Abstract
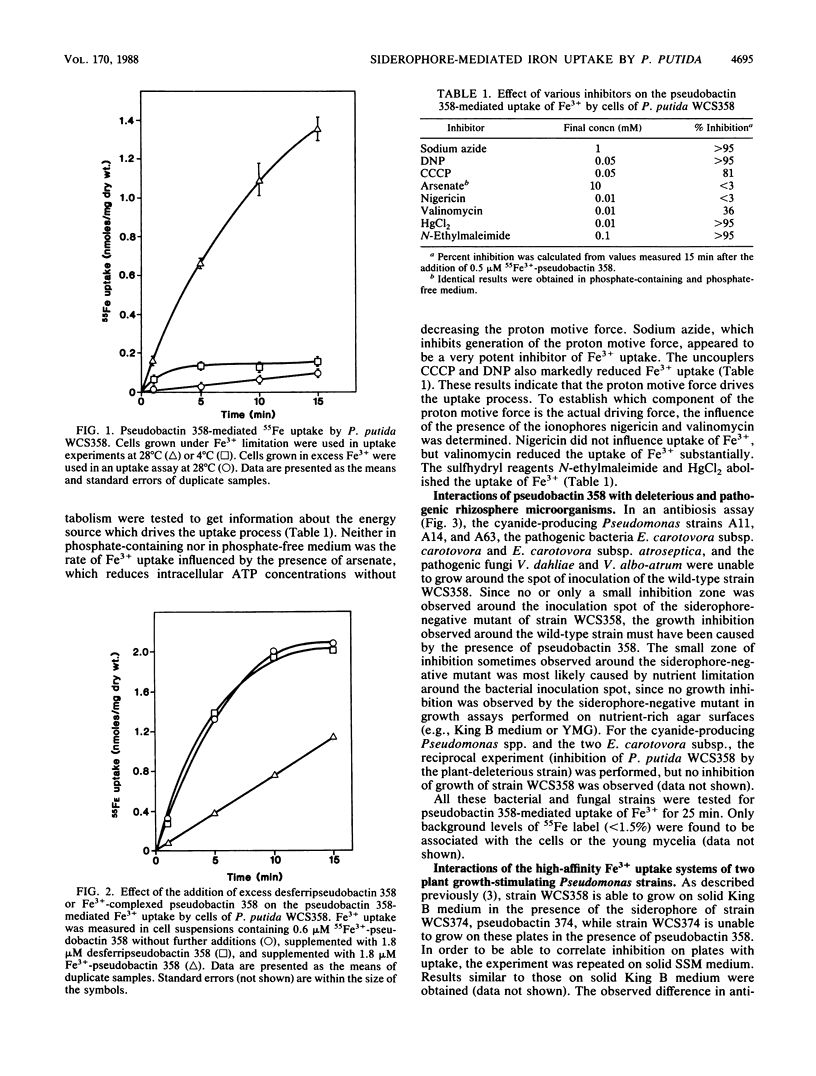
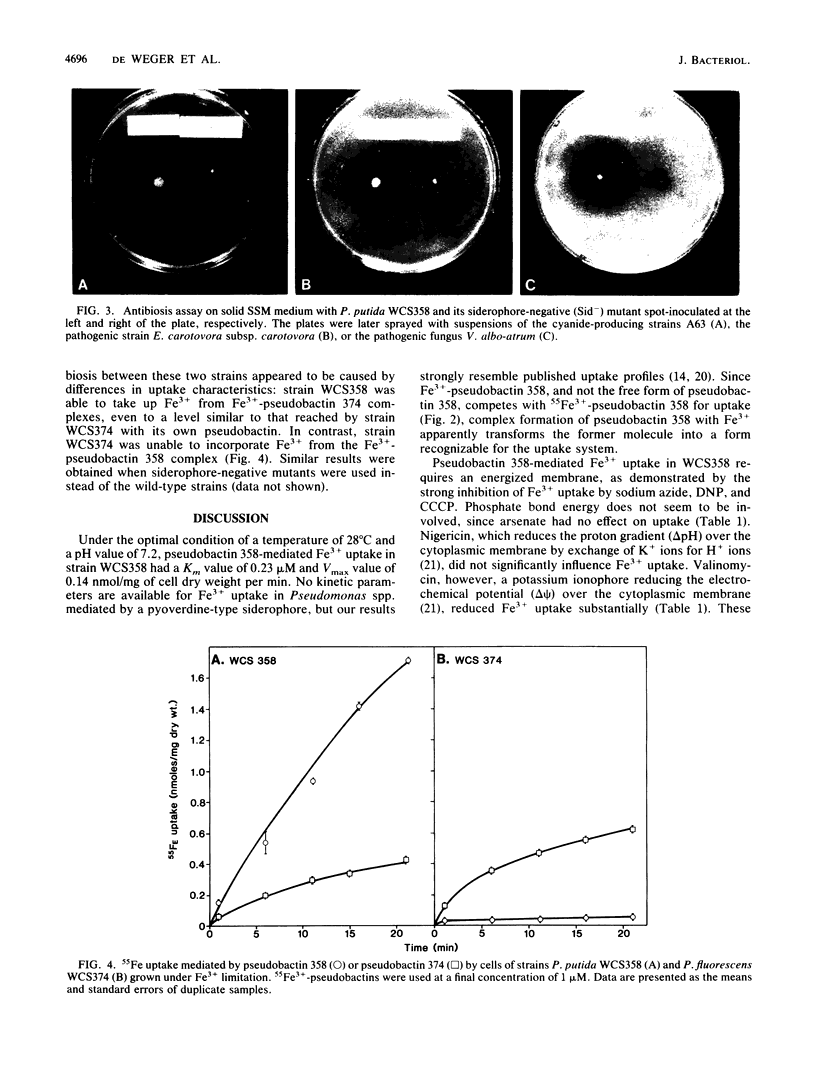
Under iron-limited conditions, Pseudomonas putida WCS358 produces a siderophore, pseudobactin 358, which is essential for the plant growth-stimulating ability of this strain. Cells of strain WCS358, provided that they have been grown under Fe3+ limitation, take up 55Fe3+ from the 55Fe3+-labeled pseudobactin 358 complex with Km and Vmax values of 0.23 microM and 0.14 nmol/mg of cell dry weight per min, respectively. Uptake experiments with cells treated with various metabolic inhibitors showed that this Fe3+ uptake process was dependent on the proton motive force. Furthermore, strain WCS358 was shown to be able to take up Fe3+ complexed to the siderophore of another plant-beneficial P. fluorescens strain, WCS374. The tested pathogenic rhizobacteria and rhizofungi were neither able to grow on Fe3+-deficient medium in the presence of pseudobactin 358 nor able to take up 55Fe3+ from 55Fe3+-pseudobactin 358. The same applies for three cyanide-producing Pseudomonas strains which are supposed to be representatives of the minor pathogens. These results indicate that the extraordinary ability of strain WCS358 to compete efficiently for Fe3+ is based on the fact that the pathogenic and deleterious rhizosphere microorganisms, in contrast to strain WCS358 itself, are not able to take up Fe3+ from Fe3+-pseudobactin 358 complexes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buyer J. S., Leong J. Iron transport-mediated antagonism between plant growth-promoting and plant-deleterious Pseudomonas strains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):791–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Iron uptake with ferripyochelin and ferric citrate by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):581–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.581-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Jr, Warren G. J. An iron-antagonized fungistatic agent that is not required for iron assimilation from a fluorescent rhizosphere pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):163–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.163-170.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Proton motive force in growing Streptococcus lactis and Staphylococcus aureus cells under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):369–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.369-376.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marugg J. D., van Spanje M., Hoekstra W. P., Schippers B., Weisbeek P. J. Isolation and analysis of genes involved in siderophore biosynthesis in plant-growth-stimulating Pseudomonas putida WCS358. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):563–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.563-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe C., Winkelmann G. Kinetic studies on the specificity of chelate-iron uptake in Aspergillus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):837–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.837-842.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., Jann B., Jann K., Lugtenberg B. Lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas spp. that stimulate plant growth: composition and use for strain identification. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1441–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1441-1446.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., van Boxtel R., van der Burg B., Gruters R. A., Geels F. P., Schippers B., Lugtenberg B. Siderophores and outer membrane proteins of antagonistic, plant-growth-stimulating, root-colonizing Pseudomonas spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):585–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.585-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



