Abstract
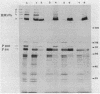
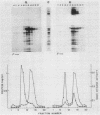
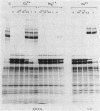
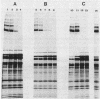
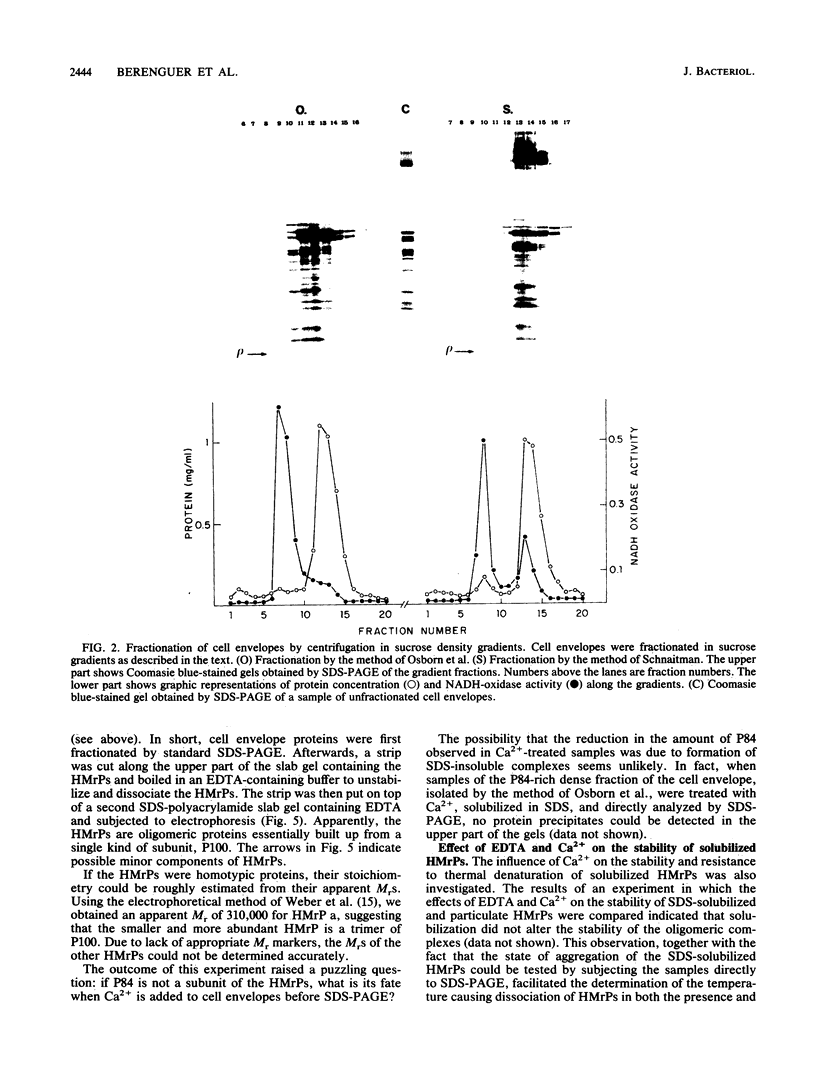
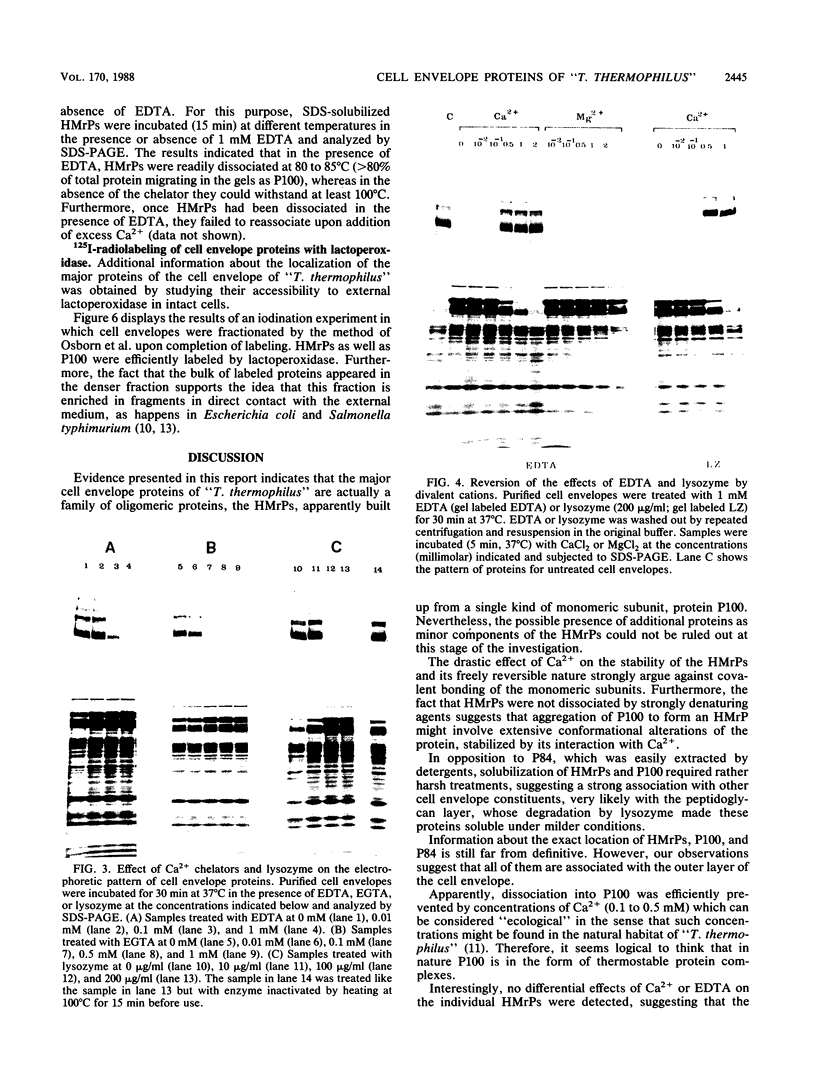
The major cell envelope proteins of the gram-negative thermophilic eubacterium "Thermus thermophilus" gave an electrophoretical pattern characterized by two well-defined groups of bands. One of them showed up as four regularly spaced proteins (HMrPs) with Mrs higher than 310,000, a value corresponding to the smaller HMrP. The second one was formed by two proteins with Mrs of 100,000 (P100) and 84,000 (P84). HMrPs P100 and P84 were apparently located in the outer layer of the cell envelope, as indicated by their accessibility, in intact cells, to external lactoperoxidase and by their association, in fractionation experiments, with a high-density membrane fraction devoided of NADH-oxidase activity. Removal of Ca2+ unstabilized the HMrPs, which dissociated into P100 when heated at 80 to 85 degrees C in 10% (wt/vol) sodium dodecyl sulfate, indicating that HMrPs were oligomeric complexes of P100. In the presence of Ca2+, HMrPs were extremely stable, withstanding prolonged incubation in boiling 10% (wt/vol) sodium dodecyl sulfate-2% (vol/vol) beta-mercaptoethanol. Solubilization of P100 and HMrPs by detergents was severely constrained by interactions with the peptidoglycan layer of the cell envelope.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amelunxen R. E., Singleton R., Jr Thermophilic glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase. Experientia Suppl. 1976;26:107–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7675-9_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Life at high temperatures. Evolutionary, ecological, and biochemical significance of organisms living in hot springs is discussed. Science. 1967 Nov;158(3804):1012–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3804.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeze H., Brock T. D. Thermostable aldolase from Thermus aquaticus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):541–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.541-550.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pask-Hughes R., Williams R. A. Extremely thermophilic gram-negative bacteria from hot tap water. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jun;88(2):321–328. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]