Abstract
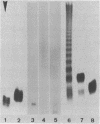
Two strains of the gliding phototrophic bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus were investigated for the presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). With both strains, all fractions of hot phenol-water extracts and the extracted cell residues from whole cells or cell homogenates were found to be free from characteristic LPS constituents, such as 3-hydroxy fatty acids, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate, heptoses, or O-chain sugars. Phenolchloroform-petroleum ether extracts were also free from precipitable LPS. A lipid A fraction could not be obtained, and there was no hint for glucosamine as a possible lipid A backbone amino sugar. Absence of LPS was confirmed by sodium deoxycholate gel electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brade H., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Differential determination of the 3-Deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid residues in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castenholz R. W. Thermophilic blue-green algae and the thermal environment. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):476–504. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.476-504.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens U. J., Drews G., Weckesser J. Primary structure of the peptidoglycan from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6714. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.471-478.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Porin from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):199–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.199-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Debrunner-Vossbrinck B. A., Oyaizu H., Stackebrandt E., Ludwig W. Gram-positive bacteria: possible photosynthetic ancestry. Science. 1985;229:762–765. doi: 10.1126/science.11539659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]