Abstract
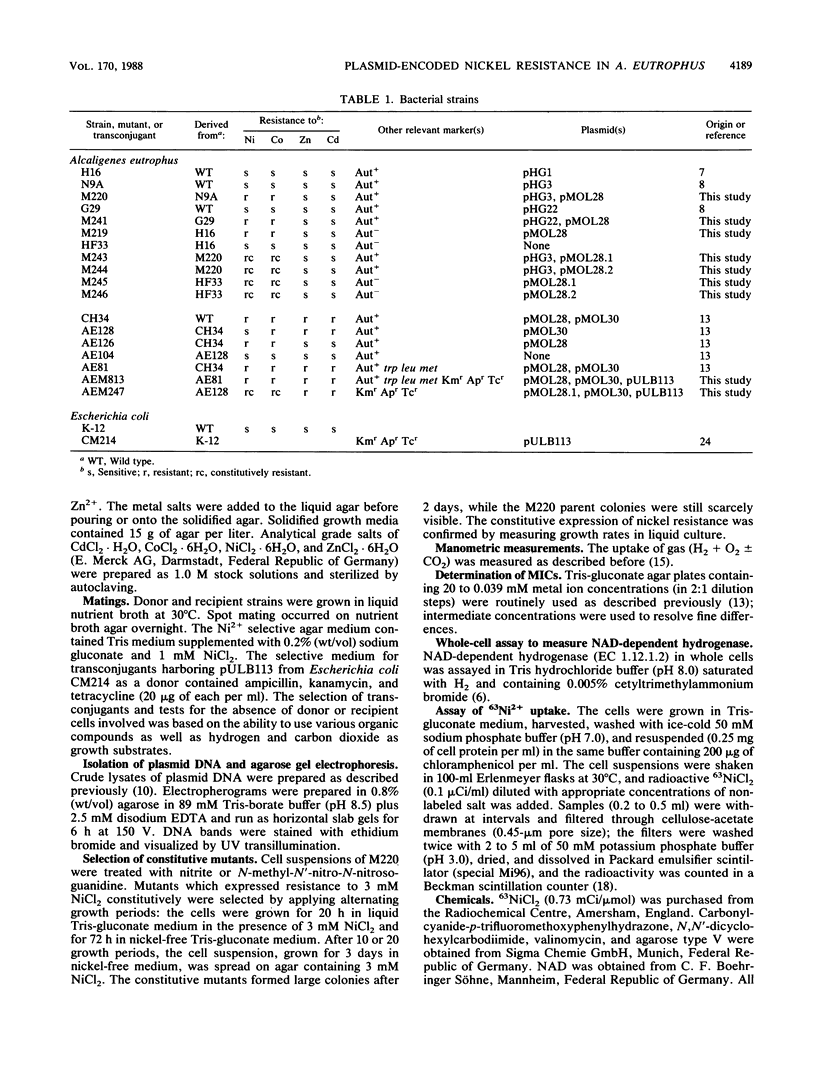
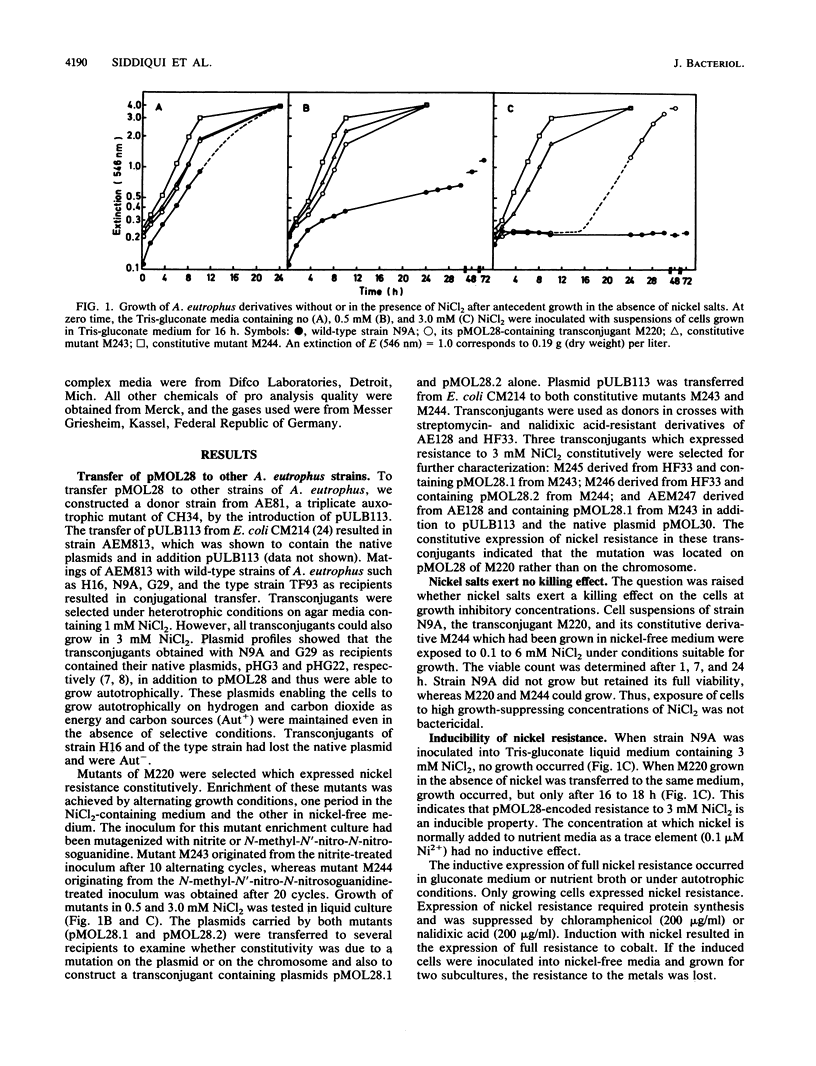
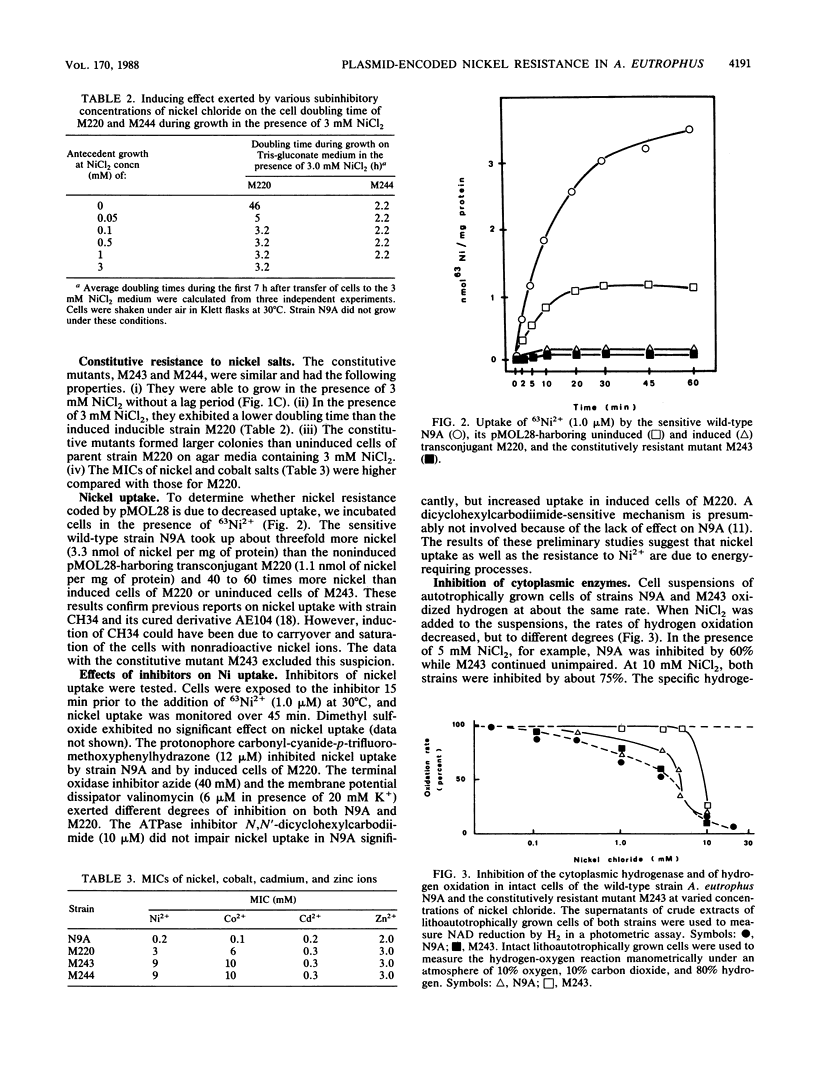
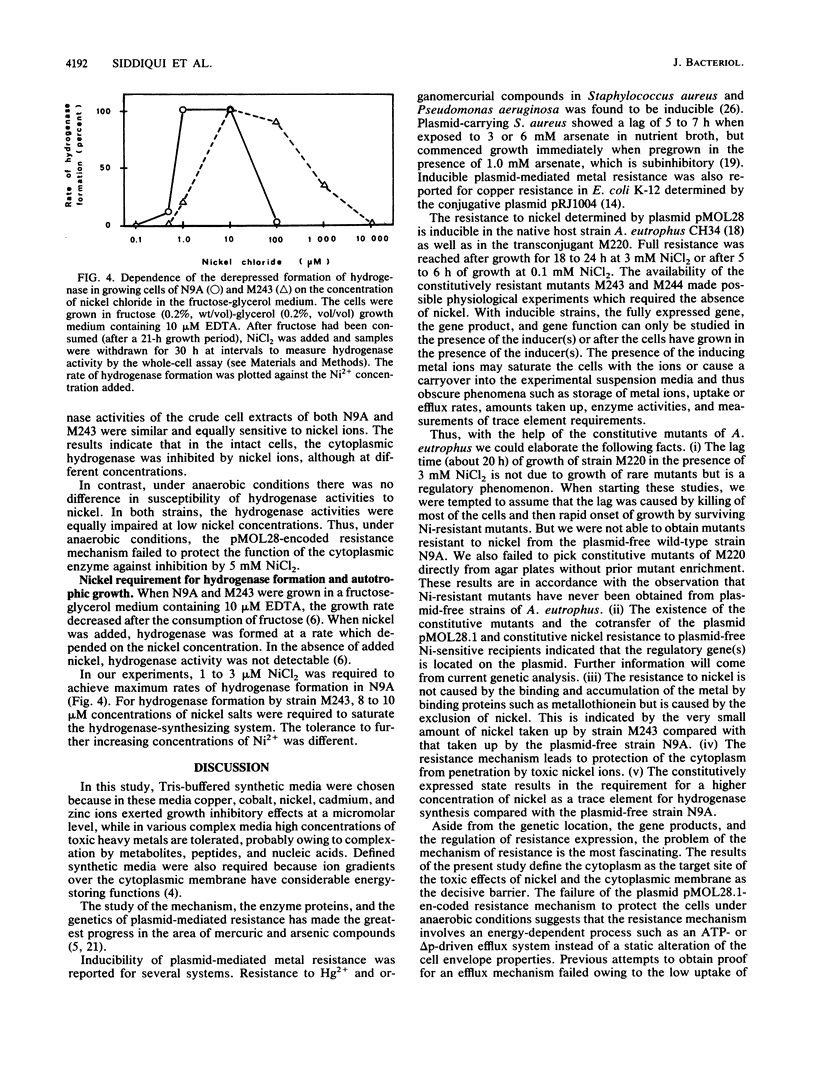
The nickel and cobalt resistance plasmid pMOL28 was transferred by conjugation from its natural host Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34 to the susceptible A. eutrophus N9A. Strain N9A and its pMOL28-containing transconjugant M220 were studied in detail. At a concentration of 3.0 mM NiCl2, the wild-type N9A did not grow, while M220 started to grow at its maximum exponential growth rate after a lag of 12 to 24 h. When grown in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations (0.5 mM) of nickel salt, M220 grew actively at 3 mM NiCl2 without a lag, indicating that nickel resistance is an inducible property. Expression of nickel resistance required active growth in the presence of nickel salts at a concentration higher than 0.05 mM. Two mutants of M220 were isolated which expressed nickel resistance constitutively. When the plasmids, pMOL28.1 and pMOL28.2, carried by the mutants were transferred to strains H16 and CH34, the transconjugants expressed constitutive nickel resistance. This indicates that the mutation is plasmid located. Both mutants expressed constitutive resistance to nickel and cobalt. Physiological studies revealed the following differences between strain N9A and its pMOL28.1-harboring mutant derivatives. (i) The uptake of 63NiCl2 occurred more rapidly in the susceptible strain and reached a 30- to 60-fold-higher amount that in the pMOL28.1-harboring mutant; (ii) in intact cells of the susceptible strain N9A, the cytoplasmic hydrogenase was inhibited by 1 to 5 nM NiCl2, whereas 10 mM Ni2+ was needed to inhibit the hydrogenase of mutant cells; (iii) the minimal concentration of nickel chloride for the derepressed synthesis of cytoplasmic hydrogenase was lower in strain N9A (1 to 3 microM) than in the constitutive mutant (8 to 10 microM).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTHA R., ORDAL E. J. NICKEL-DEPENDENT CHEMOLITHOTROPHIC GROWTH OF TWO HYDROGENOMONAS STRAINS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1015–1019. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1015-1019.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. I., Galperin MYu, Glagolev A. N., Skulachev V. P. Utilization of energy stored in the form of Na+ and K+ ion gradients by bacterial cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. The genetics and biochemistry of mercury resistance. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(2):117–140. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Heine E., Finck A., Friedrich C. G. Nickel requirement for active hydrogenase formation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1144–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1144-1149.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Hogrefe C., Schlegel H. G. Naturally occurring genetic transfer of hydrogen-oxidizing ability between strains of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.198-205.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Meyer M., Schlegel H. G. Transfer and expression of the herbicide-degrading plasmid pJP4 in aerobic autotrophic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Feb;134(2):92–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00407938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich C. G., Schneider K., Friedrich B. Nickel in the catalytically active hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):42–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.42-48.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergeay M., Houba C., Gerits J. Extrachromosomal inheritance controlling resistance to cadmium, cobalt, copper and zinc ions: evidence from curing in a Pseudomonas [proceedings]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1978 May;86(2):440–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergeay M., Nies D., Schlegel H. G., Gerits J., Charles P., Van Gijsegem F. Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34 is a facultative chemolithotroph with plasmid-bound resistance to heavy metals. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):328–334. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.328-334.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D., Camakaris J., Lee B. T., Luke R. K. Inducible plasmid-mediated copper resistance in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):939–943. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Schlegel H. G. Mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus defective in autotrophic metabolism. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00402299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Cammack R., Schlegel H. G. Content and localization of FMN, Fe-S clusters and nickel in the NAD-linked hydrogenase of Nocardia opaca 1b. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):75–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Schlegel H. G., Jochim K. Effect of nickel on activity and subunit composition of purified hydrogenase from Nocardia opaca 1 b. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 1;138(3):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Budd K., Leahy K. M., Shaw W. V., Hammond D., Novick R. P., Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H., Rosenberg H. Inducible plasmid-determined resistance to arsenate, arsenite, and antimony (III) in escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):983–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.983-996.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., Mallick S., Maier R. J. Nickel uptake in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1398–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1398-1402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O. Organization, expression, and evolution of genes for mercury resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:607–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gijsegem F., Toussaint A. Chromosome transfer and R-prime formation by an RP4::mini-Mu derivative in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis. Plasmid. 1982 Jan;7(1):30–44. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Murphy S. D., Silver S. Mercury and organomercurial resistances determined by plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):197–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.197-208.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


