Abstract
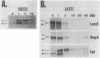
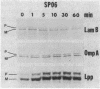
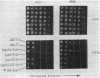
A deletion mutation (lpp delta 9 delta 13 delta 14) in the signal peptide of the major outer membrane lipoprotein of Escherichia coli (Lpp) was found to cause severe effects on cell physiology, resulting in cessation of growth within 10 min of induction of lpp delta 9 delta 13 delta 14 expression and rapid cell death. Further investigation revealed that lpp delta 9 delta 13 delta 14 expression caused slow processing of several other exported proteins. The origin of this effect was traced to depolarization of the electrochemical potential across the cytoplasmic membrane, which is known to be required for efficient protein export. Analysis of the processing rate of the mutant, either prior to complete depolarization or in a suppressor strain in which depolarization does not occur, indicates that the mutant protein was capable of secretion at a rate which, while less than that of the wild type, was reasonably rapid compared with the rates of other E. coli secreted proteins. The existence of this type of signal peptide mutation suggests that the cell may have a mechanism to avoid membrane damage from secretory proteins carrying membrane-active signal peptides which is bypassed by the lpp delta 9 delta 13 delta 14 mutant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Randall L. L. The requirement for energy during export of beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli is fulfilled by the total protonmotive force. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):895–900. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr The synthesis of export-defective proteins can interfere with normal protein export in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12193–12200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Gierasch L. M., Zlotnick A., Lear J. D., DeGrado W. F. In vivo function and membrane binding properties are correlated for Escherichia coli lamB signal peptides. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1096–1099. doi: 10.1126/science.3158076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Wickner W. Trigger factor: a soluble protein that folds pro-OmpA into a membrane-assembly-competent form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Date T., Goodman J. M., Wickner W. T. Procoat, the precursor of M13 coat protein, requires an electrochemical potential for membrane insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Date T., Zwizinski C., Ludmerer S., Wickner W. Mechanisms of membrane assembly: effects of energy poisons on the conversion of soluble M13 coliphage procoat to membrane-bound coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):827–831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Importance of secondary structure in the signal sequence for protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghrayeb J., Inouye M. Nine amino acid residues at the NH2-terminal of lipoprotein are sufficient for its modification, processing, and localization in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):463–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Schwartz M. Evidence for a coupling of synthesis and export of an outer membrane protein in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):15–19. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Duffaud G., Inouye M. Structural requirement at the cleavage site for efficient processing of the lipoprotein secretory precursor of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):10970–10975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A. Requirement for membrane potential in active transport of glutamine by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.221-225.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt S., Inouye S., Inouye M. A functional prolipoprotein signal peptide with a deletion of four amino acid residues from the hydrophobic region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7965–7969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt S., Inouye S., Inouye M. Effect of amino acid substitutions at the signal peptide cleavage site of the Escherichia coli major outer membrane lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1835–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Inouye S., Inouye M. Effects of replacing serine and threonine residues within the signal peptide on the secretion of the major outer membrane lipoprotein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6195–6200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Inouye S., Ito H., Itakura K., Inouye M. Effects of the complete removal of basic amino acid residues from the signal peptide on secretion of lipoprotein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7141–7148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Blomberg C. Trans-membrane translocation of proteins. The direct transfer model. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):175–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]