Abstract
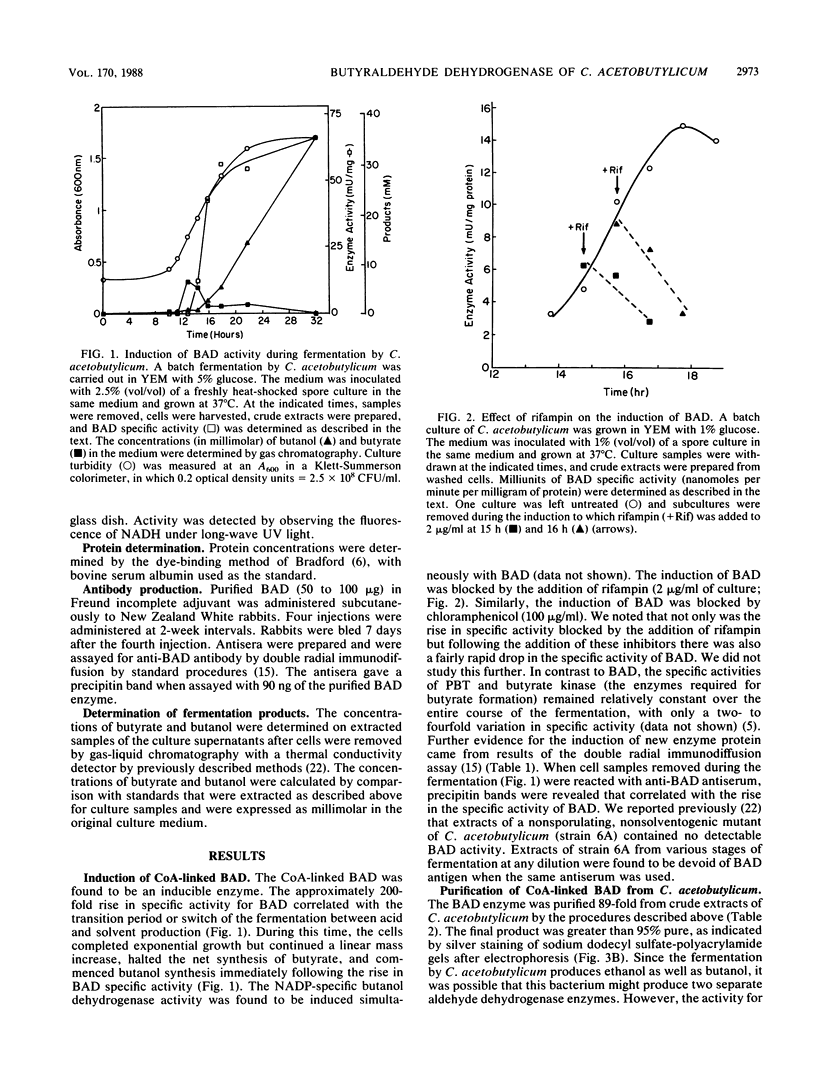
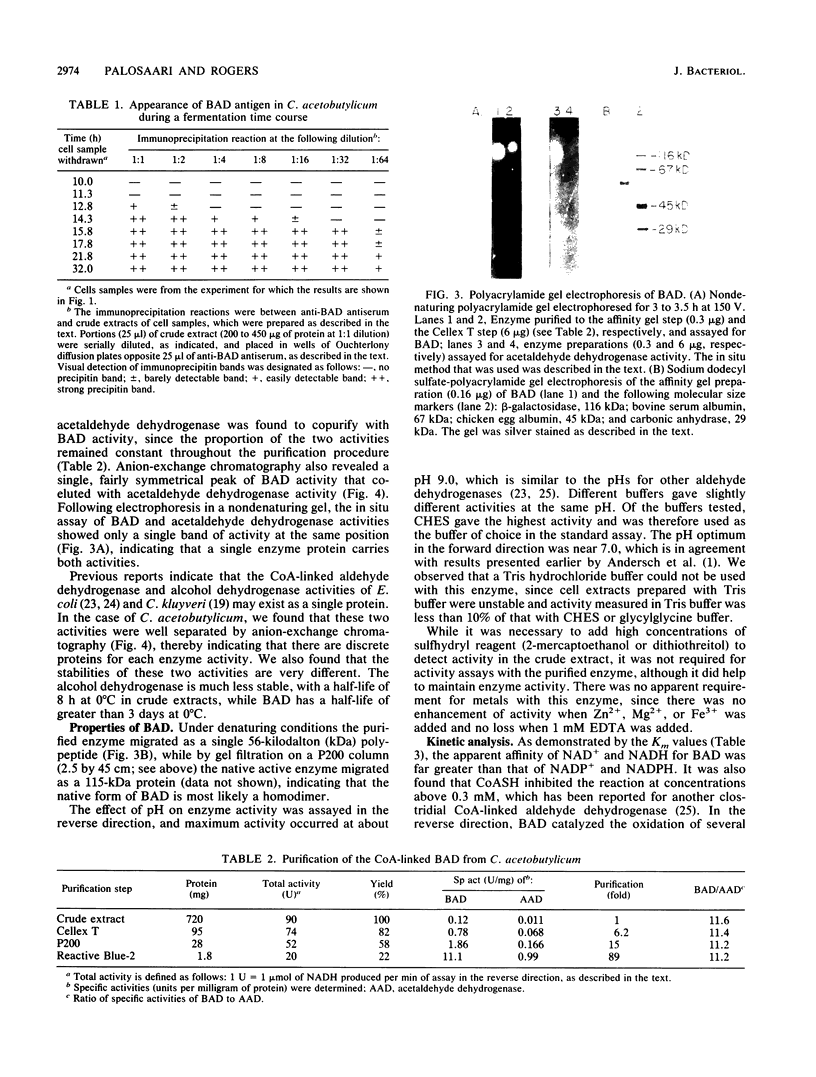
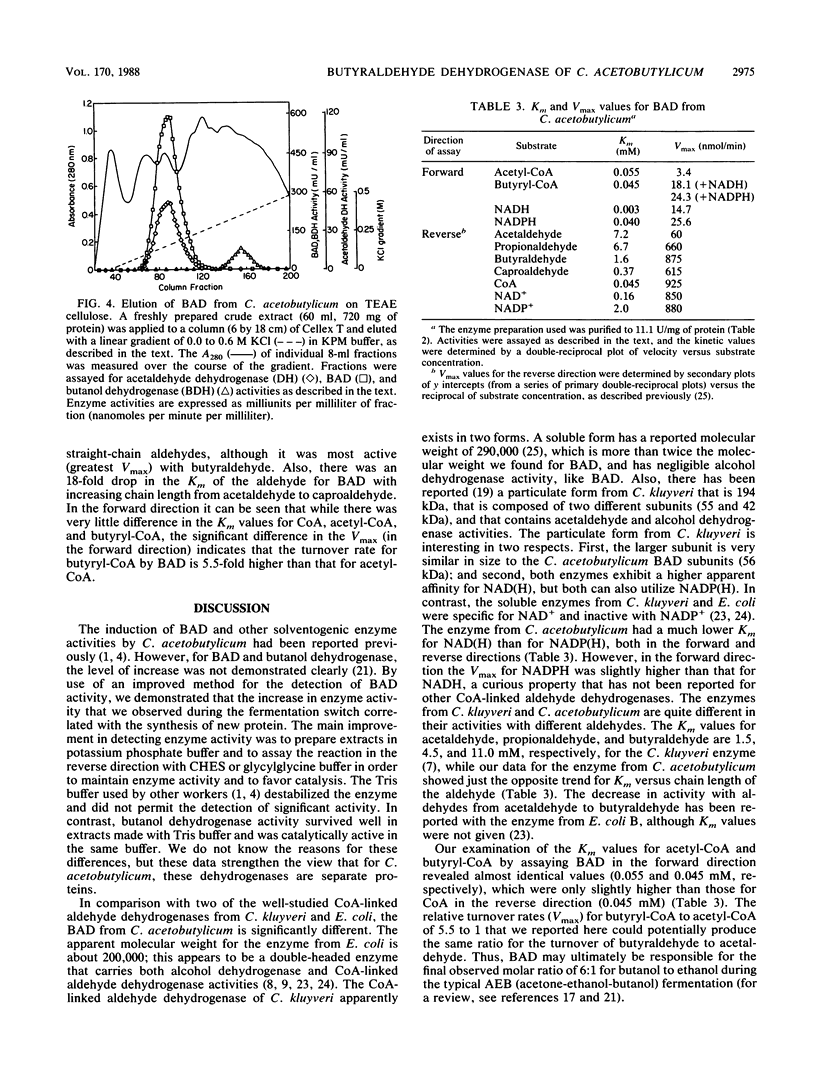
The coenzyme A (CoA)-linked butyraldehyde dehydrogenase (BAD) from Clostridium acetobutylicum was characterized and purified to homogeneity. The enzyme was induced over 200-fold, coincident with a shift from an acidogenic to a solventogenic fermentation, during batch culture growth. The increase in enzyme activity was found to require new protein synthesis since induction was blocked by the addition of rifampin and antibody against the purified enzyme showed the appearance of enzyme antigen beginning at the shift of the fermentation and increasing coordinately with the increase in enzyme specific activity. The CoA-linked acetaldehyde dehydrogenase was copurified with BAD during an 89-fold purification, indicating that one enzyme accounts for the synthesis of the two aldehyde intermediates for both butanol and ethanol production. Butanol dehydrogenase activity was clearly separate from the BAD enzyme activity on TEAE cellulose. A molecular weight of 115,000 was determined for the native enzyme, and the enzyme subunit had a molecular weight of 56,000 indicating that the active form is a homodimer. Kinetic constants were determined in both the forward and reverse directions. In the reverse direction both the Vmax and the apparent affinity for butyraldehyde and caproaldehyde were significantly greater than they were for acetaldehyde, while in the forward direction, the Vmax for butyryl-CoA was fivefold that for acetyl-CoA. These and other properties of BAD indicate that this enzyme is distinctly different from other reported CoA-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON R. M., STADTMAN E. R. The oxidation of acetaldehyde to acetyl coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):873–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahl H., Gottwald M., Kuhn A., Rale V., Andersch W., Gottschalk G. Nutritional Factors Affecting the Ratio of Solvents Produced by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):169–172. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.169-172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker F. C., Schooley D. A. Analysis and purification of acyl coenzyme A thioesters by reversed-phase ion-pair liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. P., Cronan J. E., Jr Acetaldehyde coenzyme A dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):179–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.179-184.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham P. R., Clark D. P. The use of suicide substrates to select mutants of Escherichia coli lacking enzymes of alcohol fermentation. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):487–493. doi: 10.1007/BF00338087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R., Stephenson M. Studies on the acetone-butyl alcohol fermentation: Nutritional and other factors involved in the preparation of active suspensions of Cl. acetobutylicum (Weizmann). Biochem J. 1941 Dec;35(12):1320–1331. doi: 10.1042/bj0351320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmanis M. G. Butyrate kinase from Clostridium acetobutylicum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):617–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmanis M. G., Gatenbeck S. Intermediary Metabolism in Clostridium acetobutylicum: Levels of Enzymes Involved in the Formation of Acetate and Butyrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1277-1283.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiu S. F., Zhu C. X., Yan R. T., Chen J. S. Butanol-Ethanol Dehydrogenase and Butanol-Ethanol-Isopropanol Dehydrogenase: Different Alcohol Dehydrogenases in Two Strains of Clostridium beijerinckii (Clostridium butylicum). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):697–703. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.697-703.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Woods D. R. Acetone-butanol fermentation revisited. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):484–524. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.484-524.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. W., Morris J. G. Oxygen and the growth and metabolism of Clostridium acetobutylicum. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Nov;68(3):307–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers P., Palosaari N. Clostridium acetobutylicum Mutants That Produce Butyraldehyde and Altered Quantities of Solvents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2761–2766. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2761-2766.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph F. B., Purich D. L., Fromm H. J. Coenzyme A-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. I. Partial purification, properties, and kinetic studies of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5539–5545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt B. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity of a complex particle from E. coli. Biochimie. 1975;57(9):1001–1004. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. T., Kaplan N. O. Purification, properties, and kinetic mechanism of coenzyme A-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase from Clostridium kluyveri. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Sep;203(2):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWAROG R., WOLFE R. S. Enzymatic phosphorylation of butyrate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2474–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWAROG R., WOLFE R. S. ROLE OF BUTYRYL PHOSPHATE IN THE ENERGY METABOLISM OF CLOSTRIDIUM TETANOMORPHUM. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:112–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.112-117.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., WOLFE R. S. Purification and role of phosphotransbutyrylase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:1948–1952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]