Abstract
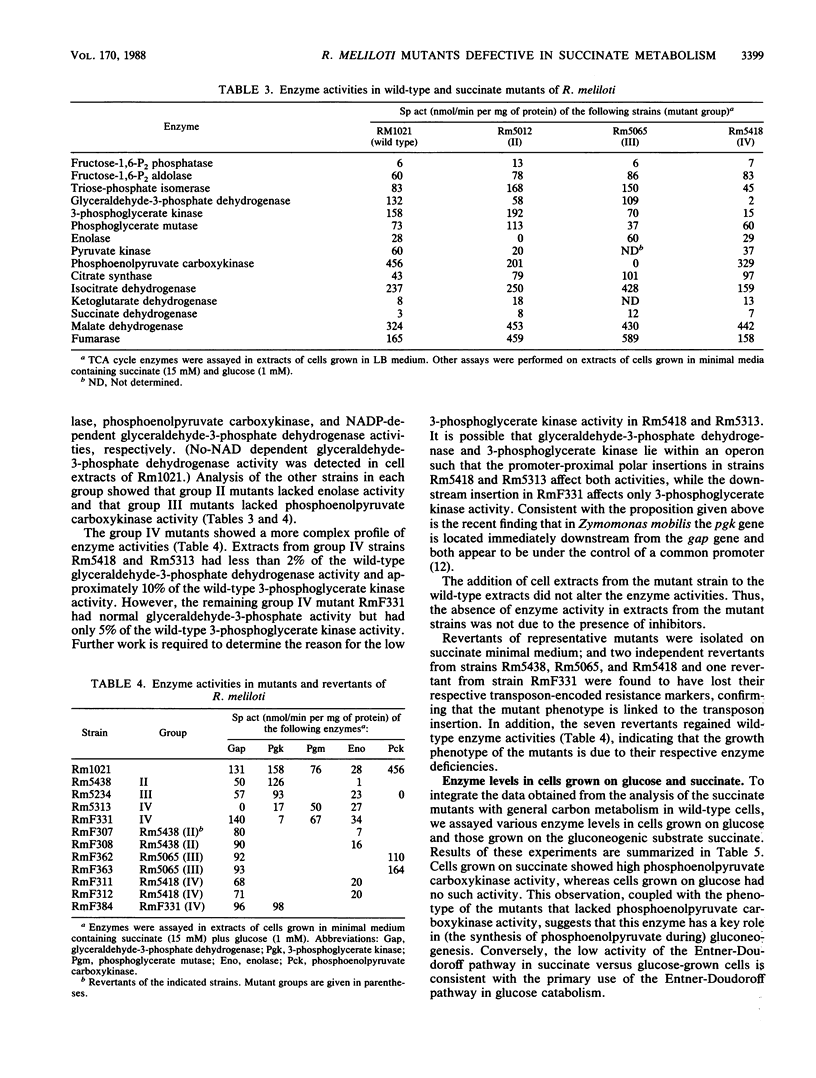
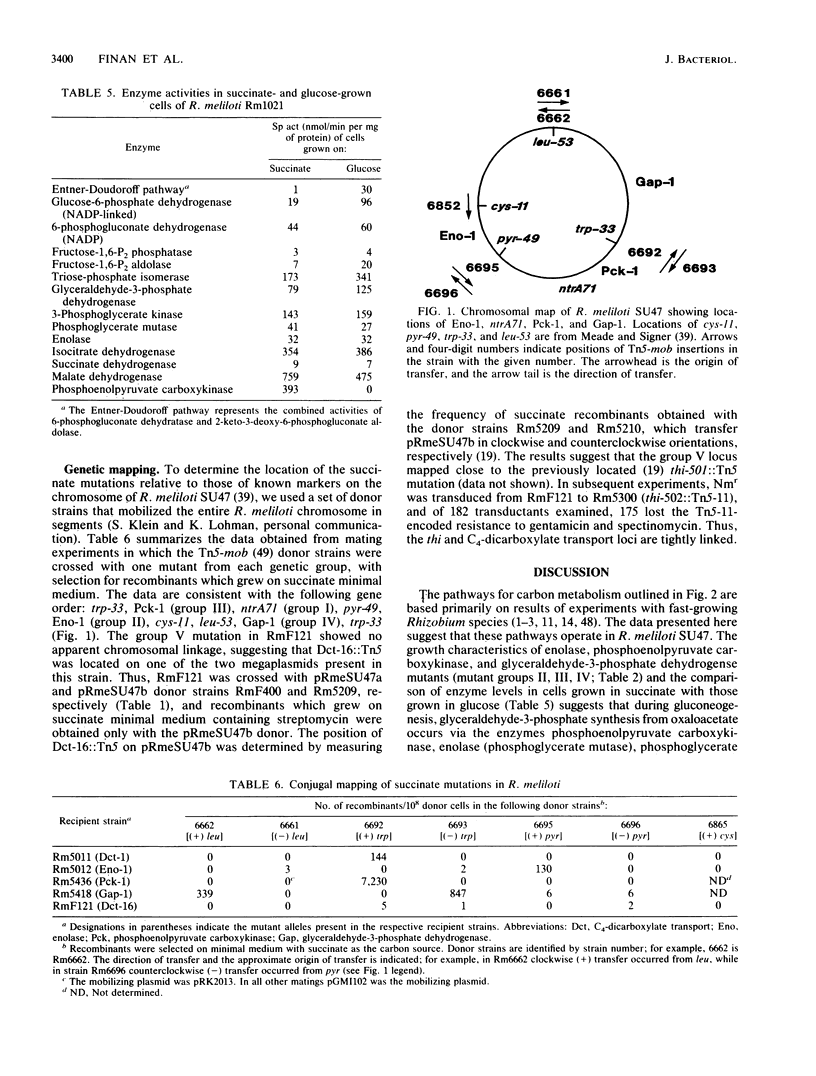
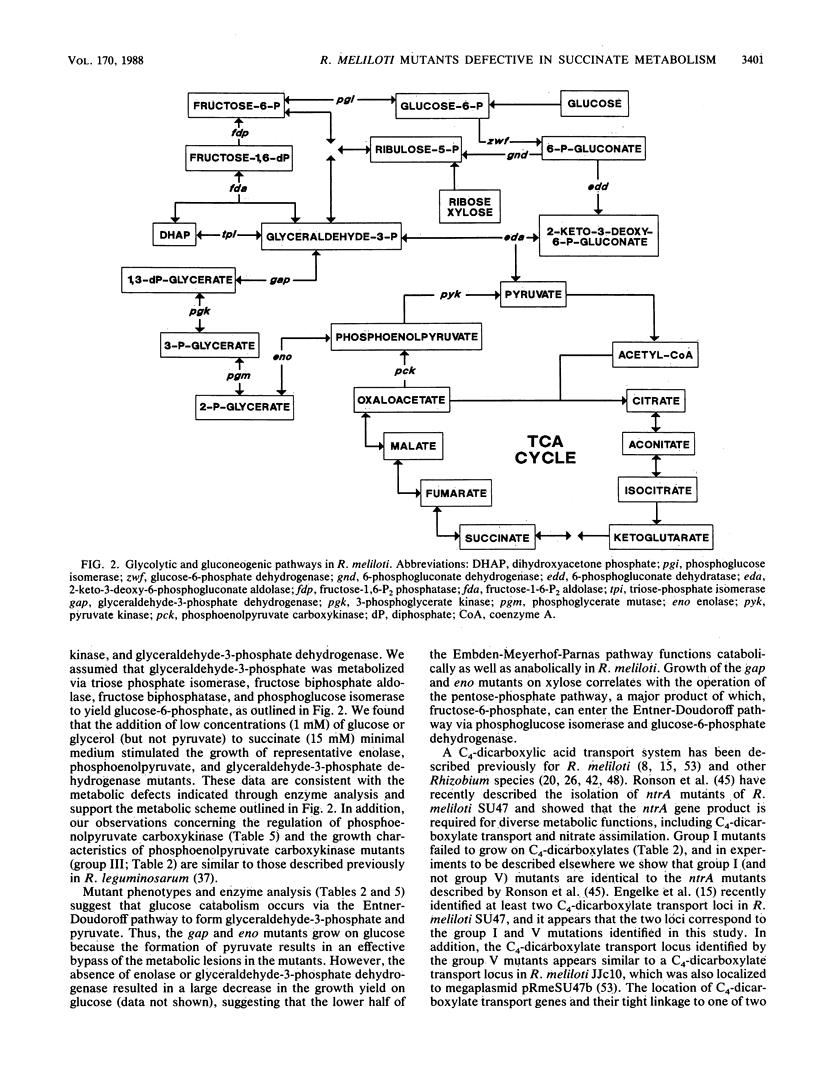
We characterized mutants of Rhizobium meliloti SU47 that were unable to grow on succinate as the carbon source. The mutants fell into five groups based on complementation of the succinate mutations by individual recombinant plasmids isolated from a R. meliloti clone bank. Enzyme analysis showed that mutants in the following groups lacked the indicated common enzyme activities: group II, enolase (Eno); group III, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck); group IV, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gap), and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (Pgk). Mutants in groups I and V lacked C4-dicarboxylate transport (Dct-) activity. Wild-type cells grown on succinate as the carbon source had high Pck activity, whereas no Pck activity was detected in cells that were grown on glucose as the carbon source. It was found that in free-living cells, Pck is required for the synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate during gluconeogenesis. In addition, the enzymes of the lower half of the Embden-Meyerhoff-Parnas pathway were absolutely required for gluconeogenesis. Eno, Gap, Pck, and one of the Dct loci (ntrA) mapped to different regions of the chromosome; the other Dct locus was tightly linked to a previously mapped thi locus, which was located on the megaplasmid pRmeSU47b.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias A., Cerveńansky C., Gardiol A., Martínez-Drets G. Phosphoglucose isomerase mutant of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):409–414. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.409-414.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias A., Gardiol A., Martínez-Drets G. Transport and catabolism of D-mannose in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1069–1072. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1069-1072.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P. C., Darzins A., Maitra P. K. Gluconeogenic mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: genetic linkage between fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and phosphoglycerate kinase. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):1099–1107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Shapiro L., Hodgson D. A. Generation of a Tn5 promoter probe and its use in the study of gene expression in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen J. F., Turner G. L. Nitrogen fixation by the bacteroid fraction of breis of soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerveñanský C., Arias A. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in pleiotropic carbohydrate-negative mutant strains of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1027-1030.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Ingram L. O. Phosphoglycerate kinase gene from Zymomonas mobilis: cloning, sequencing, and localization within the gap operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1926–1933. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1926-1933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G. F., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Genetic manipulations in Rhizobium meliloti utilizing two new transposon Tn5 derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00331029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. J., Fraenkel D. G. alpha-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase mutant of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):415–419. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.415-419.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Hartweig E., LeMieux K., Bergman K., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. General transduction in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):120–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.120-124.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Kunkel B., De Vos G. F., Signer E. R. Second symbiotic megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti carrying exopolysaccharide and thiamine synthesis genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.66-72.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Wood J. M., Jordan D. C. Succinate transport in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):193–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.193-202.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Wood J. M., Jordan D. C. Symbiotic properties of C4-dicarboxylic acid transport mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1403–1413. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1403-1413.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G. Mutants in glucose metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:317–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Novel one-step cloning vector with a transposable element: application to the Myxococcus xanthus genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):270–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.270-275.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiol A., Arias A., Cerveñansky C., Martínez-Drets G. Succinate dehydrogenase mutant of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1621–1623. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1621-1623.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. J., Hinze H., Holzer H. Assay of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in crude yeast extracts. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):576–584. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Maitra P. K. Properties of Escherichia coli mutants deficient in enzymes of glycolysis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):398–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.398-410.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Signer E. R., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6231–6235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Phibbs P. V., Jr Alternative pathways of carbohydrate utilization in pseudomonads. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:359–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Wyk J. C. Multiple forms of Pseudomonas multivorans glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases: differences in size, pyridine nucleotide specificity, and susceptibility to inhibition by adenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1107–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1107-1117.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch W. H., MacLeod J., Franklin M. Effect of temperature on the activity and synthesis of glucose-catabolizing enzymes in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Oct;21(10):1560–1572. doi: 10.1139/m75-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra P. K., Lobo Z. A kinetic study of glycolytic enzyme synthesis in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):475–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Signer E. R. Genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2076–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reibach P. H., Streeter J. G. Evaluation of active versus passive uptake of metabolites by Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.47-52.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Astwood P. M., Downie J. A. Molecular cloning and genetic organization of C4-dicarboxylate transport genes from Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):903–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.903-909.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Astwood P. M., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Deduced products of C4-dicarboxylate transport regulatory genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum are homologous to nitrogen regulatory gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7921–7934. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowers M. D. Carbon metabolism in Rhizobium species. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:89–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Signer E. R. Catabolite-repression-like phenomenon in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1197–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1197-1200.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Chan Y. K., Wheatcroft R., Yang A. F., Han S. H. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for C4-dicarboxylate transport and symbiotic nitrogen fixation are located on a megaplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):927–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.927-934.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


