Abstract
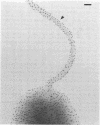
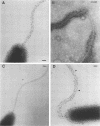
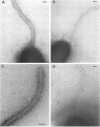
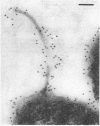
Monoclonal antibodies with group and type specificity for lipopolysaccharide antigens were used in combination with protein A-colloidal gold labeling and transmission electron microscopy to demonstrate the presence of lipopolysaccharide antigens on both the sheathed flagellum and the cell surface of Inaba and Ogawa strains of Vibrio cholerae O:1. Labeling was associated with the sheath of the flagellum rather than the core, and flagellar cores were not labeled. Flagellum and cell shared a common set of lipopolysaccharide antigens characteristic of the strain serotype.
Full text
PDF


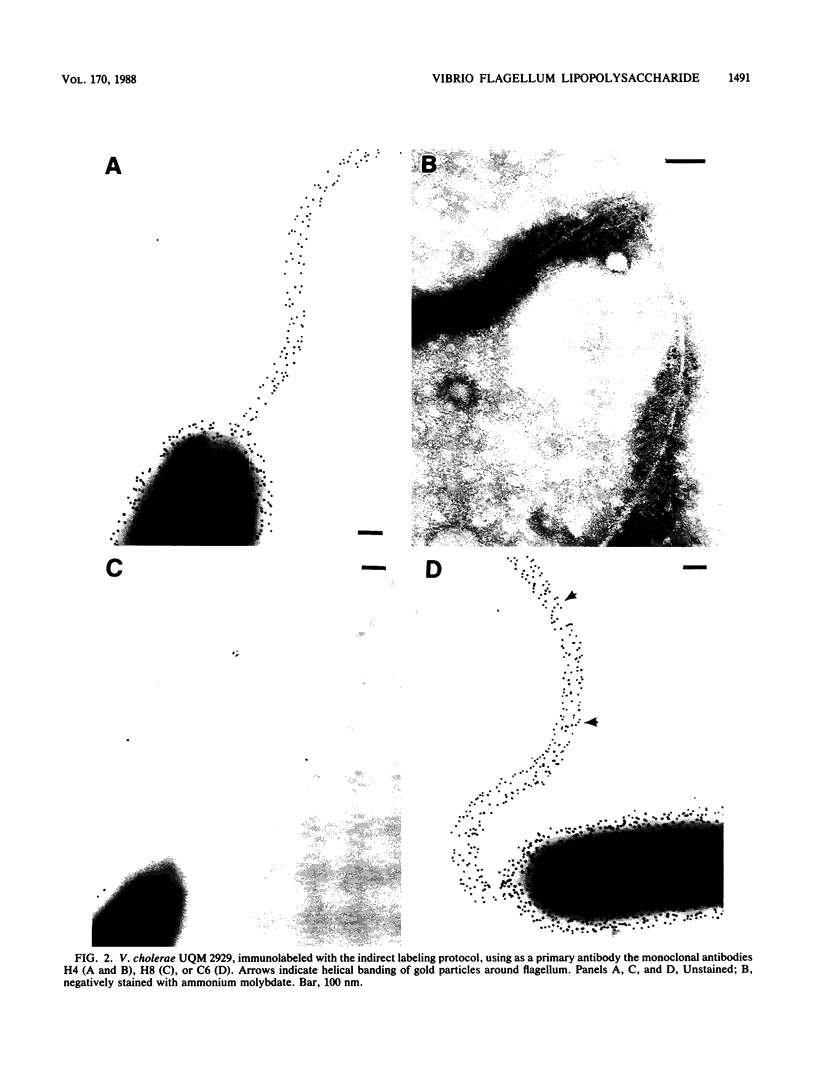
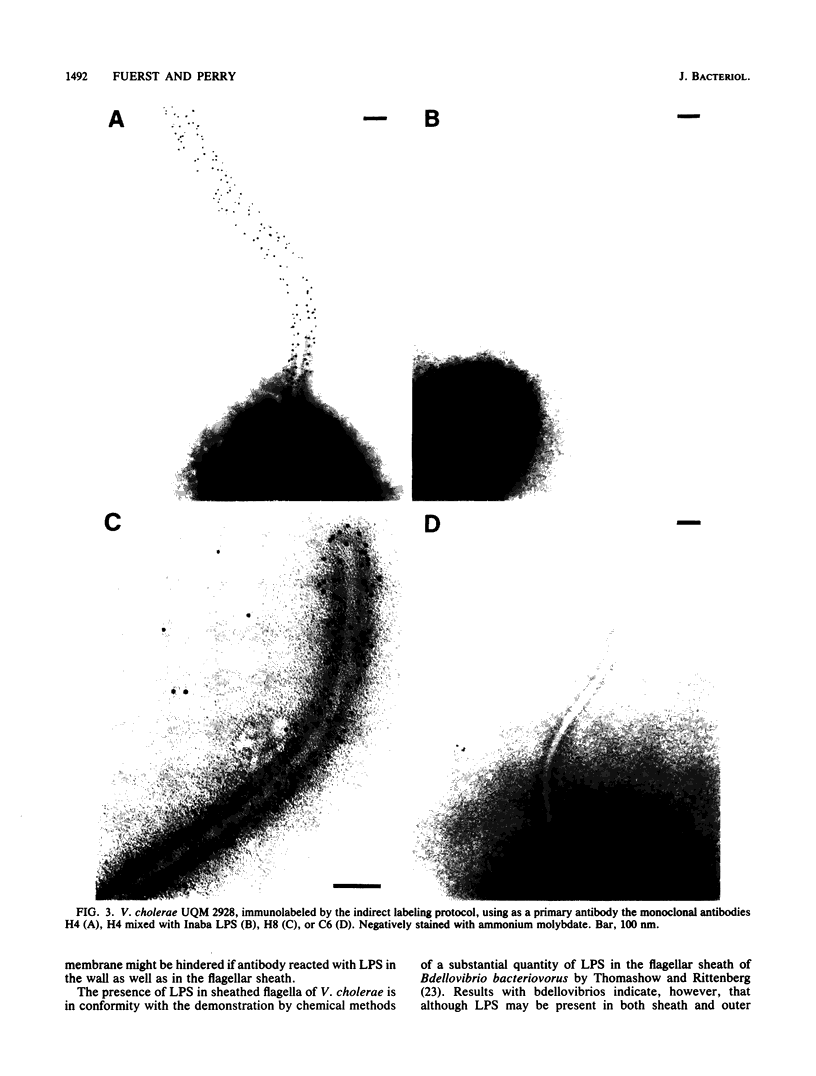


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attridge S. R., Rowley D. The role of the flagellum in the adherence of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):864–872. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENENSON A. S., ISLAM M. R., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd RAPID IDENTIFICATION OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE BY DARKFIELD MICROSCOPY. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:827–831. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis D. S., Sharma K. D., Kamat R. S. Role of bacterial adhesion in the pathogenesis of cholera. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):43–51. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis D. S., Sharma K. D., Kamat R. S. Role of somatic antigen of Vibrio cholerae in adhesion to intestinal mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):53–61. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. N., Narendranathan R. Antibacterial immunity to Vibrio cholerae in rats. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Sep;22(2):133–141. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLLETT E. A., GORDON J. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF VIBRIO FLAGELLA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Aug;32:235–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst J. A. Bacterial sheathed flagella and the rotary motor model for the mechanism of bacterial motility. J Theor Biol. 1980 Jun 21;84(4):761–774. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(80)80032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., KERRIDGE D., HORNE R. W. THE FINE STRUCTURE AND MODE OF ATTACHMENT OF THE SHEATHED FLAGELLUM OF VIBRIO METCHNIKOVII. J Cell Biol. 1963 Aug;18:327–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Holme T. Monoclonal antibodies against group- and type-specific lipopolysaccharide antigens of Vibrio cholerae O:1. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):480–485. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.480-485.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Holme T. Rapid detection of Vibrio cholerae O:1 by motility inhibition and immunofluorescence with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):291–294. doi: 10.1007/BF02013655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Rosén A., Holme T. Monoclonal antibodies against Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):449–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.449-454.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Mechanisms of disease and immunity in cholera: a review. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S105–S112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranitzky K. W., Mulholland A., Larson A. D., Eubanks E. R., Hart L. T. Characterization of a flagellar sheath protein of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.597-603.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., Lam M. Y., MacDonald L. A., Hancock R. E. Visualization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa O antigens by using a protein A-dextran-colloidal gold conjugate with both immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3531–3538. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3531-3538.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Heuzenroeder M. W., Yeadon J., Leavesley D. I., Reeves P. R., Rowley D. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the O antigens of the Inaba and Ogawa serotypes of the Vibrio cholerae O1 lipopolysaccharides and their potential for vaccine development. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.272-277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Synergistic protective effect in rabbits of immunization with Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide and toxin/toxoid. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.735-740.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Rittenberg S. C. Isolation and composition of sheathed flagella from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1047–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1047-1054.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Role of motility in experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.387-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zykin L. F. Izoliatsiia i nekotorye svoistva kletochnykh komponentov kholernogo vibriona. I. Poluchenie kletochnykh struktur i issledovanie antigennykh svoistv vibriona tipa ogava. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1968 Dec;45(12):38–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]