Abstract
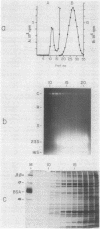
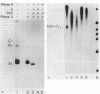
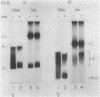
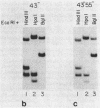
Concurrent viral replication is normally required to activate bacteriophage T4 late promoters; replication is thought to provide a template structure which is competent for late transcription. Transcription from plasmid-borne T4 late promoters, however, is independent of replication in vivo and in vitro. In this work, we have shown that, when the late gene 23 promoter is located on a plasmid, its utilization in vivo depends upon the ability of host DNA gyrase to maintain some degree of negative superhelicity. This suggests that an alternative pathway exists for activation of late promoters: DNA which is under sufficient negative torsional stress is already competent for late transcription. We also describe a method for isolating ternary complexes of plasmid DNA, RNA polymerase, and nascent RNA which have initiated transcription in vivo. The topoisomer distribution of such ternary complexes prepared from T4-infected cells showed that, late in infection, transcriptional activity resides primarily in the subset of the plasmid population with the most negatively supercoiled topoisomers. However, the overall transcriptional pattern in these ternary complexes indicated that both vector and T4 sequences are actively transcribed. Much of this transcriptional activity could be independent of gp55, the T4-specific RNA polymerase-binding protein that confers late promoter recognition.
Full text
PDF


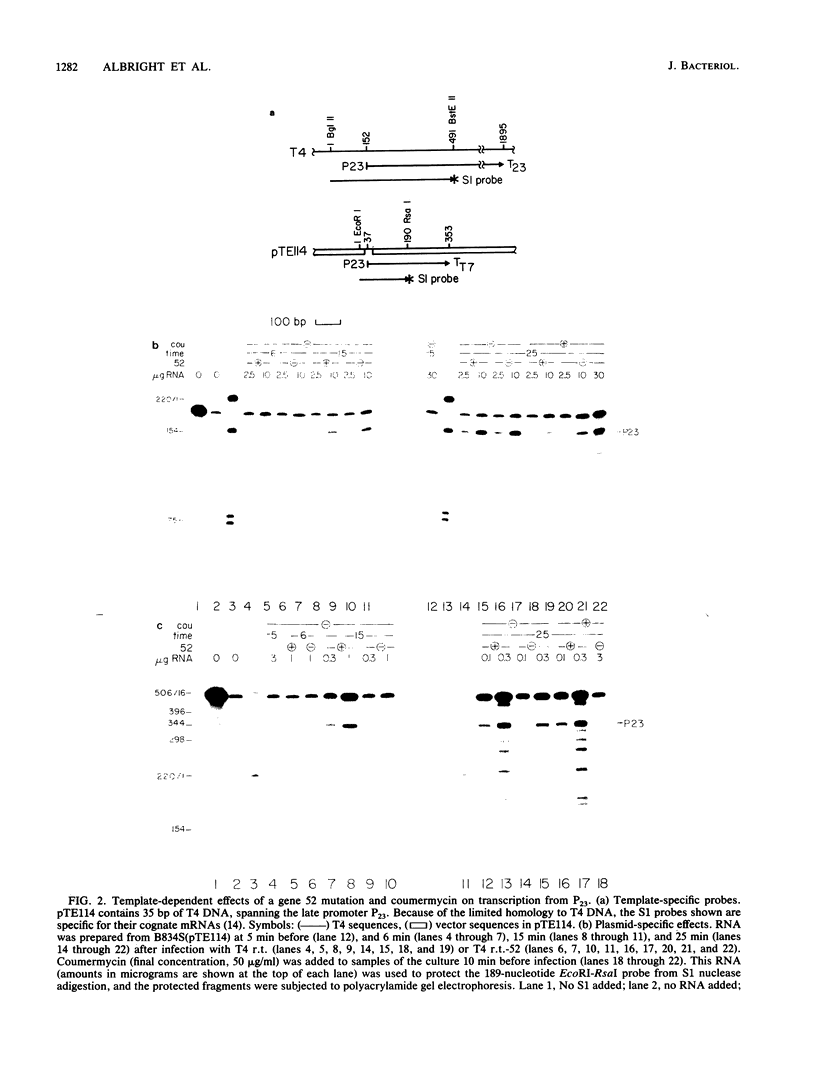

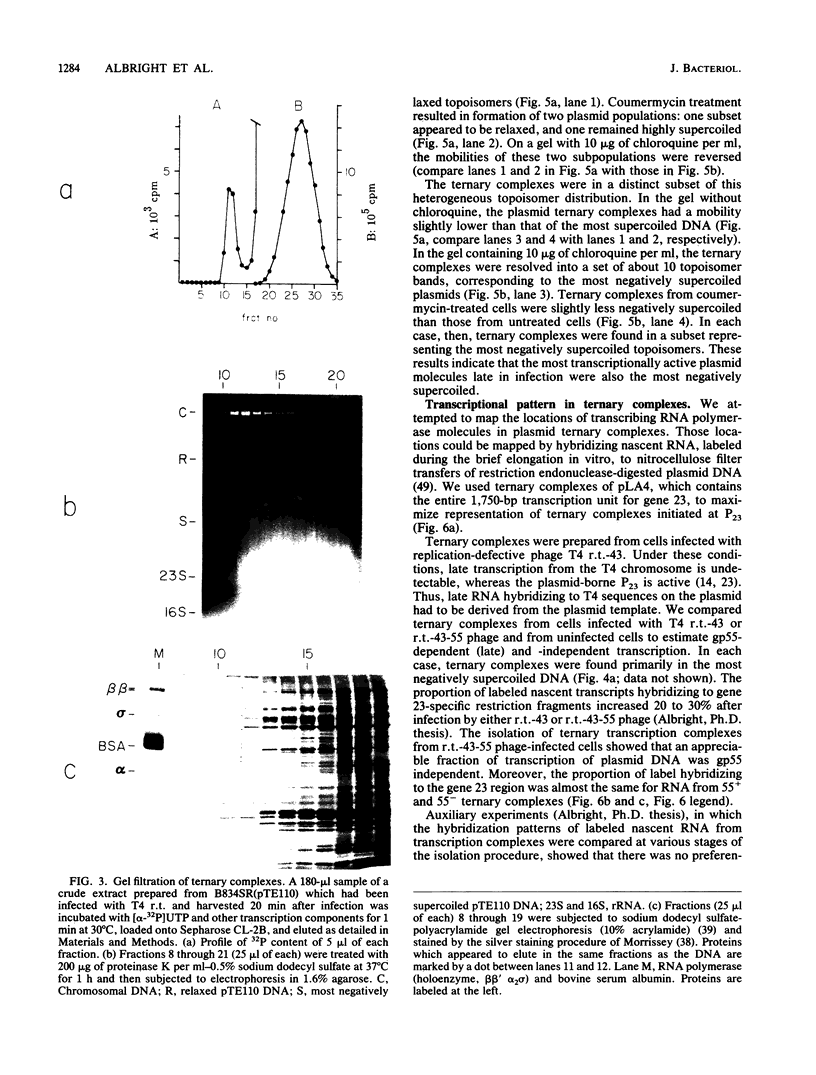





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Barry J., Bedinger P., Formosa T., Jongeneel C. V., Kreuzer K. N. Studies on DNA replication in the bacteriophage T4 in vitro system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):655–668. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Geiduschek E. P. Site-specific cleavage of bacteriophage T4 DNA associated with the absence of gene 46 product function. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):77–88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.77-88.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Geiduschek E. P. Topoisomerization of plasmid DNA in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedinger P., Hochstrasser M., Jongeneel C. V., Alberts B. M. Properties of the T4 bacteriophage DNA replication apparatus: the T4 dda DNA helicase is required to pass a bound RNA polymerase molecule. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand-Burggraf E., Schnarr M., Lefevre J. F., Daune M. Effect of superhelicity on the transcription from the tet promoter of pBR322. Abortive initiation and unwinding experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7741–7752. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. Supercoiling response of the lac ps promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):587–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Cate R. L., Perlmutter A. P. Precise location of two promoters for the beta-lactamase gene of pBR322. S1 mapping of ribonucleic acid isolated from Escherichia coli or synthesized in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9205–9210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Kolb A., Buc H. Isolation of plasmid-protein complexes from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):105–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Geiduschek E. P. Gel electrophoretic separation of transcription complexes: an assay for RNA polymerase selectivity and a method for promoter mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1851–1867. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. C., Young E. T. T4 late transcripts are initiated near a conserved DNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):369–371. doi: 10.1038/299369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Burgess R. R. In vitro transcription by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. Initiation of RNA synthesis on relaxed, closed circular template. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5866–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha A., Szybalski W., Salser W., Geiduschek E. P., Pulitzer J. F., Bolle A. Controls and polarity of transcription during bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 28;59(2):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. The stability of native DNA-RNA complexes during in vivo phiX-174 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1107–1114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Formation of an RNA primer for initiation of replication of ColE1 DNA by ribonuclease H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2450–2454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs K. A., Albright L. M., Shibata D. K., Geiduschek E. P. Genetic complementation by cloned bacteriophage T4 late genes. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):31–45. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.31-45.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs K. A., Geiduschek E. P. Regulation of expression of cloned bacteriophage T4 late gene 23. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):46–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.46-59.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano Y., Miyashita T., Nakamura H., Kuroki K., Nagata A., Imamoto F. In vivo correlation between DNA supercoiling and transcription. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Regulation of transcription in the segment of the bacteriophage T4 genome containing three of the head protein genes: plasmid-specific and phage chromosome-specific effects. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Elliott T., Rabussay D. P., Geiduschek E. P. Initiation of transcription at phage T4 late promoters with purified RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Bacteriophage T4 late promoters: mapping 5' ends of T4 gene 23 mRNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: bacteriophage T4 gene 55 protein suffices for directing late promoter recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5101–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Zentner P. G., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription at bacteriophage T4 variant late promoters. An application of a newly devised promoter-mapping method involving RNA chain retraction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14256–14265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Alberts B. M. A defective phage system reveals bacteriophage T4 replication origins that coincide with recombination hot spots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3345–3349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Morris D. R. Positively supercoiled plasmid DNA is produced by treatment of Escherichia coli with DNA gyrase inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):2999–3017. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manes S. H., Pruss G. J., Drlica K. Inhibition of RNA synthesis by oxolinic acid is unrelated to average DNA supercoiling. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):420–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.420-423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K. Biochemistry of deoxyribonucleic acid-defective amber mutants of bacteriophage T4. 3. Nucleotide pools. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7430–7438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Van Houwe G., Bolle A., Epstein R. Fate of cloned bacteriophage T4 DNA after phage T4 infection of clone-bearing cells. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. Gyrase-dependent initiation of bacteriophage T4 DNA replication: interactions of Escherichia coli gyrase with novobiocin, coumermycin and phage DNA-delay gene products. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D., Minner C., Bernstein H., Bernstein C. DNA elongation rates and growing point distributions of wild-type phage T4 and a DNA-delay amber mutant. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 5;106(4):963–981. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Christensen A., Young E. T., Stormo G., Gold L. Translational regulation of expression of the bacteriophage T4 lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5813–5826. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Gold L. M., Huang W. M. The identification of prereplicative bacteriophage T4 proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5499–5501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbye K. M., Basu S. K., Margolin P. Loss of DNA topoisomerase I activity alters many cellular functions in Salmonella typhimurium. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):785–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Rosenberg M. A promoter of pBR322 activated by cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3365–3377. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Attachment of nascent RNA molecules to superhelical DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):565–579. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Enzymic synthesis of RNA from T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P. Coupling of late transcription to viral replication in bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Cascino A., Geiduschek E. P. Uncoupling of late transcription from DNA replication in bacteriophage T4 development. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. R., Bennett G. N. Characterization of the beta-lactamase promoter of pBR322. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2517–2533. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in intracellular bacteriophage T4 DNA. Evidence that a linear DNA duplex can be supercoiled in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):659–677. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. Intermediates in transcription initiation from the E. coli lac UV5 promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Saito H. High-frequency transduction of pBR322 by cytosine-substituted T4 bacteriophage: evidence for encapsulation and transfer of head-to-tail plasmid concatemers. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Esch F. S., Geiduschek E. P. Identification of the gene encoding an RNA polymerase-binding protein of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):597–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.597-599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]