Abstract
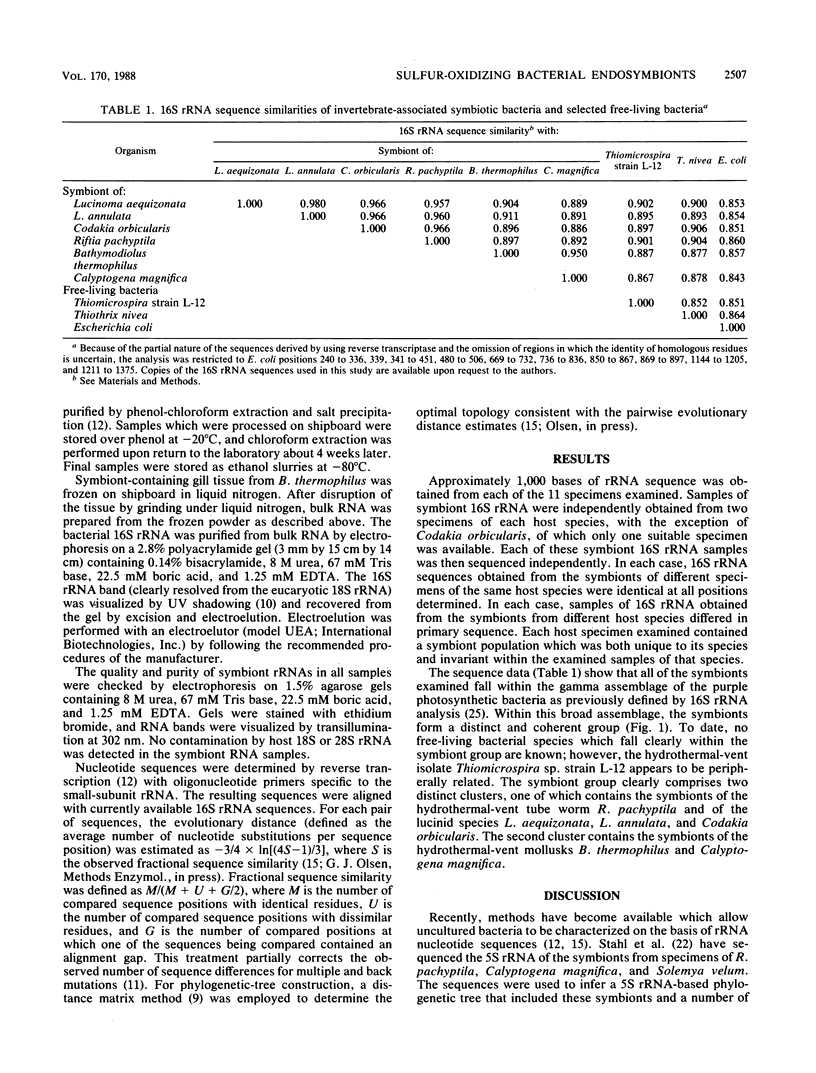
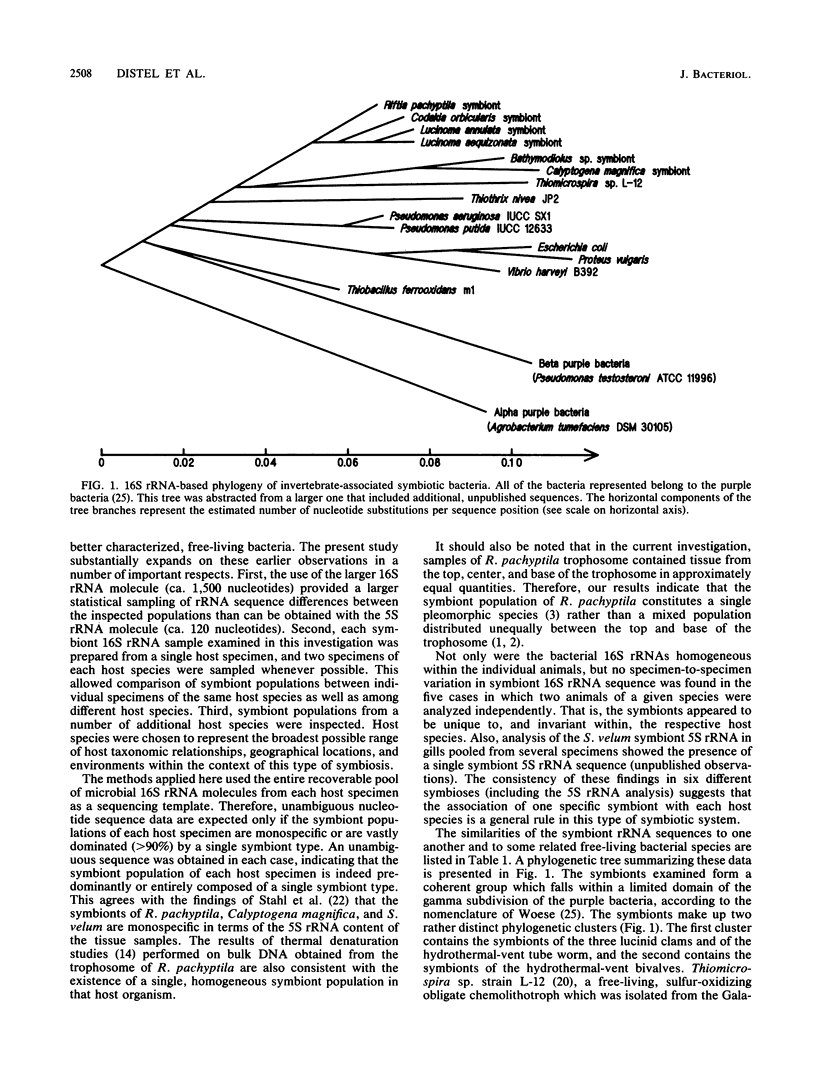
The 16S rRNAs from the bacterial endosymbionts of six marine invertebrates from diverse environments were isolated and partially sequenced. These symbionts included the trophosome symbiont of Riftia pachyptila, the gill symbionts of Calyptogena magnifica and Bathymodiolus thermophilus (from deep-sea hydrothermal vents), and the gill symbionts of Lucinoma annulata, Lucinoma aequizonata, and Codakia orbicularis (from relatively shallow coastal environments). Only one type of bacterial 16S rRNA was detected in each symbiosis. Using nucleotide sequence comparisons, we showed that each of the bacterial symbionts is distinct from the others and that all fall within a limited domain of the gamma subdivision of the purple bacteria (one of the major eubacterial divisions previously defined by 16S rRNA analysis [C. R. Woese, Microbiol. Rev. 51: 221-271, 1987]). Two host specimens were analyzed in five of the symbioses; in each case, identical bacterial rRNA sequences were obtained from conspecific host specimens. These data indicate that the symbioses examined are species specific and that the symbiont species are unique to and invariant within their respective host species.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavanaugh C. M., Gardiner S. L., Jones M. L., Jannasch H. W., Waterbury J. B. Prokaryotic Cells in the Hydrothermal Vent Tube Worm Riftia pachyptila Jones: Possible Chemoautotrophic Symbionts. Science. 1981 Jul 17;213(4505):340–342. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4505.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felbeck H. Chemoautotrophic Potential of the Hydrothermal Vent Tube Worm, Riftia pachyptila Jones (Vestimentifera). Science. 1981 Jul 17;213(4505):336–338. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4505.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Margoliash E. Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science. 1967 Jan 20;155(3760):279–284. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3760.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassur S. M., Whitlock H. W., Jr UV shadowing--a new and convenient method for the location of ultraviolet-absorbing species in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Stahl D. A., Olsen G. J., Heller D. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the genera Thiobacillus and Thiomicrospira by 5S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.75-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau G. H., Hedges J. I. Carbon-13 depletion in a hydrothermal vent mussel: suggestion of a chemosynthetic food source. Science. 1979 Feb 16;203(4381):648–649. doi: 10.1126/science.203.4381.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Jannasch H. W. Physiological characteristics of Thiomicrospira sp. Strain L-12 isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):161–165. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.161-165.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Analysis of hydrothermal vent-associated symbionts by ribosomal RNA sequences. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4647.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



