Abstract
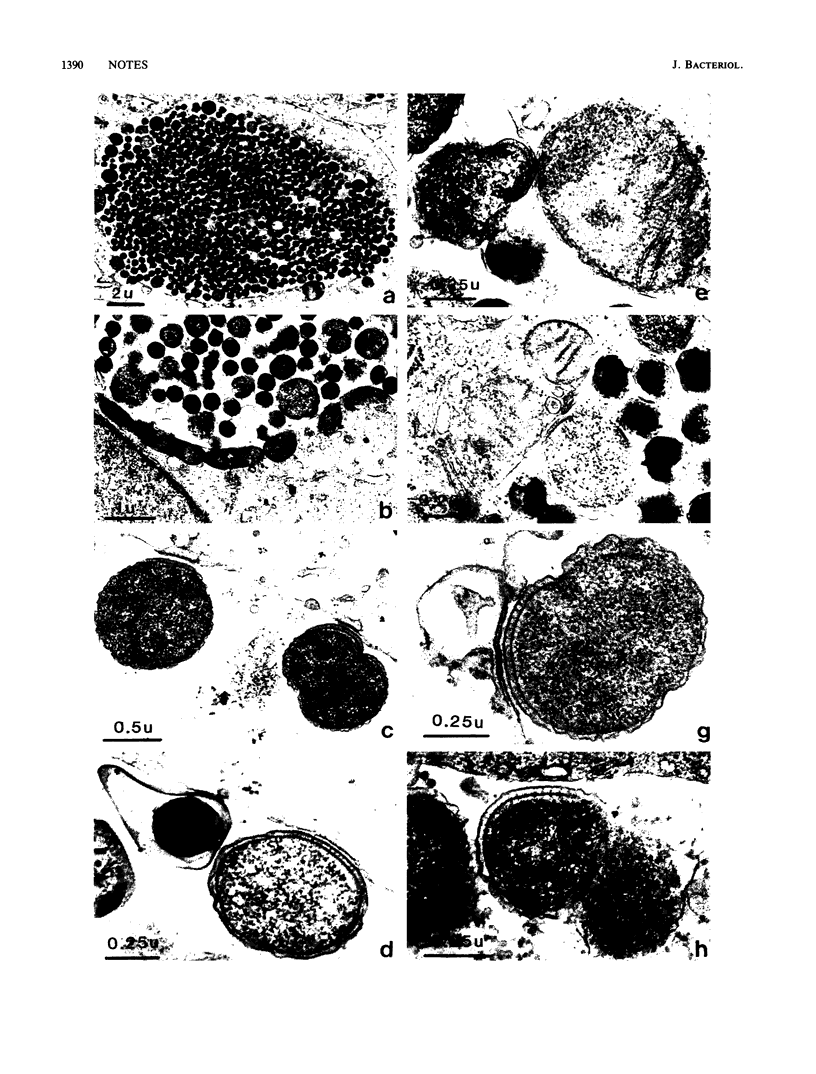
Ultrastructural analysis of the growth cycles of Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia psittaci showed that the chlamydial cell envelope became rigid and septated at the time of the reorganization from reticulate to elementary body. This process occurred in the immediacy of the inclusion membrane and in close proximity with the mitochondria or the endoplasmic reticulum of the host cell.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos M. M., Hatch T. P. Use of HeLa cell guanine nucleotides by Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):98–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.98-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. J., Leonard K., Arad T., Pitt T., Zhang Y. X., Zhang L. H. Structural studies of the outer envelope of Chlamydia trachomatis by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90409-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Unique ultrastructure in the elementary body of Chlamydia sp. strain TWAR. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3757–3763. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3757-3763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Poffenroth L., Wilt J. C., Kordová N. The effect of purification on the ultrastructure and infectivity of egg-attenuated Chlamydia psittaci (6BC). Can J Microbiol. 1975 Oct;21(10):1448–1463. doi: 10.1139/m75-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Al-Hossainy E., Silverman J. A. Adenine nucleotide and lysine transport in Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.662-670.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A. Fine structures of cell envelopes of Chlamydia organisms as revealed by freeze-etching and negative staining techniques. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1355–1363. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1355-1363.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Manire G. P. Electron Microscopic Observations on the Fine Structure of Cell Walls of Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1332–1337. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1332-1337.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Glucose Metabolism of L Cells Before and After Infection with Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1189–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1189-1196.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., de la Maza L. M. Characterization of Chlamydia DNA by restriction endonuclease cleavage. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):604–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.604-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. M., Swenson C. E., Schachter J. Ultrastructure of Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the mouse oviduct. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Sep;88(3):244–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears P., Storz J. Changes in the ultrastructure of Chlamydia psittaci produced by treatment of the host cell with DEAE-dextran and cycloheximide. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 May;67(2):152–160. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Matsumoto A., Manire G. P., Higashi N. Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the envelopes of mature elementary bodies and developmental reticulate forms of Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):355–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.355-360.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L. M., Peterson E. M. Scanning electron microscopy of McCoy cells infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Apr;36(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L. M., Plunkett M. J., Carlson E. J., Peterson E. M., Czarniecki C. W. Ultrastructural analysis of the anti-chlamydial activity of recombinant murine interferon-gamma. Exp Mol Pathol. 1987 Aug;47(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(87)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]