Abstract
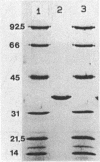
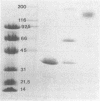
Malate dehydrogenase (MDH; EC 1.1.1.37) from the thermophilic green nonsulfur bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus was purified by a two-step procedure involving affinity chromatography and gel filtration. The enzyme consists of identical subunits which had molecular weights of approximately 35,000. In its active form at 55 degrees C, it formed tetramers. At lower temperatures, inactive dimers and trimers existed. Antibodies against the purified enzyme were produced, and immunotitration and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays showed that there was an immunochemical homology between the MDH from C. aurantiacus and MDHs from several other bacteria. The amino acid composition of C. aurantiacus MDH was similar to those of other MDHs. The N-terminal amino acid sequence was enriched with hydrophobic amino acids, which showed a high degree of functional similarity to amino acids at the N-terminal ends of both Escherichia coli and Thermus flavus MDHs. The activity of the native enzyme was inhibited by high concentrations of substrate and had temperature and pH optima consistent with the optimal growth conditions for the organism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Rossman M. G., Grau U. M., Zuber H., Frank G., Tratschin J. D. Thermal stability and protein structure. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 11;18(25):5698–5703. doi: 10.1021/bi00592a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz A. A., Lubrano T. Separation and quantitation of lactic dehydrogenase isoenzymes by disc electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Aug;20(2):246–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel R. C., Meezan E., Brendel K. Metachromatic staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 of the proline-rich calf thymus histone, H1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 16;626(2):432–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima S., Saiki T., Beppu T. Physicochemical and catalytic properties of thermostable malate dehydrogenase from an extreme thermophile Thermus flavus AT-62. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;613(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. Nearest-neighbor relationships of the constituent polypeptides in plastoquinol-plastocyanin oxidoreductase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 12;848(3):324–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama M., Matsubara N., Yamamoto K., Iijima S., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Nucleotide sequence of the malate dehydrogenase gene of Thermus flavus and its mutation directing an increase in enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14178–14183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson B. K., Castenholz R. W. A phototrophic gliding filamentous bacterium of hot springs, Chloroflexus aurantiacus, gen. and sp. nov. Arch Microbiol. 1974;100(1):5–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00446302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schär H. P., Zuber H. Structure and function of L-lactate dehydrogenases from thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria. I) Isolation and characterization of lactate dehydrogenases from thermophilic and mesophilic bacilli. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Jul;360(7):795–807. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1979.360.2.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirevåg R. Photoassimilation of acetate and metabolism of carbohydrate in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):105–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00447309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Natvig J. B., Husby G., Juul J. The complete amino acid sequence of a prototype immunoglobulin-lambda light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein AR. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1950561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram T. K., Wright I. P., Wilkinson A. E. Malate dehydrogenase from thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria. Molecular size, subunit structure, amino acid composition, immunochemical homology, and catalytic activity. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2017–2022. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland P., McAlister-Henn L. Isolation and expression of the Escherichia coli gene encoding malate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1074–1079. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1074-1079.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tayeh M. A., Madigan M. T. Malate dehydrogenase in phototrophic purple bacteria: purification, molecular weight, and quaternary structure. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4196–4202. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4196-4202.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel R. F., Entian K. D., Mecke D. Cloning and sequence of the mdh structural gene of Escherichia coli coding for malate dehydrogenase. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(1):36–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00423133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]