Abstract
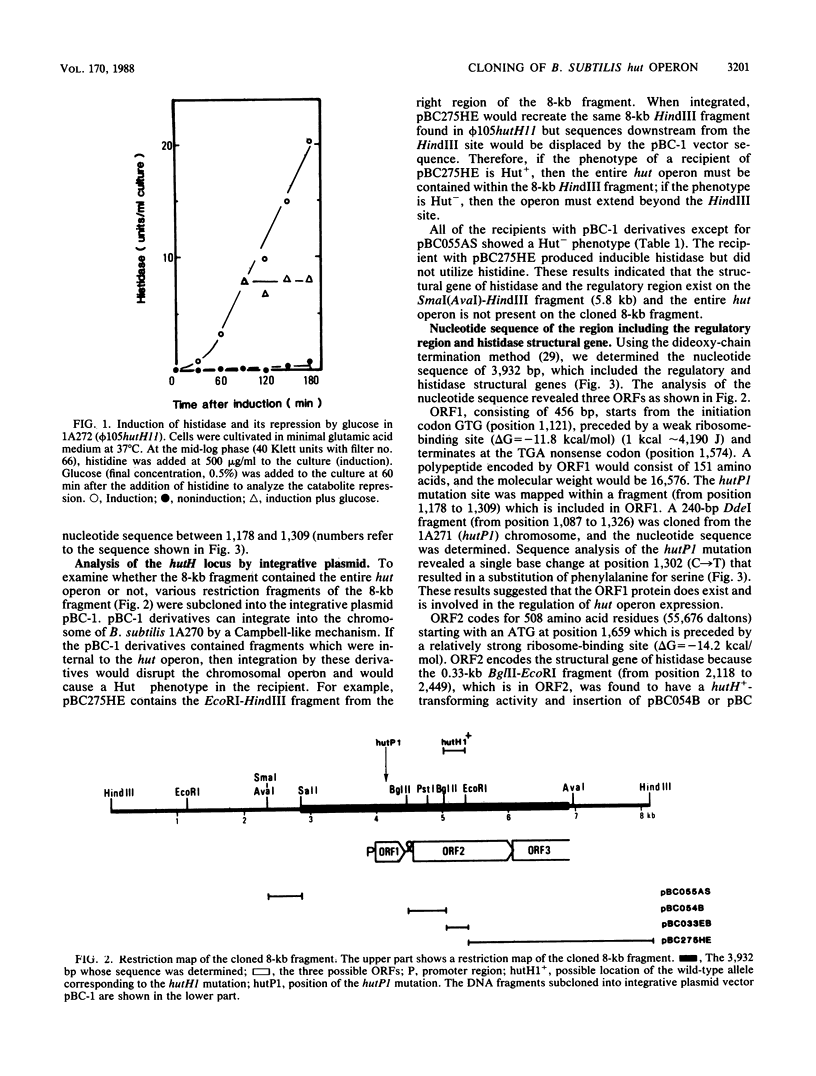
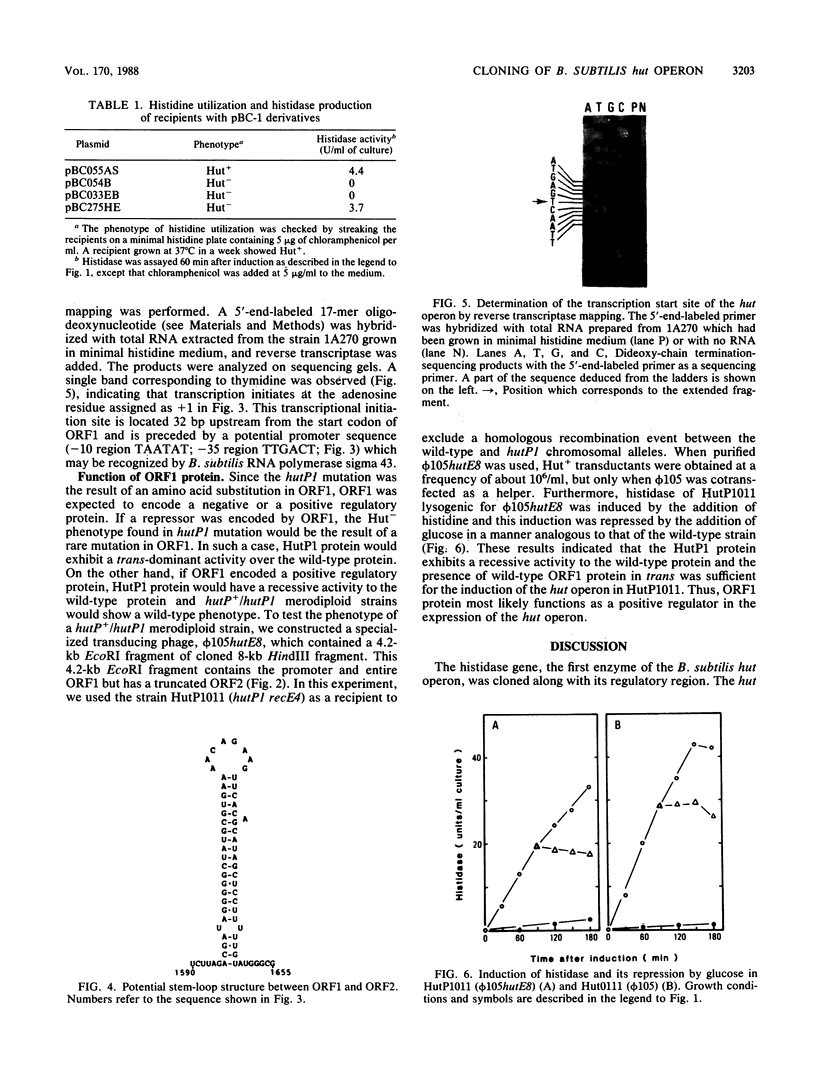
An 8-kilobase HindIII fragment carrying the histidase gene (hutH) and its regulatory region (hutP), from the Bacillus subtilis histidine utilization (hut) operon, was cloned in the temperate bacteriophage phi 105. Histidine utilization was restored in a hutH1 mutant by the specialized transducing phage (phi 105hutH11). The histidase gene in phi 105hutH11 was inducible and was shown to be under catabolite repression. The nucleotide sequence of 3,932 base pairs including the hutH and hutP loci revealed three open reading frames (ORFs). The molecular weights of ORF1 and ORF2 proteins were calculated to be 16,576 (151 amino acid residues) and 55,675 (508 amino acid residues), respectively. Reverse transcriptase mapping experiments showed that the putative promoter for the hut operon could be recognized by RNA polymerase sigma 43. The transcript starts at an adenosine residue 32 base pairs upstream from the initiation codon of ORF1. hutH+-transforming activity was found in ORF2, indicating that ORF2 encoded the histidase. A hutP1 mutation was determined as a substitution of an amino acid in ORF1. By using a specialized transducing phage containing the wild-type ORF1 gene, it was demonstrated that the presence of ORF1 protein in trans was absolutely required for the induction of the hut operon in a hutP1 mutant. These data strongly suggested that ORF1 encodes a positive regulator of the hut operon.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenberg M., Magasanik B. Physical maps of Klebsiella aerogenes and Salmonella typhimurium hut genes. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.664-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan S. A., Eades L. J., Janssen K. A., Lomax M. I., Bender R. A. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of the histidine utilization (hut) genes of Klebsiella aerogenes and deletions lacking regions of hut DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):92–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00327420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugaichuk U. D., Deadman M., Errington J., Savva D. Restriction enzyme analysis of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 105 DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Aug;130(8):2165–2167. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-8-2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A., Magasanik B. Induction and repression of the histidine-degrading enzymes of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5165–5178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consevage M. W., Porter R. D., Phillips A. T. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of histidine utilization genes from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):138–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.138-146.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman D. W., Sonenshein A. L. Purification of aconitase from Bacillus subtilis and correlation of its N-terminal amino acid sequence with the sequence of the citB gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3062–3067. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3062-3067.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Fujita T. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis gluconate operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1237–1252. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Fujita T., Miwa Y., Nihashi J., Aratani Y. Organization and transcription of the gluconate operon, gnt, of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13744–13753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Developmental and genetic regulation of Bacillus subtilis genes transcribed by sigma 28-RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Magasanik B. Gene order of the histidine utilization (hut) operons in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1025–1031. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1025-1031.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTWELL L. H., MAGASANIK B. THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF HISTIDASE INDUCTION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Mol Biol. 1963 Oct;7:401–420. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Gerson S. L., Magasanik B. Isolation of super-repressor mutants in the histidine utilization system of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):583–593. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.583-593.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimhi Y., Magasanik B. Genetic basis of histidine degradation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3545–3548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Neidhardt F. C. Formation and operation of the histidine-degrading pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1800–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1800-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Wright A. A bacterial gene involved in transcription antitermination: regulation at a rho-independent terminator in the bgl operon of E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin L., Magnusson K., Rutberg L. Identification of the promoter of the Bacillus subtilis sdh operon. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3232–3236. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3232-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. R., Clarke P. H. The effect of nitrogen limitation on catabolite repression of amidase, histidase and urocanase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):377–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Resistance to catabolite repression of histidase and proline oxidase during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6288–6296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Modulation of Bacillus subtilis levansucrase gene expression by sucrose and regulation of the steady-state mRNA level by sacU and sacQ genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):380–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.380-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Magasanik B. The two operons of the histidine utilization system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3330–3341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Specialized transduction of the Salmonella hut operons by coliphage lambda: deletion analysis of the hut operons employing lambda-phut. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):208–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Bott K. F. Nutritional factors influencing the development of competence in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1439–1449. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1439-1449.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]