Abstract
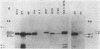
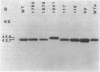
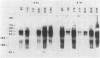
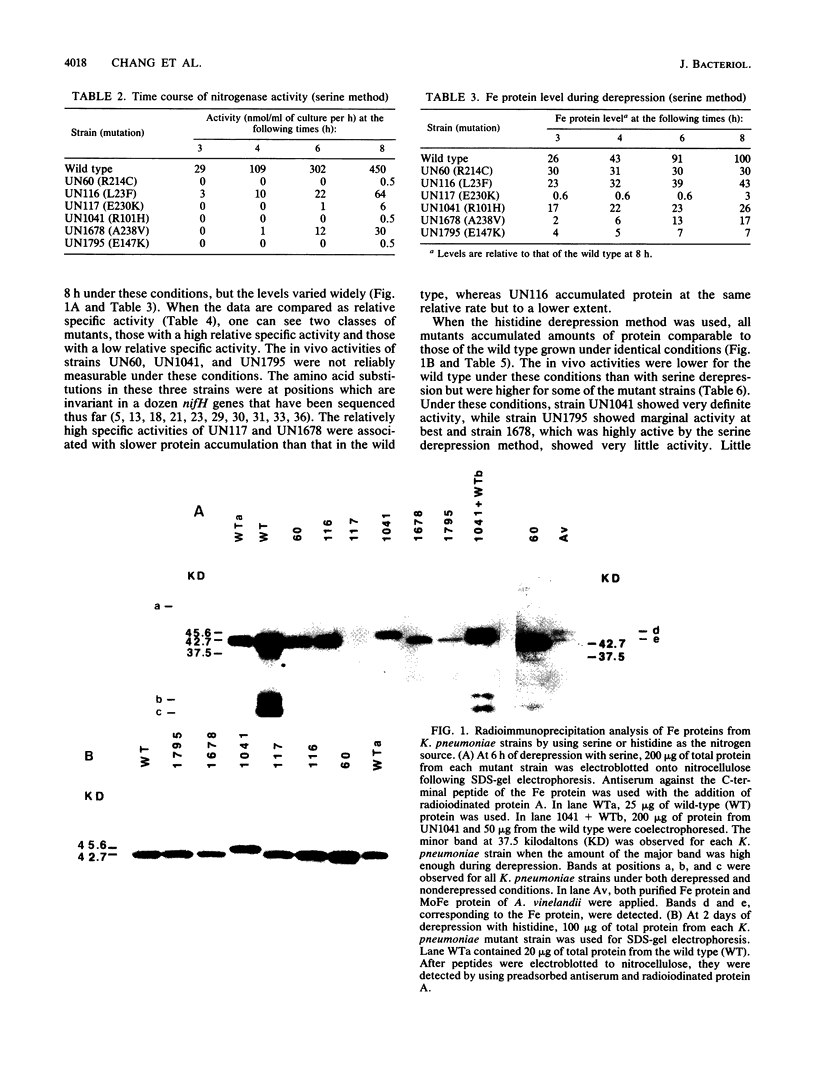
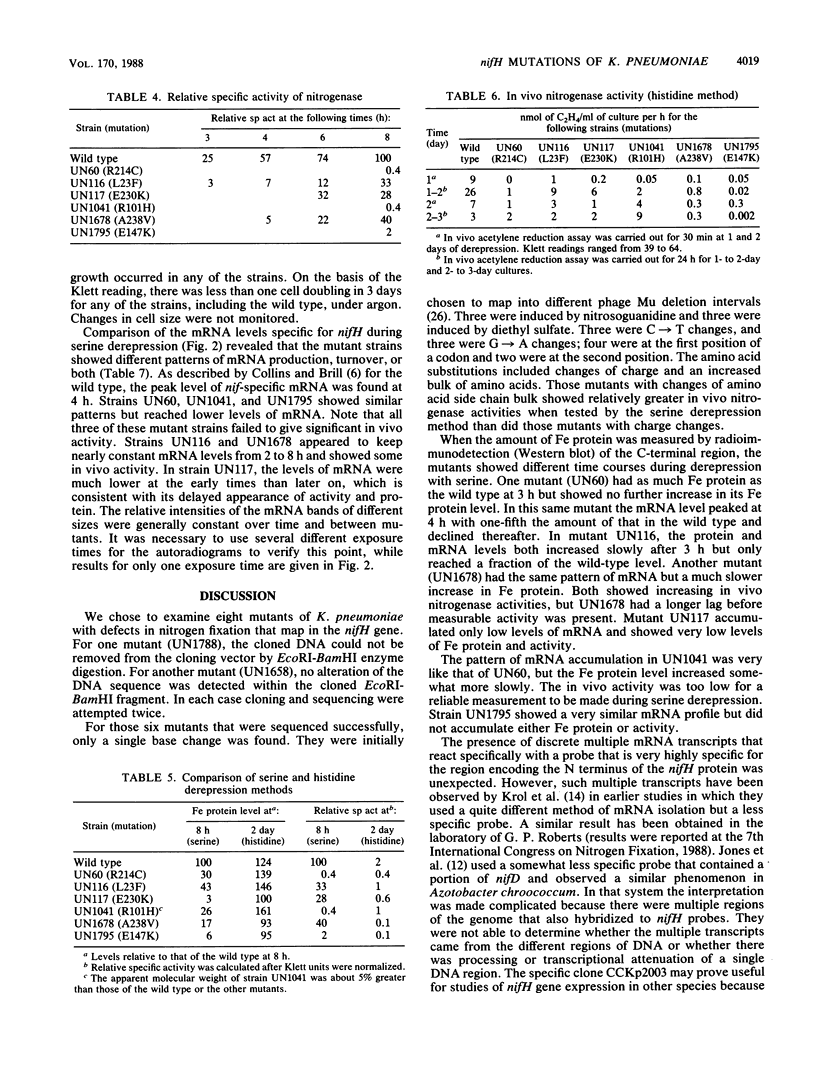
Nucleotide changes in the nifH gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae were identified by DNA cloning and sequencing of six selected mutant strains. The strains were UN60, C-640-GC----TGC; UN116, C-67-TC----TTC; UN117, G-688-AG----AAG; UN1041, CG-302-C----CAC; UN1678, GC-713-C----GTC; and UN1795, G-439-AG----AAG. Their corresponding amino acid substitutions were UN60, Arg-214----Cys; UN116, Leu-23----Phe; UN117, Glu-230----Lys; UN1041, Arg-101----His; UN1678, Ala-238----Val; and UN1795, Glu-147----Lys. Results from Western and Northern blots of the mutant strains showed significant reductions in both steady-state levels of the accumulated Fe protein and nifH mRNA during derepression in the presence of serine. The relative specific activities of the nitrogenases in strains UN60, UN1041, and UN1795 were less than 2% of the wild type, whereas those in UN116, UN117, and UN1678 were between 28 and 40% of the wild type during enhanced derepression with serine. The residues of Arg-101 (UN1041), Glu-147 (UN1795), and Arg-214 (UN60) were invariant in sequences of a dozen diazotrophs that have been examined thus far. In UN1041, in which Arg-101 of the Fe protein was replaced by His, the Fe protein had a larger apparent molecular weight than that of the other strains on sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis, as detected with rabbit antiserum raised against the C-terminal peptide of the wild-type Fe protein. The reduced levels of nifH mRNA in point mutant strains suggests that nifH (the gene or gene product) may be involved in self-regulation. mRNA transcripts of different sizes were detected when a nifH-specific probe, CCKp2003, was used in the Northern blot hybridization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill W. J. Biochemical genetics of nitrogen fixation. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Sep;44(3):449–467. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.3.449-467.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. C., Chen J. S., Johnson J. L. Structural features of multiple nifH-like sequences and very biased codon usage in nitrogenase genes of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):162–172. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.162-172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Brill W. J. Control of Klebsiella pneumoniae nif mRNA synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. C. Hydrazine as a substrate and inhibitor of Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 1;204(1):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filler W. A., Kemp R. M., Ng J. C., Hawkes T. R., Dixon R. A., Smith B. E. The nifH gene product is required for the synthesis or stability of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. J. An apparatus for simultaneous manual solid-phase synthesis of multiple peptide analogs. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Woodley P., Robson R. Cloning and organisation of some genes for nitrogen fixation from Azotobacter chroococcum and their expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):318–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00330980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A. J., Hontelez J. G., Roozendaal B., van Kammen A. On the operon structure of the nitrogenase genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum and Azotobacter vinelandii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4147–4157. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Rice D., Haselkorn R. Nucleotide sequence of a cyanobacterial nifH gene coding for nitrogenase reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson W. H. Molecular basis of biological nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:419–459. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope M. R., Murrell S. A., Ludden P. W. Covalent modification of the iron protein of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum by adenosine diphosphoribosylation of a specific arginine residue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3173–3177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius I. M., Rawlings D. E., O'Neill E. G., Jones W. A., Kirby R., Woods D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the nitrogenase iron protein of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):367–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.367-370.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinto C., De La Vega H., Flores M., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A., Pardo M. A., Azpiroz R., De Lourdes Girard M., Calva E., Palacios R. Nitrogenase reductase: A functional multigene family in Rhizobium phaseoli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1170–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C., Howard J. B. Crystallization of the Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase iron protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12733–12734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Gene-product relationships of the nif regulon of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):210–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.210-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. C., Dean D. R., Burgess B. K. Iron-molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis in Azotobacter vinelandii requires the iron protein of nitrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14327–14332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Rolfe B. G., Shine J. Biological nitrogen fixation: primary structure of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH and nifD genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Rolfe B. G., Shine J. Biological nitrogen fixation: primary structure of the Rhizobium trifolii iron protein gene. DNA. 1983;2(2):149–155. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Rolfe B. G., Shine J. Nitrogenase structural genes are unlinked in the nonlegume symbiont Parasponia rhizobium. DNA. 1983;2(2):141–148. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. C., Kobori J. A., Siu G., Hood L. E. Specific-primer-directed DNA sequencing. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto D. J., Morrison D., Davis L. C., Takemoto L. J. C-terminal peptides of rhodopsin. Determination of the optimum sequence for recognition of retinal transducin. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):309–312. doi: 10.1042/bj2350309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Kondorosi A. Nucleotide sequence of the R.meliloti nitrogenase reductase (nifH) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5711–5723. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]