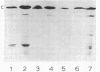
Abstract
Different preparations of the methylreductase were tested in a simplified methylcoenzyme M methylreductase assay with artificial electron donors under a nitrogen atmosphere. ATP and Mg2+ stimulated the reaction. Tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium (II), chromous chloride, chromous acetate, titanium III citrate, 2,8-diaminoacridine, formamidinesulfinic acid, cob(I)alamin (B12s), and dithiothreitol were tested as electron donors; the most effective donor was titanium III citrate. Methylreductase (component C) was prepared by 80% ammonium sulfate precipitation, 70% ammonium sulfate precipitation, phenyl-Sepharose chromatography, Mono Q column chromatography, DEAE-cellulose column chromatography, or tetrahydromethanopterin affinity column chromatography. Methylreductase preparations which were able to catalyze methanogenesis in the simplified reaction mixture contained contaminating proteins. Homogeneous component C obtained from a tetrahydromethanopterin affinity column was not active in the simplified assay but was active in a methylreductase assay that contained additional protein components.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankel-Fuchs D., Thauer R. K. Methane formation from methyl-coenzyme M in a system containing methyl-coenzyme M reductase, component B and reduced cobalamin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J. Systems for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:237–255. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellefson W. L., Wolfe R. S. Component C of the methylreductase system of Methanobacterium. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4259–4262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellefson W. L., Wolfe R. S. Role of component C in the methylreductase system of Methanobacterium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8388–8389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Leigh J. A., Rinehart K. L., Wolfe R. S. Formaldehyde activation factor, tetrahydromethanopterin, a coenzyme of methanogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1976–1980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Wolfe R. S. Tetrahydromethanopterin, a carbon carrier in methanogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9447–9455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Wolfe R. S. Tetrahydromethanopterin-dependent methanogenesis from non-physiological C1 donors in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):696–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.696-701.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Romesser J. A., Wolfe R. S. Preparation of coenzyme M analogues and their activity in the methyl coenzyme M reductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Wolfe R. S. ATP activation and properties of the methyl coenzyme M reductase system in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.851-857.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Wolfe R. S. Methyl coenzyme M reductase from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Resolution and properties of the components. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1891–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle D. P., Jr, Wolfe R. S. Component A of the methyl coenzyme M methylreductase system of Methanobacterium: resolution into four components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll K. M., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Tanner R. S., Wolfe R. S. Structure of component B (7-mercaptoheptanoylthreonine phosphate) of the methylcoenzyme M methylreductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4238–4242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière P. E., Escalante-Semerena J. C., Wolfe R. S. Component A2 of the methylcoenzyme M methylreductase system from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):61–66. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.61-66.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitols E., Walker G. A., Huennekens F. M. Enzymatic conversion of vitamin B-12s to a cobamide coenzyme, alpha-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl)deoxyadenosylcobamide (adenosyl-B-12). J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1455–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]