Abstract
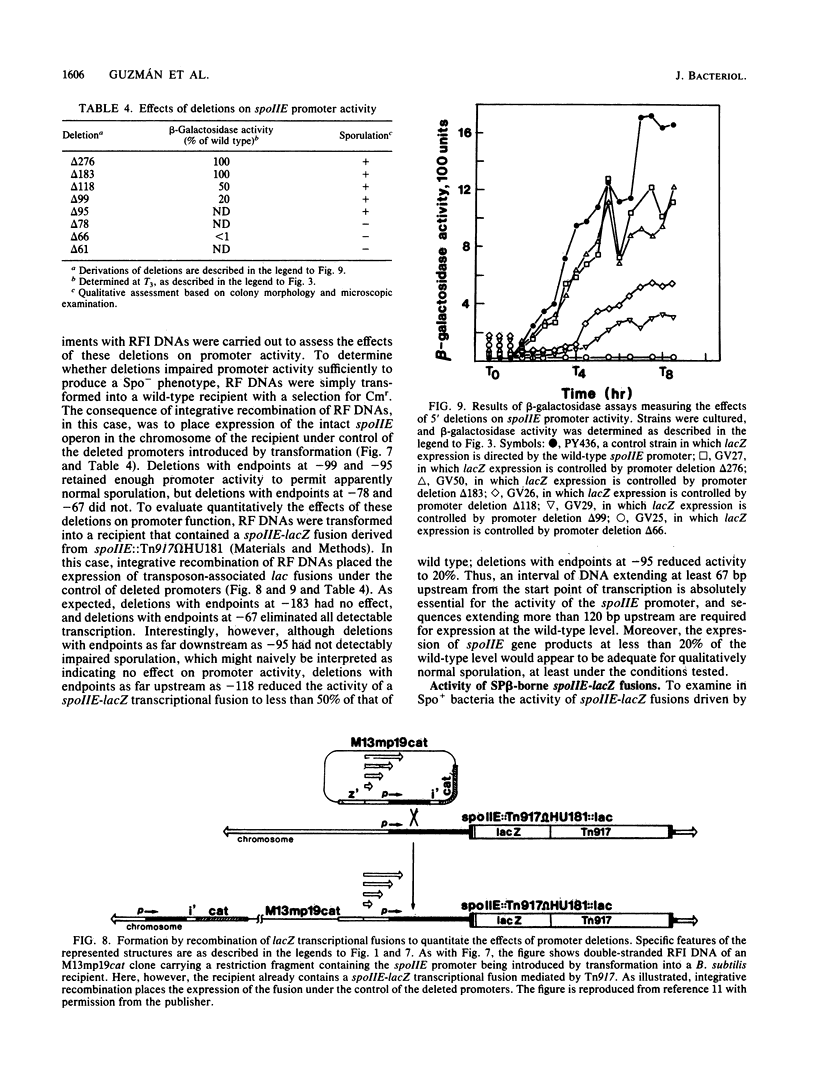
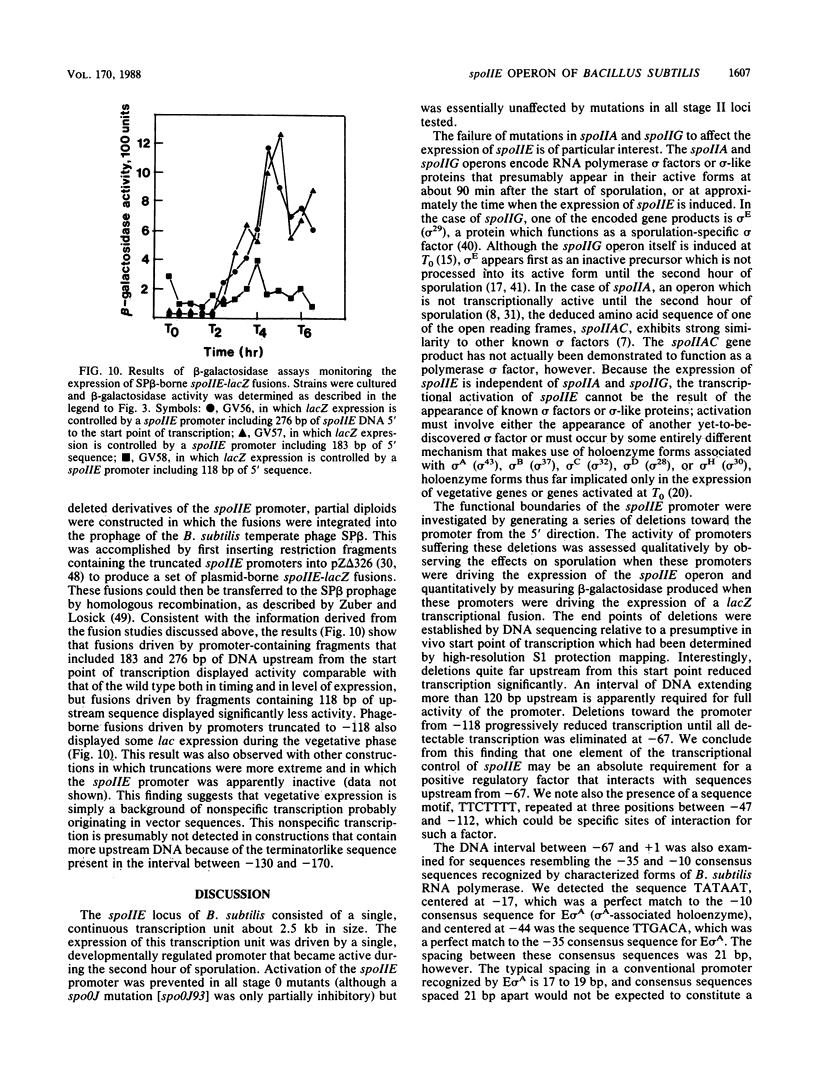
Mutations that define the spoIIE locus of Bacillus subtilis block sporulation at an early stage and recently were shown to prevent the proteolytic processing of sigma E (sigma 29) into its active form, an event that is believed to control critical changes in gene expression during the second hour of development. By taking advantage of two Tn917-mediated insertional mutations in spoIIE, we have cloned DNA spanning the locus. Gene disruption experiments with subcloned fragments transferred to integrational vectors revealed that the locus consisted of a single transcription unit about 2.5 kilobase pairs in size. Transcriptional lacZ fusions were used to show that expression of this transcription unit initiated at 1.5 h after the end of log-phase growth and depended upon the products of all spo0 loci. Expression was directed by a single promoter whose position was determined by high-resolution S1 protection mapping. A deletion analysis of the promoter region was also carried out, with novel integrational vectors based on derivatives of coliphage M13. The results indicated that a region of DNA extending from 183 to 118 base pairs upstream from the start point of transcription was required for full activity of the spoIIE promoter. The presumptive RNA polymerase-binding region of the promoter exhibited striking similarity to the spoIIG promoter and featured perfect but unusually spaced -10 and -35 consensus sequences for sigma A (sigma 43)-associated RNA polymerase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Lopez-Diaz I., Mandelstam J. Use of lacZ gene fusions to determine the dependence pattern of the sporulation gene spoIID in spo mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-2987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Wang L. F. Multiple procaryotic ribonucleic acid polymerase sigma factors. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Sep;50(3):227–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.227-243.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Mandelstam J. Use of a lacZ gene fusion to determine the dependence pattern of sporulation operon spoIIA in spo mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):2967–2976. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-2967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Piggot P. J. Nucleotide sequence of sporulation locus spoIIA in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2147–2153. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T., Shivakumar A. G., Dubnau D. Characterization of chimeric plasmid cloning vehicles in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):246–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.246-253.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. K., Cutting S., Mandelstam J. The possible DNA-binding nature of the regulatory proteins, encoded by spoIID and gerE, involved in the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Sep;133(9):2381–2391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-9-2381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordănescu S. Three distinct plasmids originating in the same Staphylococcus aureus strain. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1976 Jan-Jun;35(1-2):111–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Weaver E. A., Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr, Haldenwang W. G. The Bacillus subtilis spoIIG operon encodes both sigma E and a gene necessary for sigma E activation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):507–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.507-511.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., Moran C. P., Jr Organization and regulation of an operon that encodes a sporulation-essential sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3329–3339. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3329-3339.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Henningsen I. Selective elimination of the exonuclease activity of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli B by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):168–175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBell T. L., Trempy J. E., Haldenwang W. G. Sporulation-specific sigma factor sigma 29 of Bacillus subtilis is synthesized from a precursor protein, P31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1784–1788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Diaz I., Clarke S., Mandelstam J. spoIID operon of Bacillus subtilis: cloning and sequence. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):341–354. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Yuan R. DNA restriction enzyme from E. coli. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1110–1114. doi: 10.1038/2171110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., Banner C. D., Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Promoter for a developmentally regulated gene in Bacillus subtilis. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):783–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn M. D., Thireos G., Greer H. Temporal analysis of general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: role of positive regulatory genes in initiation and maintenance of mRNA derepression. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):520–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. B., Youngman P. J. Construction and properties of Tn917-lac, a transposon derivative that mediates transcriptional gene fusions in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):140–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Curtis C. A., de Lencastre H. Use of integrational plasmid vectors to demonstrate the polycistronic nature of a transcriptional unit (spoIIA) required for sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2123–2136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong S., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional control of the Bacillus subtilis spoIID gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):771–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.771-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R., Toye P. A., Korman R. Z., Zahler S. A. The prophage of SP beta c2dcitK1, A defective specialized transducing phage of Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1979 Jul;92(3):721–739. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandman K., Losick R., Youngman P. Genetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis spo mutations generated by Tn917-mediated insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):603–617. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bouvier J., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J. A developmental gene product of Bacillus subtilis homologous to the sigma factor of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):376–378. doi: 10.1038/312376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Bonamy C., Szulmajster J., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma factor sigma 29 is the product of the sporulation-essential gene spoIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4189–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Morrison-Plummer J., Haldenwang W. G. Synthesis of sigma 29, an RNA polymerase specificity determinant, is a developmentally regulated event in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):340–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.340-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Reznikoff W. S. Cloning DNA restriction endonuclease fragments with protruding single-stranded ends. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90329-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Perkins J. B., Losick R. A novel method for the rapid cloning in Escherichia coli of Bacillus subtilis chromosomal DNA adjacent to Tn917 insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):424–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00341443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Role of AbrB in Spo0A- and Spo0B-dependent utilization of a sporulation promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2223–2230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2223-2230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Use of a lacZ fusion to study the role of the spoO genes of Bacillus subtilis in developmental regulation. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]