Abstract
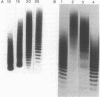
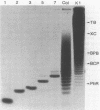
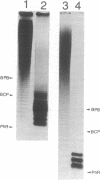
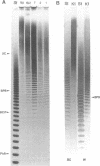
Methods were developed for the polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of capsular polysaccharides of bacteria with Escherichia coli K1 as a model. Conditions were determined for the rapid and gentle extraction of the K1 polysaccharide by incubation of the bacteria in a volatile buffer and for the subsequent removal of the putative phospholipid moiety attached to the reducing end of the polysaccharide. Detection of the polysaccharides after gel electrophoresis was carried out by fluorography of samples labeled by sodium borotritiide reduction or by combined alcian blue and silver staining. The smallest components could be detected only by fluorography, owing to diffusion during staining. Components of the E. coli K1 polysialic acid capsule ranging from monomers to 80 sialic-acid-unit-containing polymers could be separated as distinct bands in a ladderlike pattern. A maximum chain length of 160 to 230 sialyl residues was estimated for the bulk of the K1 polysaccharide from the nearly linear reciprocal relationship between the logarithm of the molecular size and the distance of migration. Gel electrophoresis of capsular polysaccharides of other bacterial species revealed different electrophoretic mobilities for each polysaccharide, with a ladderlike pattern displayed by the fastest-moving components. There are many potential applications of this facile method for the determination of the sizes of molecules present in a polydisperse polysaccharide sample. When combined with the simple method for the isolation of the capsule, as in the case of the K1 capsule, it provides an efficient tool for the characterization and comparison of the capsular polysaccharides of bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Pluschke G. Clonal analysis of descent and virulence among selected Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:185–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., GOEBEL W. F. Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature. 1957 Jan 26;179(4552):206–206. doi: 10.1038/179206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Group B streptococcal vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):458–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman M. K., Slahetka M. F., Hittner D. M., Kim J., Forino M., Gadelrab G. Polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and Alcian Blue staining of sulphated glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):707–716. doi: 10.1042/bj2210707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Bitter-Suermann D., Goridis C., Finne U. An IgG monoclonal antibody to group B meningococci cross-reacts with developmentally regulated polysialic acid units of glycoproteins in neural and extraneural tissues. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Mäkelä P. H. Cleavage of the polysialosyl units of brain glycoproteins by a bacteriophage endosialidase. Involvement of a long oligosaccharide segment in molecular interactions of polysialic acid. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1265–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Görgen I., Boulnois G. J., Timmis K. N., Bitter-Suermann D. NZB mouse system for production of monoclonal antibodies to weak bacterial antigens: isolation of an IgG antibody to the polysaccharide capsules of Escherichia coli K1 and group B meningococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Fraser B. A., Nishimura O., Robbins J. B., Liu T. Y. Lipid on capsular polysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8915–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Isolation of bacteriophages specific for the K1 polysaccharide antigen of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):548–550. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.548-550.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. C., Vimr E. R., Yu F., Bassler B., Troy F. A. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage-induced endo-N-acetylneuraminidase specific for poly-alpha-2,8-sialosyl carbohydrate units. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3553–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. C., Yu F., Troy F. A. Rapid separation of oligomers of polysialic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90670-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson I. N., Gallagher J. T. Separation of radiolabelled glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):697–705. doi: 10.1042/bj2210697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Jann B. The K antigens of Escherichia coli. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:53–79. doi: 10.1159/000407421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. Bacterial capsule--old dogmas and new tricks. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):407–415. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusecek B., Wloch H., Mercer A., Vaisänen V., Pluschke G., Korhonen T., Achtman M. Lipopolysaccharide, capsule, and fimbriae as virulence factors among O1, O7, O16, O18, or O75 and K1, K5, or K100 Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):368–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.368-379.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Boschek B., Thiele H., Stirm S. Substrate specificity of two bacteriophage-associated endo-N-acetylneuraminidases. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):367–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.367-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Stirm S. Polysialic acid depolymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:786–792. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifely M. R., Nowicka U. T., Moreno C. Analysis of the chain length of oligomers and polymers of sialic acid isolated from Neisseria meningitidis group B and C and Escherichia coli K1 and K92. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Nov 15;156:123–135. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGUIRE E. J., BINKLEY S. B. THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF COLOMINIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:247–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H., Cowman M. K. Combined alcian blue and silver staining of glycosaminoglycans in polyacrylamide gels: application to electrophoretic analysis of molecular weight distribution. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jun;155(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. W., Florini J. R. A rapid method for desalting small volumes of solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohr T. E., Troy F. A. Structure and biosynthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2332–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M. S., Oliveira E., Glode M. P., McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. M., Robbins J. B. A review: relation between invasiveness and the K1 capsular polysaccharide of Escherichia coli. Pediatr Res. 1976 Feb;10(2):82–87. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197602000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd The chemistry and biosynthesis of selected bacterial capsular polymers. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., McCloskey M. A. Role of a membranous sialyltransferase complex in the synthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. Temperature-induced alteration in the assembly process. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7377–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann W. F., Schmidt M. A., Jann B., Jann K. The structure of the capsular polysaccharide (K5 antigen) of urinary-tract-infective Escherichia coli 010:K5:H4. A polymer similar to desulfo-heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):359–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. Regulation of sialic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli: role of N-acylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):854–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.854-860.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]