Abstract
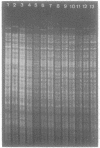
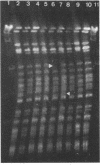
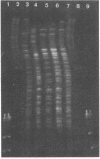
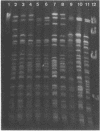
Preparations of DNA from 23 Brucella strains including 19 reference strains were compared by restriction endonuclease analysis. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis resulted in optimal resolution of fragments generated by digestion with low-cleavage-frequency restriction enzymes such as XbaI. By this technique, five electrophoretypes were distinguished in five reference strains of the different species, i.e., B. abortus, B. melitensis, B. suis, B. canis, and B. ovis. Minor profile differences allowed us to discriminate between most biovars within a species. However, the differences in the DNA patterns of different field strains of biovar 2 of B. melitensis were not sufficient to serve as markers for epidemiological studies. From the XbaI fragments, we were able to estimate the size of the genomes of B. abortus 544T and B. melitensis 16 MT. This method revealed a relationship between DNA fingerprints, species, and pathovars which could shed light on problems concerning the classification and evolution of members of the genus Brucella.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorvatn B., Lund V., Kristiansen B. E., Korsnes L., Spanne O., Lindqvist B. Applications of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA of Neisseria meningitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):763–765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.763-765.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer B. H., McCullough N. B. Homologies of deoxyribonucleic acids from Brucella ovis, canine abortion organisms, and other Brucella species. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1783–1790. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1783-1790.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer B. H., McCullough N. B. Polynucleotide homologies of Brucella deoxyribonucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.444-448.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. A general method for preparing chromatin containing intact DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakoyiannis C. K., Winter P. J., Marshall R. B. Identification of Campylobacter coli isolates from animals and humans by bacterial restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):545–549. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.545-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen B. E., Sørensen B., Spanne O., Bjorvatn B. Restriction fingerprinting and serology in a small outbreak of B15 meningococcal disease among Norwegian soldiers. Scand J Infect Dis. 1985;17(1):19–24. doi: 10.3109/00365548509070415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Macrina F. L., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A. Sequential outbreaks of infection due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit: implication of a conjugative R plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Winter P. J., Yanagawa R. Restriction endonuclease DNA analysis of Leptospira interrogans serovars icterohaemorrhagiae and hebdomadis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):808–810. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.808-810.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan M., Herring A. J., Aitken I. D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.384-389.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara M. J., Collins D. M., de Lisle G. W. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Brucella ovis and other Brucella species. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Aug;10(5):425–429. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Saffran W., Welsh J., Haas R., Goldenberg M., Cantor C. R. New techniques for purifying large DNAs and studying their properties and packaging. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):189–195. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker S. A., Fisher J. H., Jones W. D., Jr, Scoggin C. H. Restriction fragment analysis of chromosomal DNA defines different strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):210–213. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Summers W. P., Summers W. C. Structure and function of herpesvirus genomes. I. comparison of five HSV-1 and two HSV-2 strains by cleavage their DNA with eco R I restriction endonuclease. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):726–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.726-732.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]