Abstract
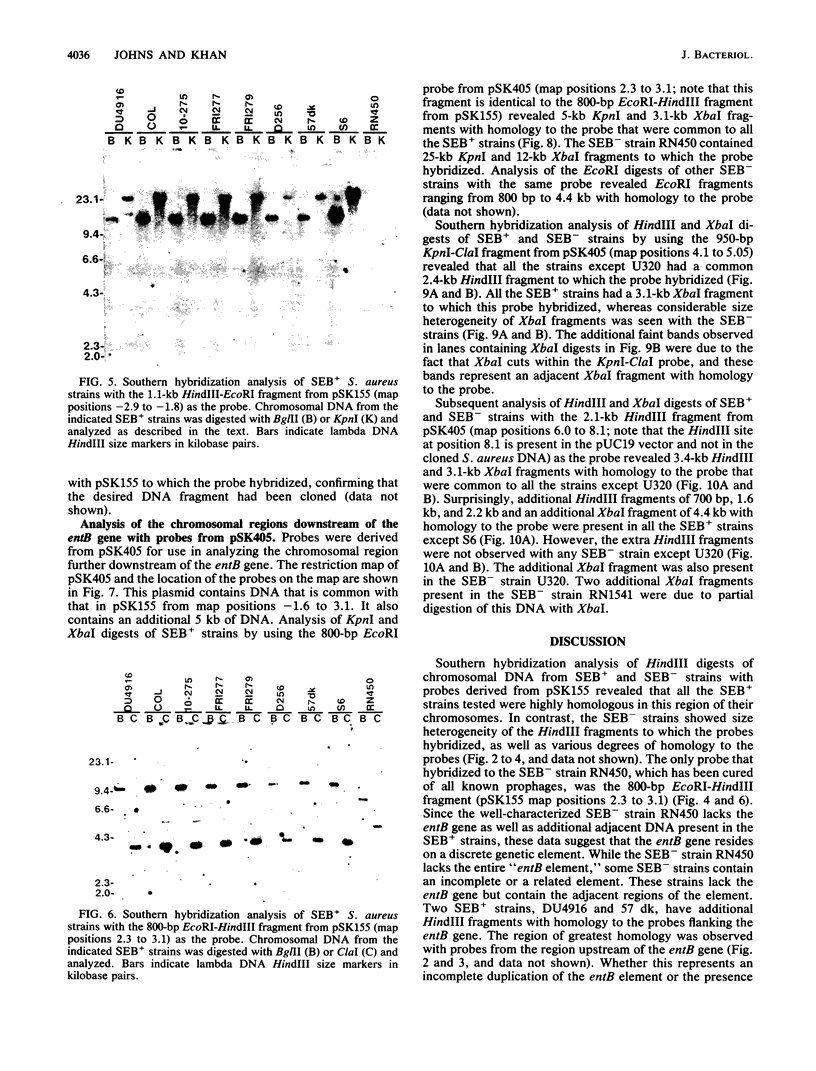
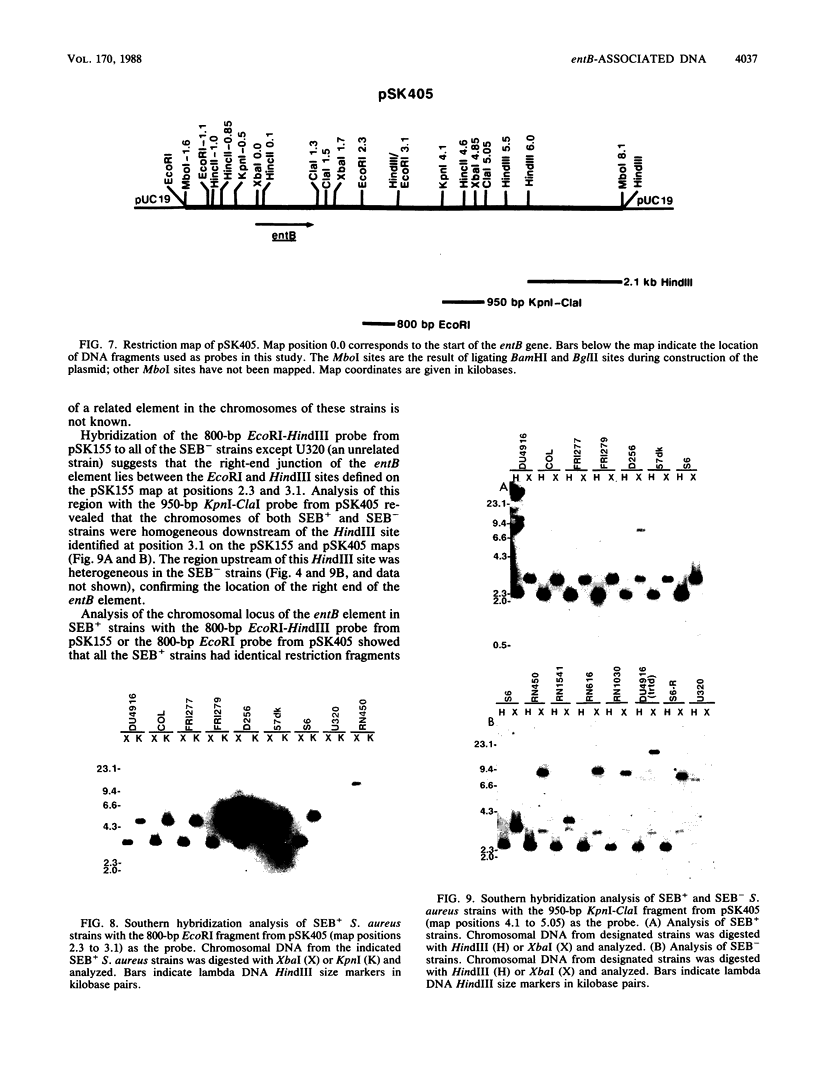
The chromosomal location of the enterotoxin B gene in Staphylococcus aureus is unknown. Southern hybridization analysis of the chromosomal DNA from several enterotoxin B (SEB)-producing strains has shown that at least 26.8 kilobases (kb) of DNA is associated with the enterotoxin B gene (entB). We have found that one end of the entB element is located approximately 1.5 kb downstream of the entB gene. The chromosomal region adjacent to this end of the entB element was found to be homologous in several SEB-producing (SEB+) and SEB-nonproducing (SEB-) S. aureus strains. The chromosomes of all the SEB+ strains studied were homologous for at least 24 kb upstream of the entB gene. Some naturally occurring SEB- strains lacked the entire entB element, while others showed variable homology to the region upstream of the entB gene. These data suggest that the entB gene is part of a discrete genetic element that is at least 26.8 kb in size.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altboum Z., Hertman I., Sarid S. Penicillinase plasmid-linked genetic determinants for enterotoxins B and C1 production in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):514–521. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.514-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A is encoded by phage. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.3160112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Genetics of bacterial enterotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:577–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. T., Brown N. C., Burlingham B. T. Morphology and physical properties of Staphylococcus bacteriophage P11-M15. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.664-671.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P. Staphylococcal enterotoxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):124–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Hallander H. O., Löfquist F. Extrachromosomal control of methicillin resistance and toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.351-358.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Plasmid-chromosomal transition of genes important in staphylococcal enterotoxin B expression. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):450–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.450-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Rapid isolation of DNA from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.283-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang I. Y., Bergdoll M. S. The primary structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. 3. The cyanogen bromide peptides of reduced and aminoethylated enterotoxin B, and the complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3518–3525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. P., L'Italien J. J., Schlievert P. M. Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type A (scarlet fever toxin) is related to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 May;203(2):354–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00333979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. P., Tomai M. A., Schlievert P. M. Bacteriophage involvement in group A streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A production. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.623-627.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Khan S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):29–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.29-33.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Novick R. P. Structural analysis of plasmid pSN2 in Staphylococcus aureus: no involvement in enterotoxin B production. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):642–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.642-649.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. Staphylococcus aureus strain DU4916--an atypical methicillin-resistant isolate? J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Prophage map of converting corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):208–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.208-219.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Integration of staphylococcal phage L54a occurs by site-specific recombination: structural analysis of the attachment sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5474–5478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Phillips S., Edelman I., Novick R. P. Tn554: isolation and characterization of plasmid insertions. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):292–305. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranelli D. M., Jones C. L., Johns M. B., Mussey G. J., Khan S. A. Molecular cloning of staphylococcal enterotoxin B gene in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5850–5854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Chromosomal locus for staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):273–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.273-278.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Genetics of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):902–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.902-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalita Z., Hertman I., Sarid S. Isolation and characterization of a plasmid involved with enterotoxin B production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):317–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.317-325.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström J. E., Löfdahl S., Philipson L. Transformation reveals a chromosomal locus of the gene(s) for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):905–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.905-915.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Hayama T. Abdominal viscera as site of emetic action for staphylococcal enterotoxin in the monkey. J Infect Dis. 1965 Oct;115(4):330–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.4.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Iandolo J. J. Purification and partial characterization of a putative precursor to staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):900–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.900-907.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. R., Ferretti J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) gene from Streptococcus pyogenes bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.144-150.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks C. R., Ferretti J. J. The gene for type A streptococcal exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin) is located in bacteriophage T12. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):531–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.531-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman L., Goering R. V., Novick R. P. Genetic control of chromosomal and plasmid recombination in Staphylococcus aureus. Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):681–702. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










