Abstract
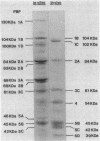
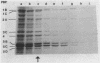
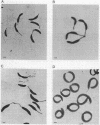
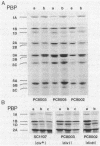
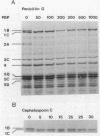
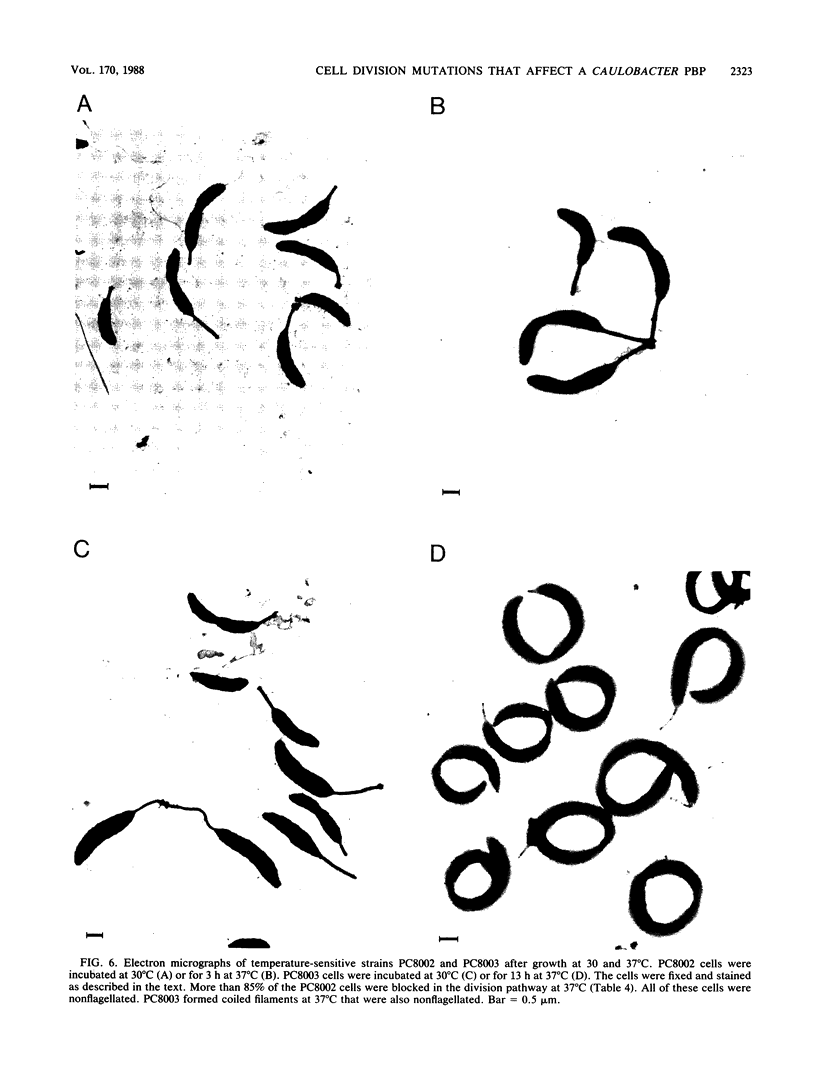
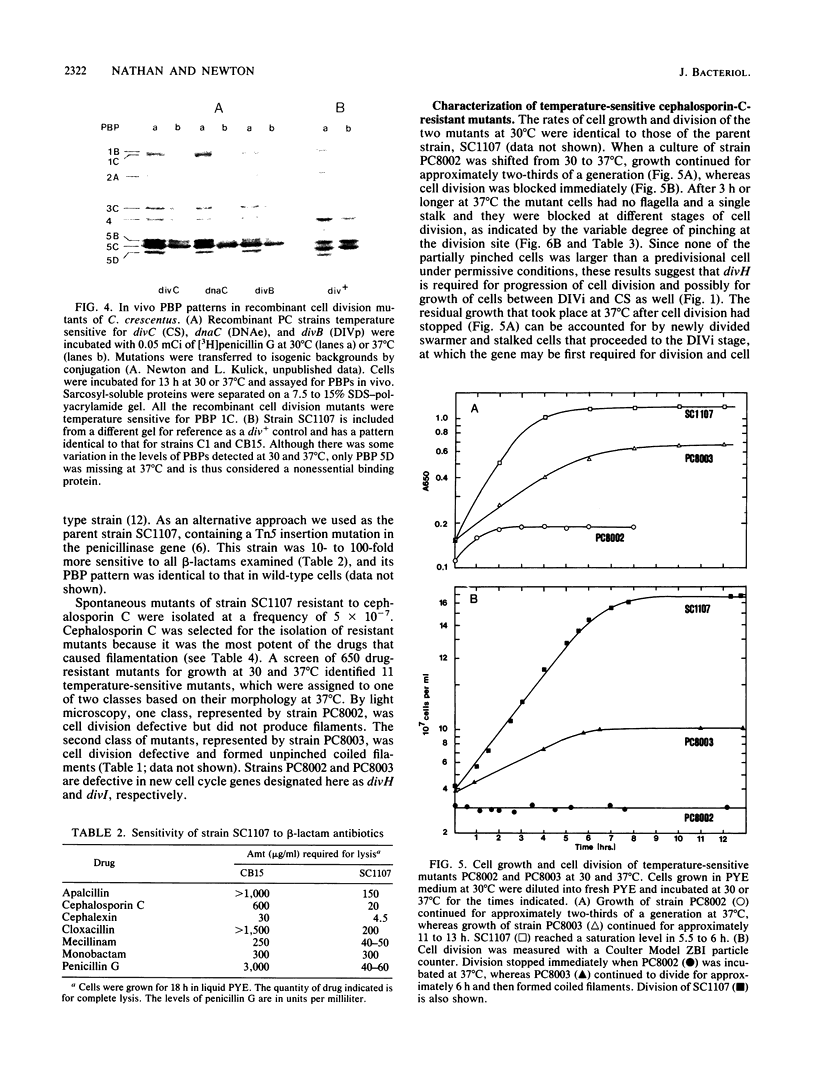
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are membrane proteins associated with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. We report the characterization of 14 PBPs in Caulobacter crescentus, using in vivo and in vitro penicillin-binding assays and experiments to determine their possible role in cell division. New conditional cell cycle mutants were isolated by selecting cephalosporin-C-resistant mutants of the beta-lactamase strain SC1107 at 30 degrees C that are also defective in cell division at 37 degrees C. They fall into two classes, represented by strains PC8002 and PC8003. Strain PC8002 produced short cells arrested at all stages of cell division at 37 degrees C and was found to contain a high-molecular-weight PBP 1B which was temperature sensitive when assayed in vivo and in vitro. Strain PC8003 was blocked at an early stage of cell division and formed tightly coiled, unpinched filaments. This cephalosporin-C-resistant strain was also defective in PBP 1B, but only when assayed in vivo. PBP 1B behaved like a high-affinity PBP, and in competition assays, beta-lactams that induced filamentation bound preferentially to PBP 1B. These results and the phenotype of mutant PC8002 suggest that PBP 1B is required for cell division, as well as for cell growth, in C. crescentus. The behavior of strain PC8003 suggests that it contains a conditionally defective gene product that interacts in some way with PBP 1B at an early stage of cell division. None of the mutants showed an allele-specific PBP pattern when assayed in vitro at the nonpermissive temperature, but all of them displayed temperature-sensitive PBP 1C (102 kilodaltons) activity. Thus, it appears that PBP 1C is inhibited at 37 degree C as a consequence of filamentous growth.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begg K. J., Donachie W. D. Cell shape and division in Escherichia coli: experiments with shape and division mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):615–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.615-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Spratt B. G., Donachie W. D. Interaction between membrane proteins PBP3 and rodA is required for normal cell shape and division in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1004-1008.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E., Neyman S. L. Correlation of penicillin-binding protein composition with different functions of two membranes in Bacillus subtilis forespores. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):498–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.498-503.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Drapeau G. R. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli K-12: probable interactions among proteins FtsQ, FtsA, and FtsZ. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1938–1942. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1938-1942.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Croft R. H. Transposon mutagenesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):620–625. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.620-625.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M., Agabian N. Envelope-associated nucleoid from Caulobacter crescentus stalked and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.294-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):148–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hatfull G. F., Salmond G. P. A new cell division operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):134–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02428043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenel E. D., Newton A. Evidence that subcellular flagellin pools in Caulobacter crescentus are precursors in flagellum assembly. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):727–732. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.727-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenel E. D., Newton A. Localization of surface structures during procaryotic differentiation: role of cell division in Caulobacter crescentus. Differentiation. 1982;21(2):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ely B. Isolation of spontaneously derived mutants of Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1977 May;86(1):25–32. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Fukuda A., Okada Y. Alteration in penicillin-binding patterns during cell cycle of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):593–595. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Fukuda A., Okada Y. The penicillin-binding proteins of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biochem. 1980 Jan;87(1):363–366. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund F., Tybring L. 6 -amidinopenicillanic acids--a new group of antibiotics. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):135–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio236135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Newton A. Mutational analysis of developmental control in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):124–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Newton A. Temporal control of the cell cycle in Caulobacter crescentus: roles of DNA chain elongation and completion. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 25;138(1):109–128. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowell M. O., Buchanan C. E. Changes in penicillin-binding proteins during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1331–1337. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1331-1337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Biochemical and genetical approaches to the mechanism of action of penicillin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):273–283. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Boyd A., Stoker N. Defective and plaque-forming lambda transducing bacteriophage carrying penicillin-binding protein-cell shape genes: genetic and physical mapping and identification of gene products from the lip-dacA-rodA-pbpA-leuS region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):569–581. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.569-581.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Pardee A. B. Penicillin-binding proteins and cell shape in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):516–517. doi: 10.1038/254516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Georgopapadakou N. H., Wells J. S. Monobactams--monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):1–16. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrana B., Newton A. Requirement of a cell division step for stalk formation in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):456–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.456-462.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Apr;96(4):502–504. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo A., Ayala J. A., de Pedro M. A., Aldea M., Vicente M. Interaction of FtsA and PBP3 proteins in the Escherichia coli septum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):985–992. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.985-992.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]