Abstract
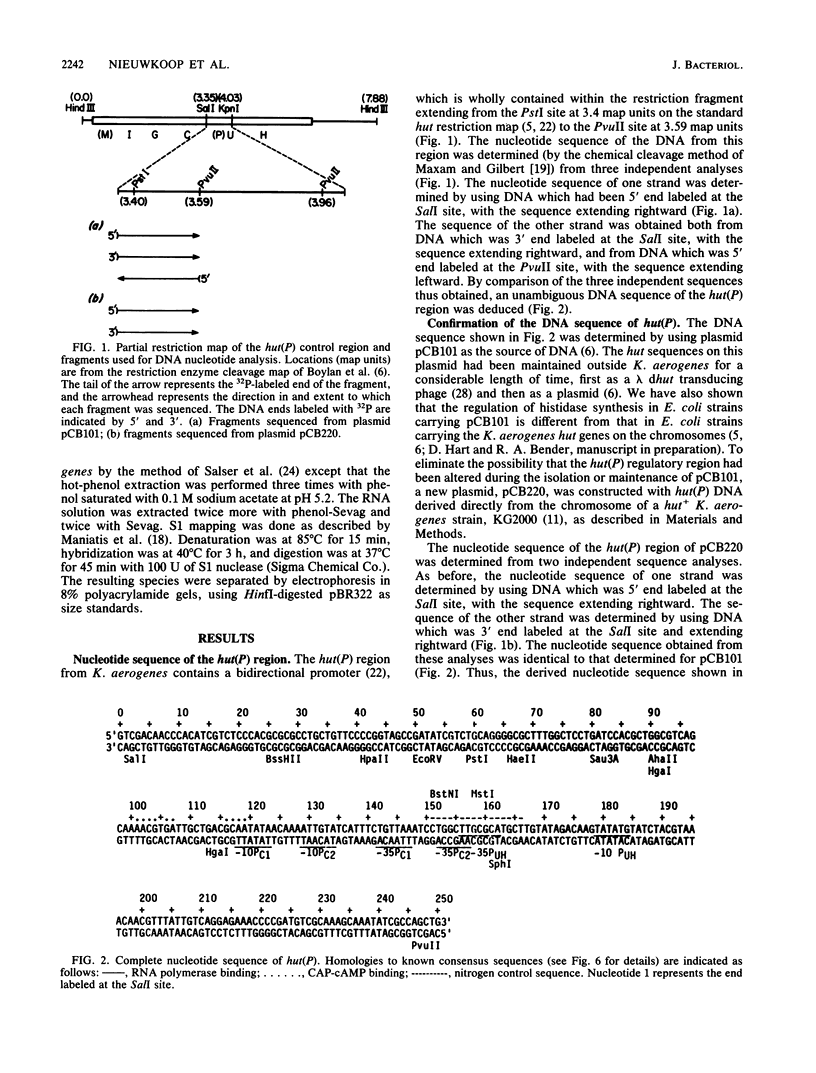
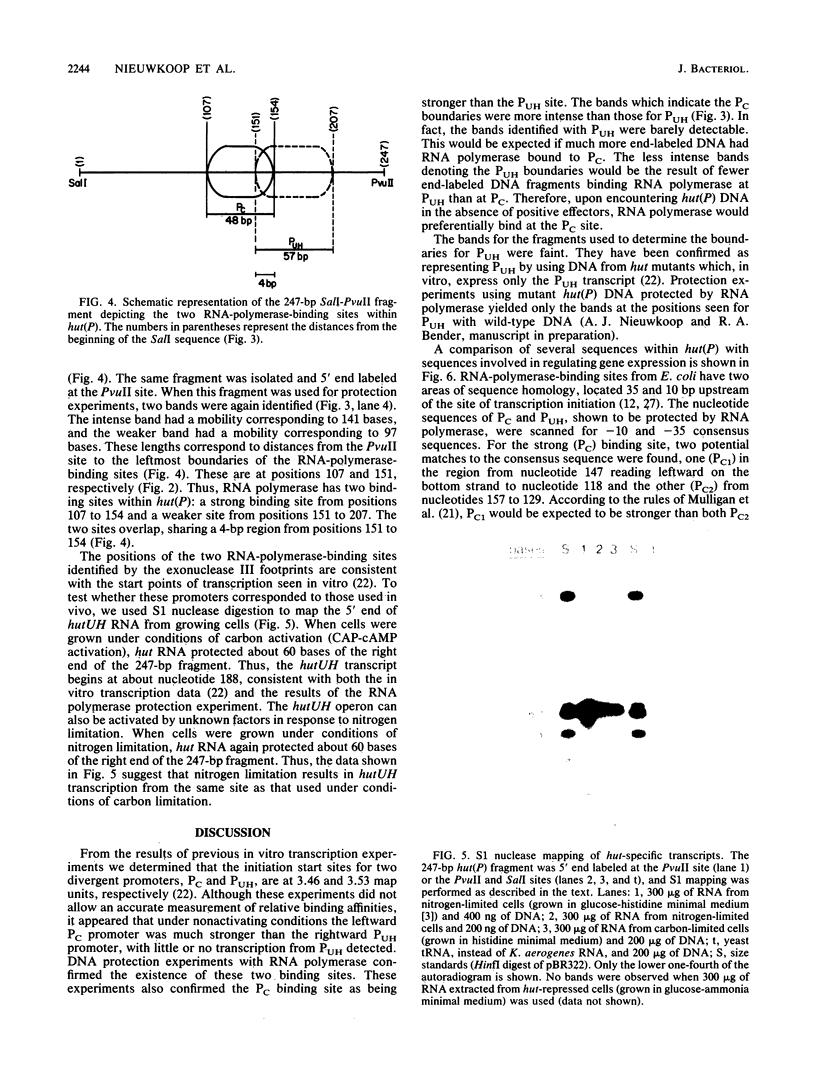
The hut(P) region (i.e., the region responsible for regulation of hutUH expression) of the Klebsiella aerogenes histidine utilization (hut) operons contains a bidirectional promoter. One transcript from this promoter encodes the hutUH operon; the role of the oppositely directed transcript is unknown, although it appears to be involved in regulating hutUH expression (A.J. Nieuwkoop, S.A. Boylan, and R.A. Bender, J. Bacteriol. 159:934-939, 1984). A 247-base-pair (bp) fragment containing hut(P) carries two RNA-polymerase-binding sites agree with the start sites of the two transcripts produced from hut(P) DNA in vitro and in vivo. The binding sites share a 4-bp region, suggesting that occupancy of the regulatory site precludes occupancy of the hutUH promoter, and vice versa. In the absence of positive effectors, the binding to the site responsible for hutUH transcription is weaker than the binding to the site responsible for regulation. The nucleotide sequence of the 250-bp fragment containing hut(P) contains two possible matches to the consensus sequence for Escherichia coli promoters, a better and worse match, corresponding in position to the stronger and weaker RNA-polymerase-binding sites, respectively. The sequence also contains a region similar to the consensus sequence for binding of the catabolite gene activator protein of E. coli. A sequence similar to the consensus for Ntr-dependent promoters was also found, overlapping both RNA-polymerase-binding sites, but it is not a functional promoter. Finally, an initiation codon preceded by a Shine-Dalgarno consensus sequence and followed by an open reading frame identifies a probable start of the hutU gene coding sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J., Kinney T., Thompson S., Rubin L., Helling R. B. Frequency-Dependent Selection for Plasmid-Containing Cells of ESCHERICHIA COLI. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):627–637. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Snyder P. M., Bueno R., Quinto M., Magasanik B. Nitrogen regulation system of Klebsiella aerogenes: the nac gene. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):444–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.444-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Bender R. A. Genetic and physical maps of Klebsiella aerogenes genes for histidine utilization (hut). Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):99–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00327421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Eades L. J., Janssen K. A., Lomax M. I., Bender R. A. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of the histidine utilization (hut) genes of Klebsiella aerogenes and deletions lacking regions of hut DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):92–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00327420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M. Deletion analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter: importance of spacing between conserved sequences around positions -12 and -24 for activation by the nifA and ntrC (glnG) products. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.545-551.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Bender R. A., Streicher S. L. Direct selection for P1-sensitive mutants of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):810–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.810-814.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hanau R. Regulation of Klebsiella pneumoniae hut operons by oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):745–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.745-750.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Magasanik B. Gene order of the histidine utilization (hut) operons in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1025–1031. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1025-1031.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M., Cohen S. N. Transformation of Salmonella typhimurium by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1072-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation in Escherichia coli: cryogenic preservation of competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):349–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.349-351.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop A. J., Boylan S. A., Bender R. A. Regulation of hutUH operon expression by the catabolite gene activator protein-cyclic AMP complex in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):934–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.934-939.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Resistance to catabolite repression of histidase and proline oxidase during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6288–6296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Gesteland R. F., Bolle A. In vitro synthesis of bacteriophage lysozyme. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):588–591. doi: 10.1038/215588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M., Goldberg R. B. Transduction of chromosomal genes between enteric bacteria by bacteriophage P1. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1105-1111.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]