Abstract
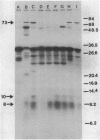
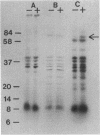
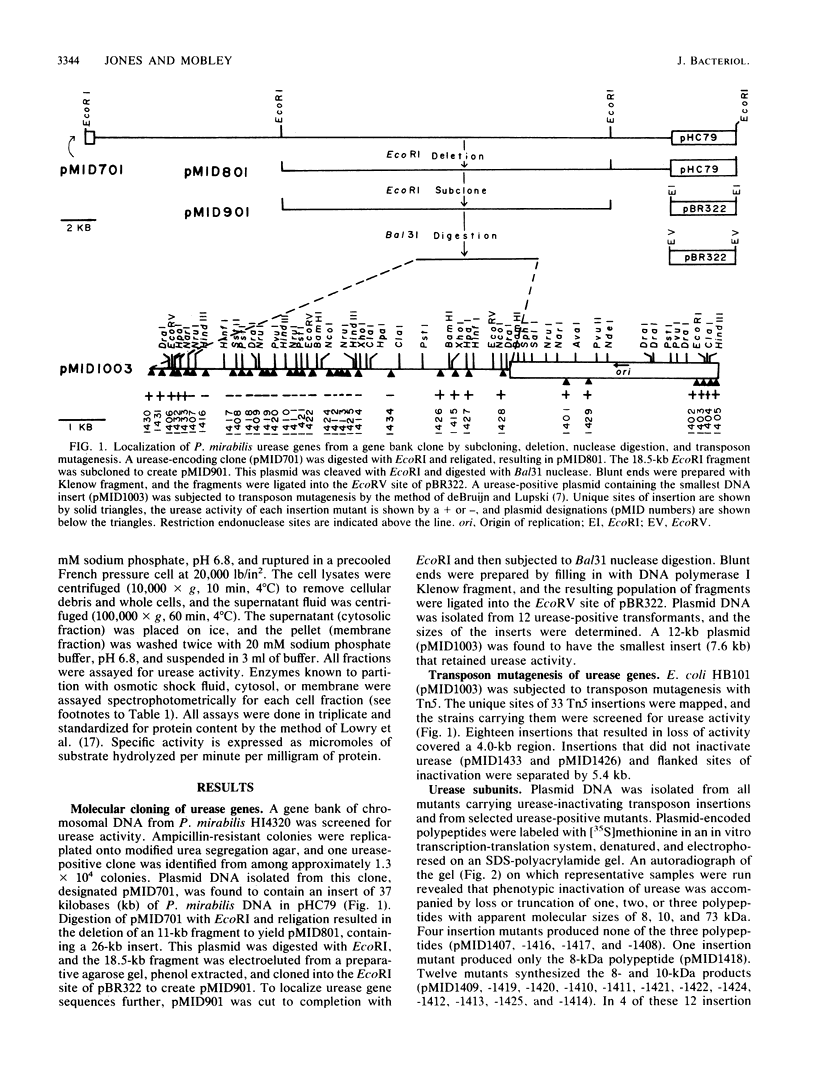
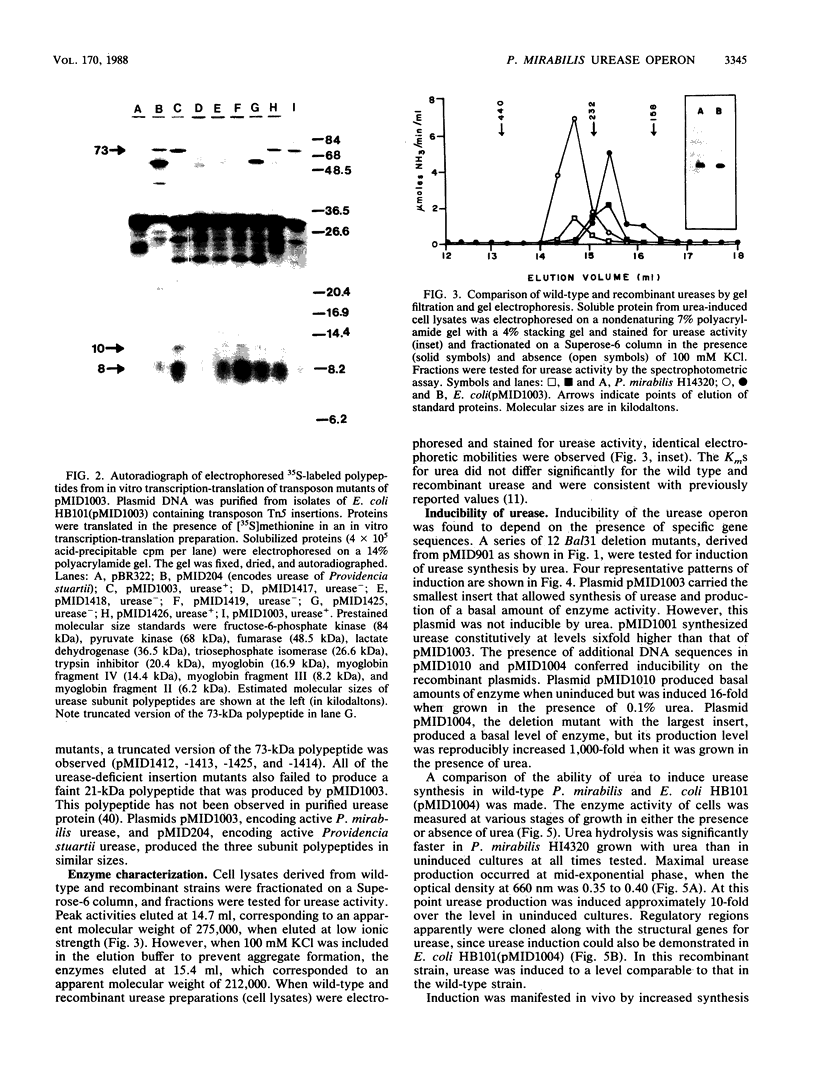
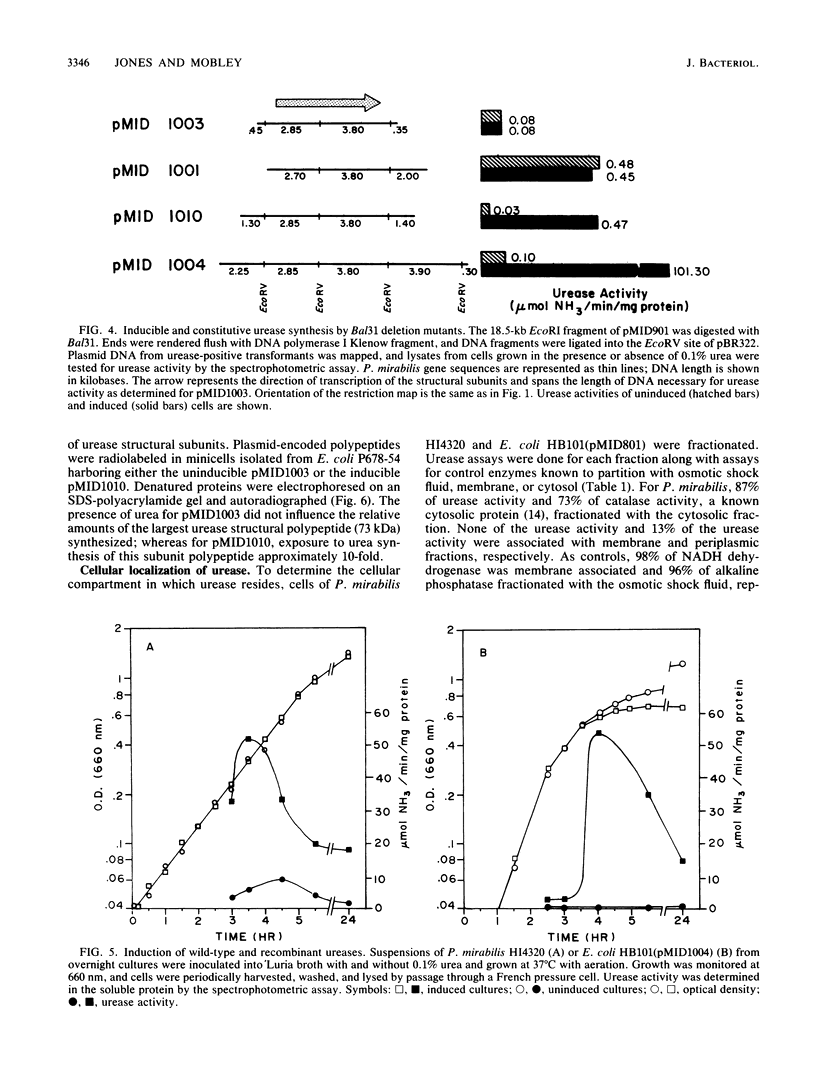
Proteus mirabilis, a cause of serious urinary tract infection, produces urease, an important virulence factor for this species. The enzyme hydrolyzes urea to CO2 and NH3, which initiates struvite or apatite stone formation. Genes encoding urease were localized on a P. mirabilis chromosomal DNA gene bank clone in Escherichia coli by deletion analysis, subcloning, Bal31 nuclease digestion, transposon Tn5 mutagenesis, and in vitro transcription-translation. A region of DNA between 4.0 and 5.4 kilobases (kb) in length was necessary for urease activity and was located within an 18.5-kb EcoRI fragment. The operon was induced by urea and encoded a multimeric, cytoplasmic enzyme comprising subunit polypeptides of 8,000, 10,000, and 73,000 daltons that were encoded by a single polycistronic mRNA and transcribed in that order. Seventeen urease-negative transposon insertions were isolated that synthesized either none of the structural subunit polypeptides, the 8,000-dalton polypeptide alone, or both the 8,000- and 10,000-dalton subunit polypeptides. The molecular weight of the native enzyme was estimated to be 212,000 by Superose-6 chromatography. Homologous sequences encoding the urease of Providencia stuartii synthesized subunit polypeptides of similar sizes and showed a similar genetic arrangement. However, restriction maps of the operons from the two species were distinct, indicating significant divergence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adegbola R. A., Old D. C., Senior B. W. The adhesins and fimbriae of Proteus mirabilis strains associated with high and low affinity for the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Nov;16(4):427–431. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-4-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adegbola R. A., Old D. C., Senior B. W. The adhesins and fimbriae of Proteus mirabilis strains associated with high and low affinity for the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Nov;16(4):427–431. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-4-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler L. W., Ichikawa T., Hasan S. M., Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Orientation of the protonmotive force in membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(1):15–27. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Role of bacterial urease in experimental pyelonephritis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:171–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.171-179.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitenbach J. M., Hausinger R. P. Proteus mirabilis urease. Partial purification and inhibition by boric acid and boronic acids. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2500917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. M., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of an Escherichia coli urease locus: evidence of DNA rearrangement. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1041–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1041-1045.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Larsson P., Lomberg H. Attachment of Proteus mirabilis to human urinary sediment epithelial cells in vitro is different from that of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):804–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.804-807.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hickman F. W., Brenner D. J., Schreiber M., Rickenbach D. G. Unusual Enterobacteriaceae. "Proteus rettgeri" that "change" into Providencia stuartii. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):373–378. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.373-378.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. E., Jr, Stamey T. A. Studies of introital colonization in women with recurrent urinary infections. X. Adhesive properties of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis: lack of correlation with urinary pathogenicity. J Urol. 1978 Sep;120(3):315–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)57152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Gargan R. A. Rapid screening for urease inhibitors. Invest Urol. 1979 Mar;16(5):327–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Genetic and biochemical diversity of ureases of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella species isolated from urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2198–2203. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2198-2203.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouve H. M., Tessier S., Pelmont J. Purification and properties of the Proteus mirabilis catalase. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;61(1):8–14. doi: 10.1139/o83-002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLaren D. M. The significance of urease in proteus pyelonephritis: a bacteriological study. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):45–56. doi: 10.1002/path.1700960106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLaren D. M. The significance of urease in proteus pyelonephritis: a histological and biochemical study. J Pathol. 1969 Jan;97(1):43–49. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. J., Cheng K. J., Gould W. D., Nickel J. C., Costerton J. W. Histochemical and biochemical urease localization in the periplasm and outer membrane of two Proteus mirabilis strains. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Oct;32(10):772–778. doi: 10.1139/m86-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Jerse A. E. Cloning of urease gene sequences from Providencia stuartii. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.161-169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Warren J. W. Urease-positive bacteriuria and obstruction of long-term urinary catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2216–2217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2216-2217.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulrooney S. B., Lynch M. J., Mobley H. L., Hausinger R. P. Purification, characterization, and genetic organization of recombinant Providencia stuartii urease expressed by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2202–2207. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2202-2207.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasaki H., Matsushima T., Sato S., Kawachi T. Purification and properties of alkaline phosphatase from the mucosa of rat small intestine. J Biochem. 1979 Nov;86(5):1225–1231. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin G. J., Braude A. I. Immobilizing antibodies in urine. II. Prevention of ascending spread of Proteus mirabilis. Invest Urol. 1974 Sep;12(2):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerbooms P. G., Verweij A. M., MacLaren D. M. Investigation of the haemolytic activity of Proteus mirabilis strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Apr;49(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00457874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerbooms P. G., Verweij A. M., MacLaren D. M. Uropathogenic properties of Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Feb;19(1):55–60. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerbooms P. G., Verweij A. M., MacLaren D. M. Vero cell invasiveness of Proteus mirabilis. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1068–1071. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1068-1071.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein I. J., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. Role of urease in the formation of infection stones: comparison of ureases from different sources. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.32-37.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlammadinger J., Szabó G. The effect of theophylline upon induced -galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1971;18(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W., Bradford N. C., Simpson D. S. The ureases of Proteus strains in relation to virulence for the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Nov;13(4):507–512. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-4-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Ofek I. Influence of pili on the virulence of Proteus mirabilis in experimental hematogenous pyelonephritis. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):664–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. J., Hausinger R. P. Purification and characterization of the nickel-containing multicomponent urease from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5963–5967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz S. E., Wray S. K., Hull S. I., Hull R. A. Multiple proteins encoded within the urease gene complex of Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1027-1033.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. W., Damron D., Tenney J. H., Hoopes J. M., Deforge B., Muncie H. L., Jr Fever, bacteremia, and death as complications of bacteriuria in women with long-term urethral catheters. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1151–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. W., Tenney J. H., Hoopes J. M., Muncie H. L., Anthony W. C. A prospective microbiologic study of bacteriuria in patients with chronic indwelling urethral catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):719–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Identification of two different hemolysin determinants in uropathogenic Proteus isolates. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2183–2190. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2183-2190.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Hull S. I., Cook R. G., Barrish J., Hull R. A. Identification and characterization of a uroepithelial cell adhesin from a uropathogenic isolate of Proteus mirabilis. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.43-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]