Abstract
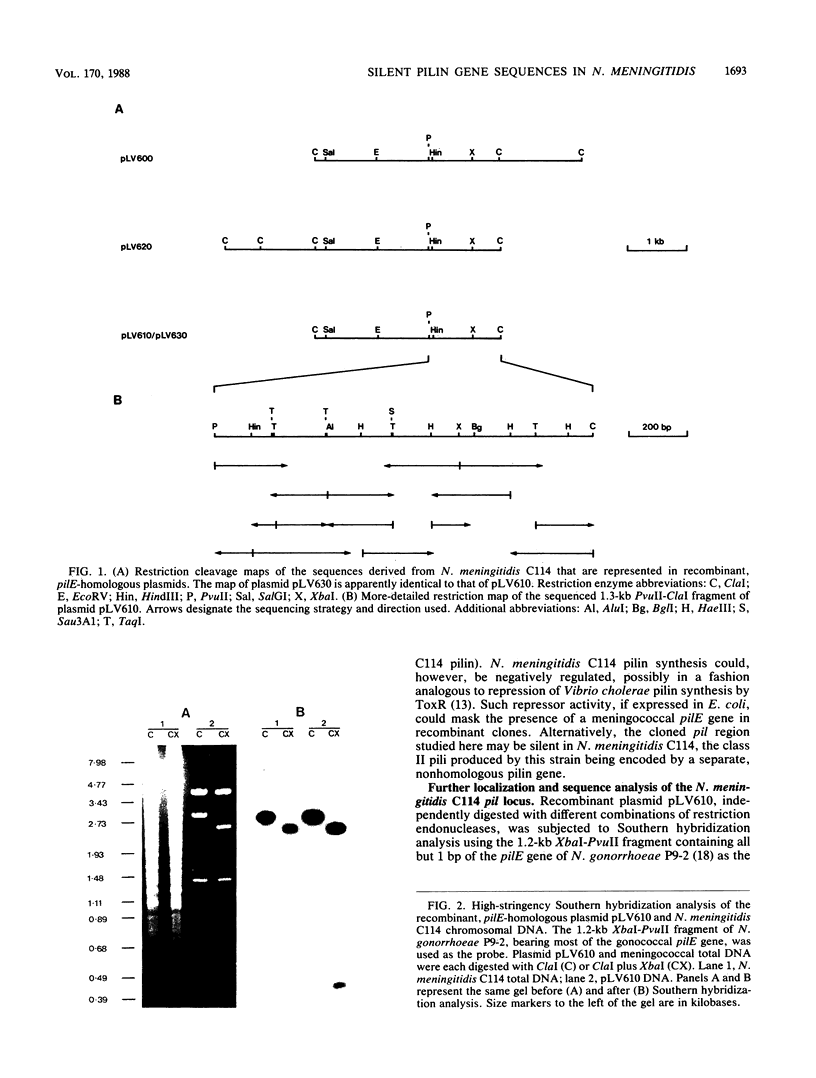
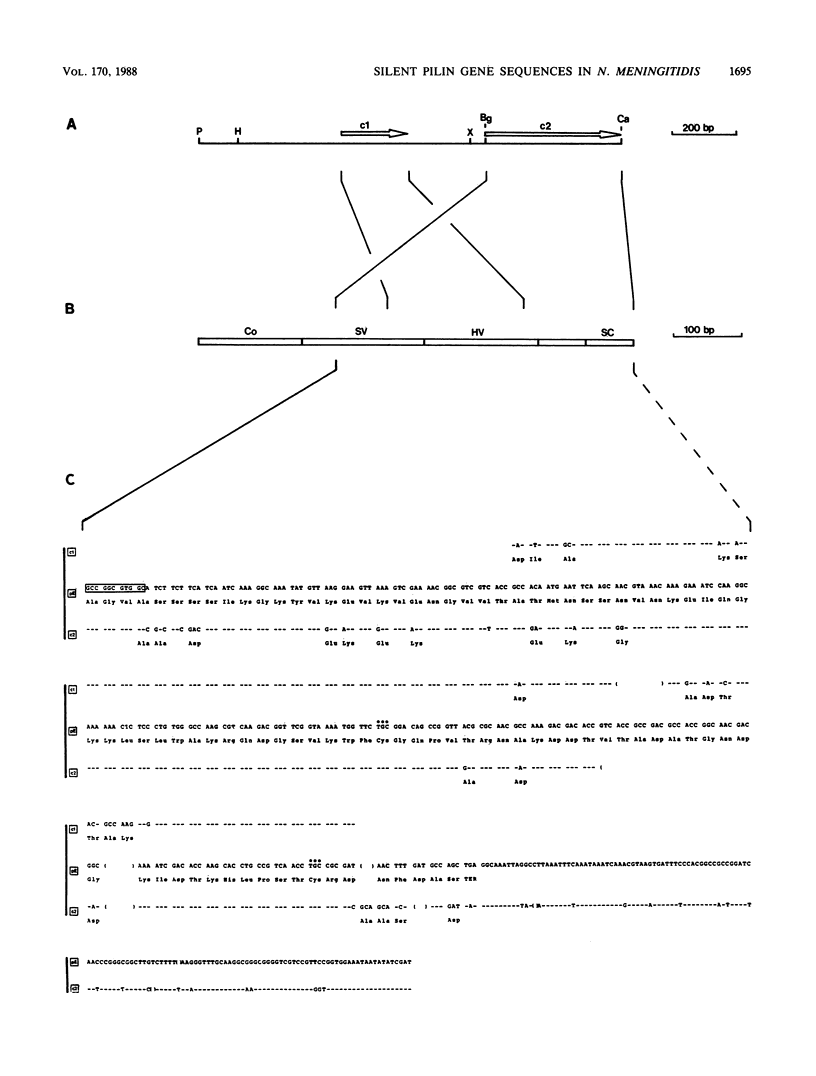
Neisseria meningitidis pili can be classified into two groups: those (referred to here as class I pili) which are similar to gonococcal pili in that they react with monoclonal antibody SM1 and those that are dissimilar to gonococcal pili in that they lack the SM1-reactive epitope (class II pili). Pilus expression in N. meningitidis C114, a class II pilus-producing isolate, was investigated. The sole genomic segment of this strain that bore extensive homology with the pilE locus of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9 was cloned in Escherichia coli. The production of the pilus structural subunit (pilin) from this meningococcal segment could not be detected by immunological and coupled in vitro transcription-translation analyses. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed the presence in the C114 genome of two variant, tandemly arranged pilin genes (copies 1 and 2). Copies 1 and 2 are partial pilin genes that constitute part of a silent meningococcal pilin gene (pil gene) region, designated pilS. Both copies are truncated, corresponding to variable domains of the gonococcal pilE gene but lacking homologous N-terminal coding sequences. Located within sequences surrounding copies 1 and 2 were several classes of repeated elements that are associated with pil loci in N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho E. L., Murphy G. L., Cannon J. G. Distribution of specific DNA sequences among pathogenic and commensal Neisseria species. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1009–1013. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1009-1013.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Robbins K., Koomey J. M., Swanson J. Piliation control mechanisms in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3890–3894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Meyer T. F. The repertoire of silent pilus genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: evidence for gene conversion. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Billyard E., Haas R., Storzbach S., So M. Pilus genes of Neisseria gonorrheae: chromosomal organization and DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson I. J., Perry A. C., Heckels J. E., Saunders J. R. Genetic analysis of variant pilin genes from Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9 cloned in Escherichia coli: physical and immunological properties of encoded pilins. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):553–561. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson I. J., Perry A. C., Virji M., Heckels J. E., Saunders J. R. Localization of antibody-binding sites by sequence analysis of cloned pilin genes from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):825–833. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A. C., Hart C. A., Nicolson I. J., Heckels J. E., Saunders J. R. Inter-strain homology of pilin gene sequences in Neisseria meningitidis isolates that express markedly different antigenic pilus types. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1409–1418. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A. C., Nicolson I. J., Saunders J. R. Structural analysis of the pilE region of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. Gene. 1987;60(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlner J., Halter R., Beyreuther K., Meyer T. F. Gene structure and extracellular secretion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae IgA protease. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):458–462. doi: 10.1038/325458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R. DNA sequence analysis on the IBM-PC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):601–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Billyard E., So M., Storzbach S., Meyer T. F. Role of chromosomal rearrangement in N. gonorrhoeae pilus phase variation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Hagblom P., Seifert H. S., So M. Antigenic variation of gonococcal pilus involves assembly of separated silent gene segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2177–2181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Whitney A. M., Rothbard J., Schoolnik G. K. Pili of Neisseria meningitidis. Analysis of structure and investigation of structural and antigenic relationships to gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1539–1553. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Brown M., Nickel P., Meyer T. F. Opacity genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: control of phase and antigenic variation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Meyer T. F. Common mechanism controlling phase and antigenic variation in pathogenic neisseriae. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Bergström S., Barrera O., Robbins K., Corwin D. Pilus- gonococcal variants. Evidence for multiple forms of piliation control. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):729–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Bergström S., Robbins K., Barrera O., Corwin D., Koomey J. M. Gene conversion involving the pilin structural gene correlates with pilus+ in equilibrium with pilus- changes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90449-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Gillespie R. M., Bhatti A. R., White L. A. Differences in the adhesive properties of Neisseria meningitidis for human buccal epithelial cells and erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.106-113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. Antigenic cross-reactivity of Neisseria pili: investigations with type- and species-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2761–2768. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Takasawa T., Yoneyama M., Yamaguchi T., Shiokawa H., Suzuki T. Fimbriae from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis: physical, chemical, and immunological properties. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):730–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.730-734.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak K., Diaz J. L., Jackson D., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: detection of antibodies to surface proteins in sera of patients with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):166–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]