Abstract
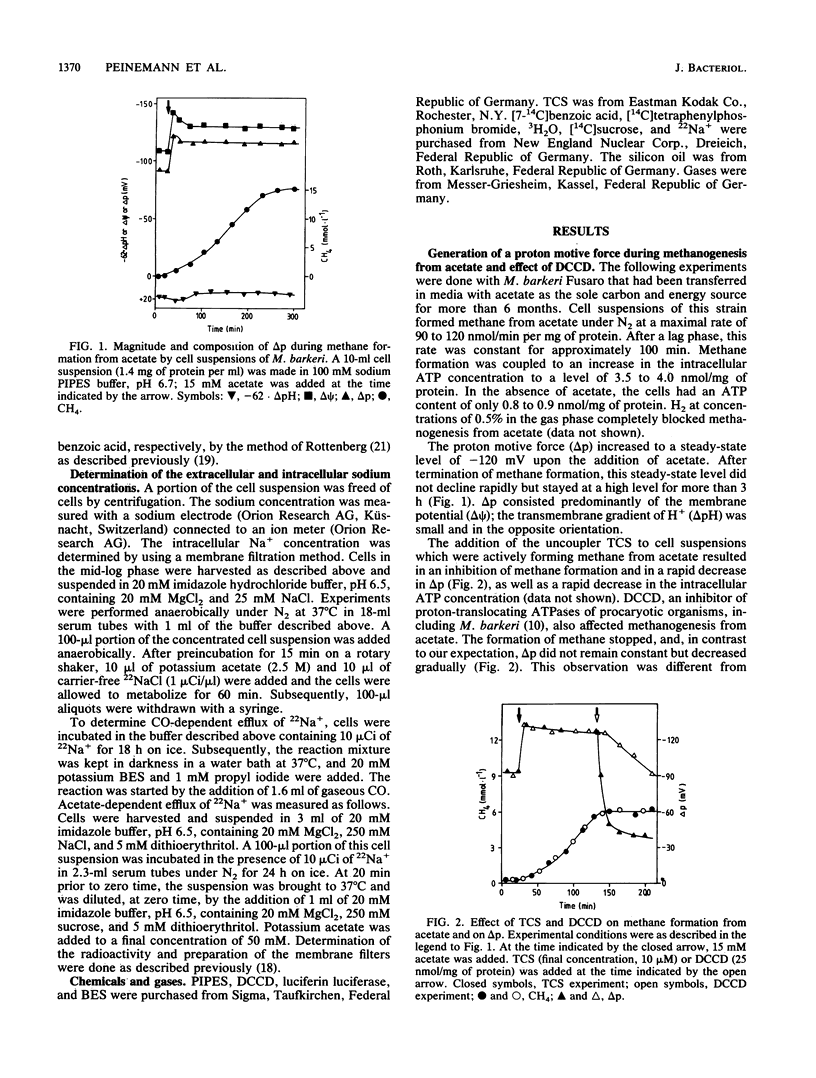
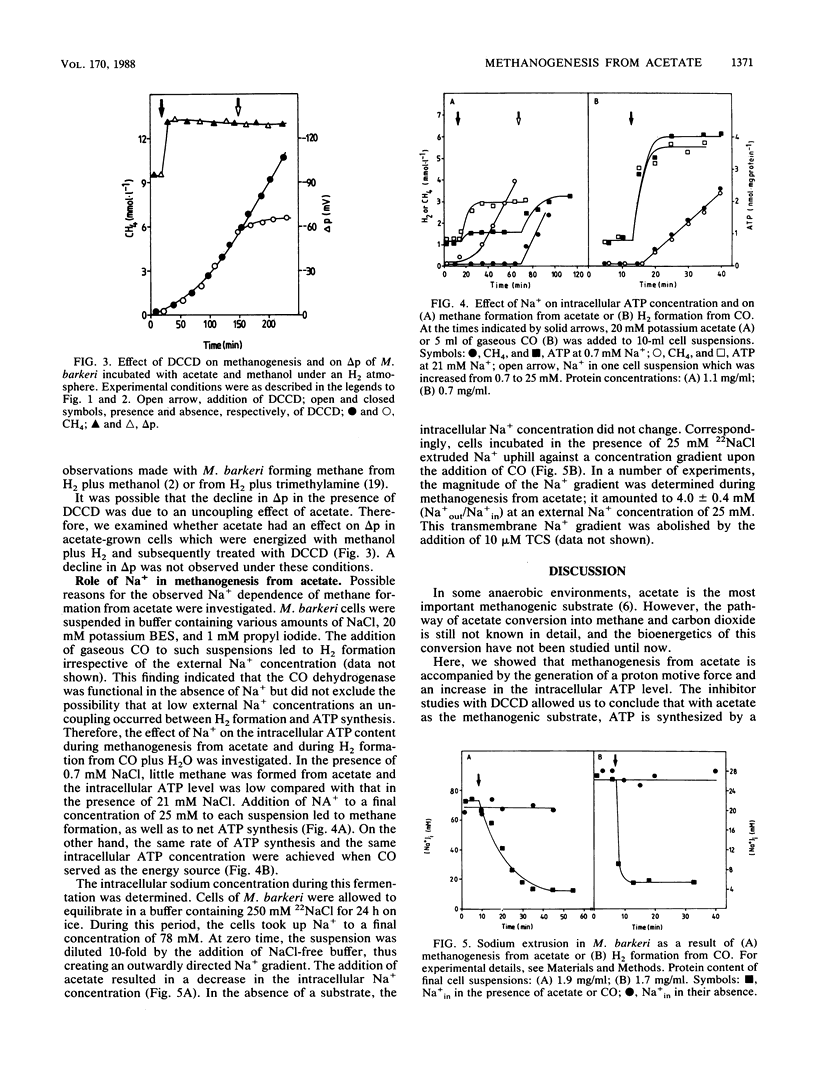
Methane formation from acetate by resting cells of Methanosarcina barkeri was accompanied by an increase in the intracellular ATP content from 0.9 to 4.0 nmol/mg of protein. Correspondingly, the proton motive force increased to a steady-state level of -120 mV. The transmembrane pH gradient however, was reversed under these conditions and amounted to +20 mV. The addition of the protonophore 3,5,3',4'-tetrachlorosalicylanilide led to a drastic decrease in the proton motive force and in the intracellular ATP content and to an inhibition of methane formation. The ATPase inhibitor N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide stopped methanogenesis, and the intracellular ATP content decreased. The proton motive force decreased also under these conditions, indicating that the proton motive force could not be generated from acetate without ATP. The overall process of methane formation from acetate was dependent on the presence of sodium ions; upon addition of acetate to cell suspensions of M. barkeri, a transmembrane Na+ gradient in the range of 4:1 (Na+ out/Na+ in) was established. Possible sites of involvement of the Na+ gradient in the conversion of acetate to methane and carbon dioxide are discussed. Na+ is not involved in the CO dehydrogenase reaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baresi L. Methanogenic cleavage of acetate by lysates of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):365–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.365-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaut M., Gottschalk G. Coupling of ATP synthesis and methane formation from methanol and molecular hydrogen in Methanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaut M., Müller V., Fiebig K., Gottschalk G. Sodium ions and an energized membrane required by Methanosarcina barkeri for the oxidation of methanol to the level of formaldehyde. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):95–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.95-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Eikmanns B., Thauer R. K. Coupling of carbon monoxide oxidation to CO2 and H2 with the phosphorylation of ADP in acetate-grown Methanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E., Prins R. A. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. 3. Experiments with 14C-labeled substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):457–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00399358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe H., Caspari D., Fiebig K., Gottschalk G. Utilization of trimethylamine and other N-methyl compounds for growth and methane formation by Methanosarcina barkeri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):494–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inatomi K. Characterization and purification of the membrane-bound ATPase of the archaebacterium Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.837-841.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W. R., Zeikus J. G. One-carbon metabolism in methanogens: evidence for synthesis of a two-carbon cellular intermediate and unification of catabolism and anabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):932–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.932-941.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J., Brand J. S. Assay of picomole amounts of ATP, ADP, and AMP using the luciferase enzyme system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):187–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., White R. H., Ferry J. G. Identification of methyl coenzyme M as an intermediate in methanogenesis from acetate in Methanosarcina spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):521–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.521-525.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller V., Blaut M., Gottschalk G. Generation of a transmembrane gradient of Na+ in Methanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 15;162(2):461–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller V., Blaut M., Gottschalk G. Utilization of Methanol plus Hydrogen by Methanosarcina barkeri for Methanogenesis and Growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):269–274. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.269-274.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT K., LIAAENJENSEN S., SCHLEGEL H. G. DIE CAROTINOIDE DER THIORHODACEAE. I. OKENON ALS HAUPTEAROTINOID VON CHROMATIUM OKENII PERTY. Arch Mikrobiol. 1963 Aug 1;46:117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



