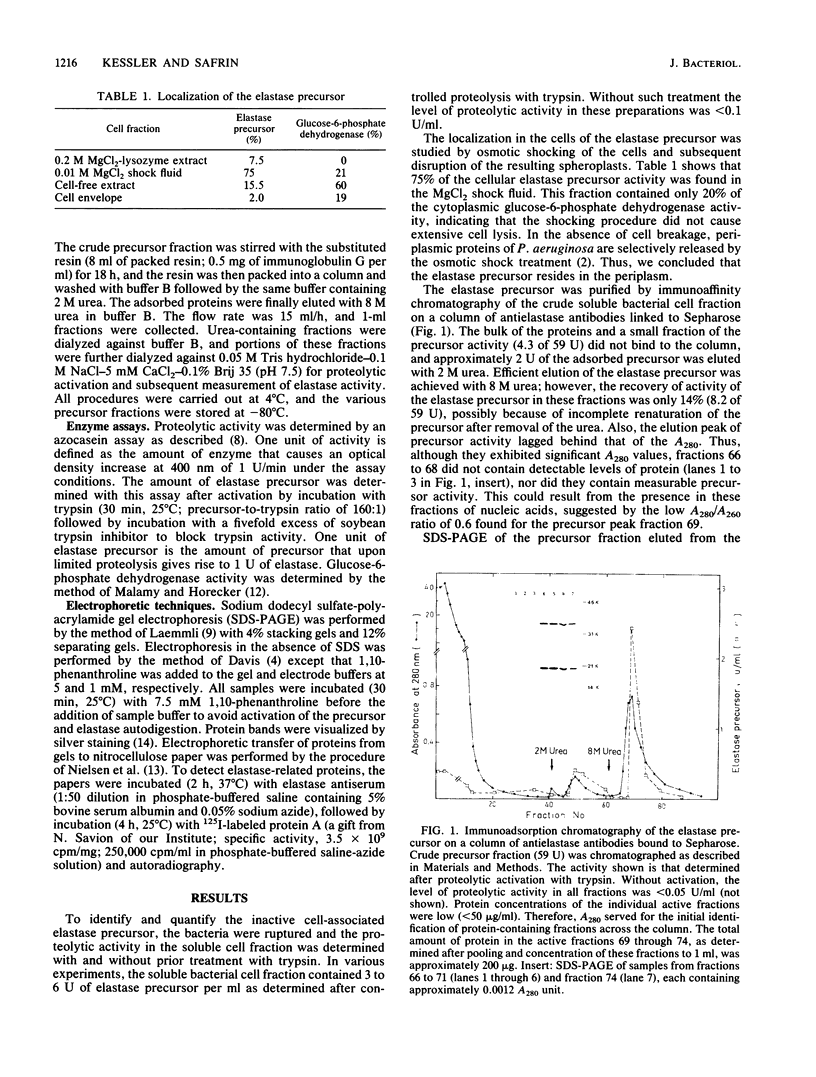
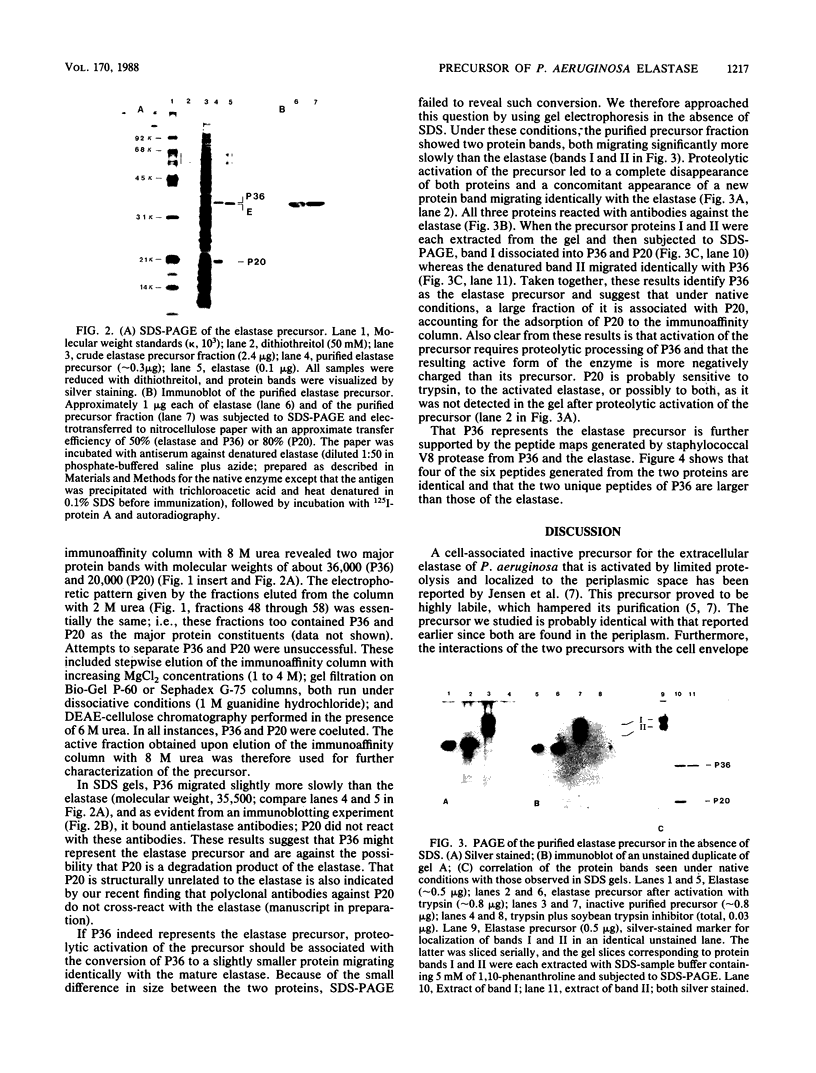
An inactive precursor of the extracellular elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was extensively purified by immunoadsorption chromatography of the soluble bacterial cell fraction on a column of Sepharose coupled to antielastase antibodies. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified precursor fraction revealed two major protein bands with molecular weights of about 36,000 (P36) and 20,000 (P20) that in the absence of sodium dodecyl sulfate were associated with each other. The following findings identify P36 as the elastase precursor and indicate that proteolytic processing of this molecule is required for activation: (i) P36 is larger than the elastase, and it binds antielastase antibodies; (ii) trypsin activation is associated with the disappearance of P36 and the appearance of a new protein band migrating identically with the elastase and reacting with antibodies against the elastase; (iii) peptide maps generated from P36 and the elastase are similar although not identical. P20 by itself was not recognized by antielastase antibodies. Its association with P36 accounts for its adsorption to the immunoaffinity column and suggests that it may serve in elastase secretion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggs M. S., Gierasch L. M. Molecular mechanisms of protein secretion: the role of the signal sequence. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:109–180. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Interactions of alkaline phosphatase and the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.325-336.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fecycz I. T., Campbell J. N. Mechanisms of activation and secretion of a cell-associated precursor of an exocellular protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 34362A. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):35–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurn B. A., Chantler S. M. Production of reagent antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):104–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Fecycz I. T., Stemke G. W., Campbell J. N. Demonstration of a cell-associated, inactive precursor of an exocellular protease produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):87–93. doi: 10.1139/m80-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler E., Israel M., Landshman N., Chechick A., Blumberg S. In vitro inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase by metal-chelating peptide derivatives. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):716–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.716-723.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Mechanism of protein excretion by gram-negative bacteria: Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):695–702. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.695-702.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M. H., HORECKER B. L. PURIFICATION AND CRYSTALLIZATION OF THE ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1893–1897. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Manchester K. L., Towbin H., Gordon J., Thomas G. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in rat tissues following cycloheximide injection, in diabetes, and after denervation of diaphragm. A simple immunological determination of the extent of S6 phosphorylation on protein blots. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12316–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferrari E. Replacement of the Bacillus subtilis subtilisin structural gene with an In vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.411-418.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Thompson L. D., Rhodes C., Banner C., Nagle J., Filpula D. Genes for alkaline protease and neutral protease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens contain a large open reading frame between the regions coding for signal sequence and mature protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.811-819.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]