Abstract
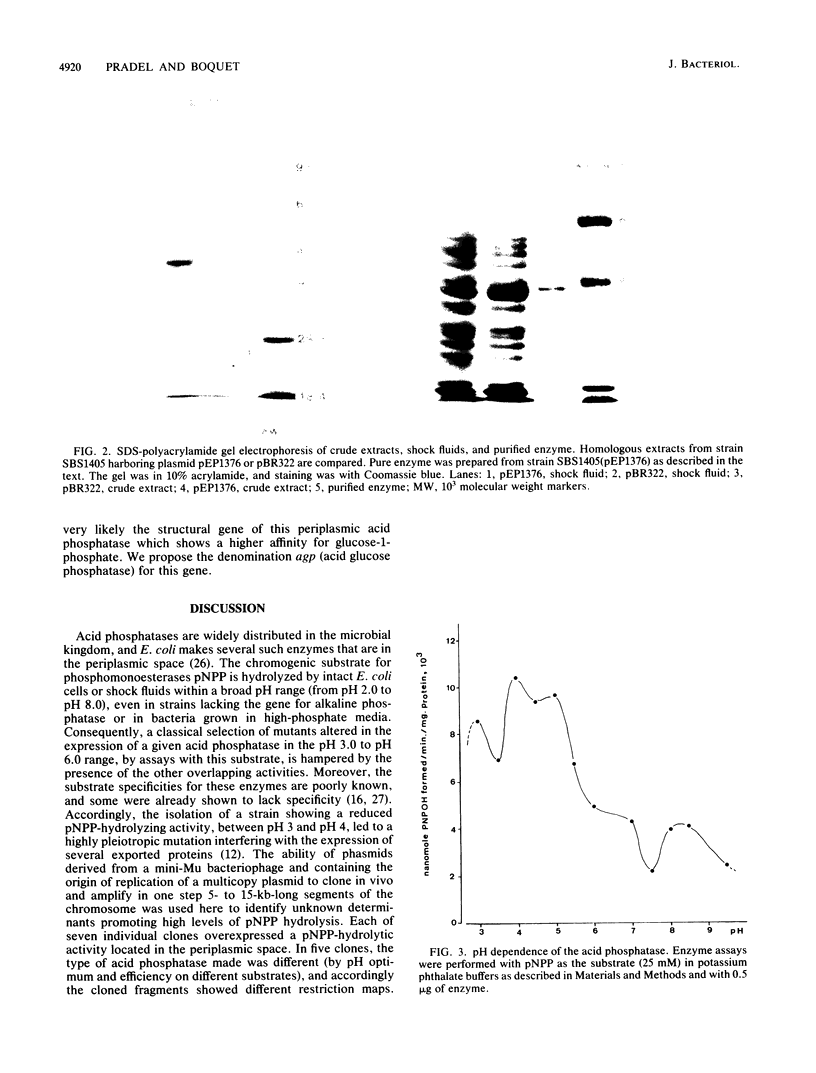
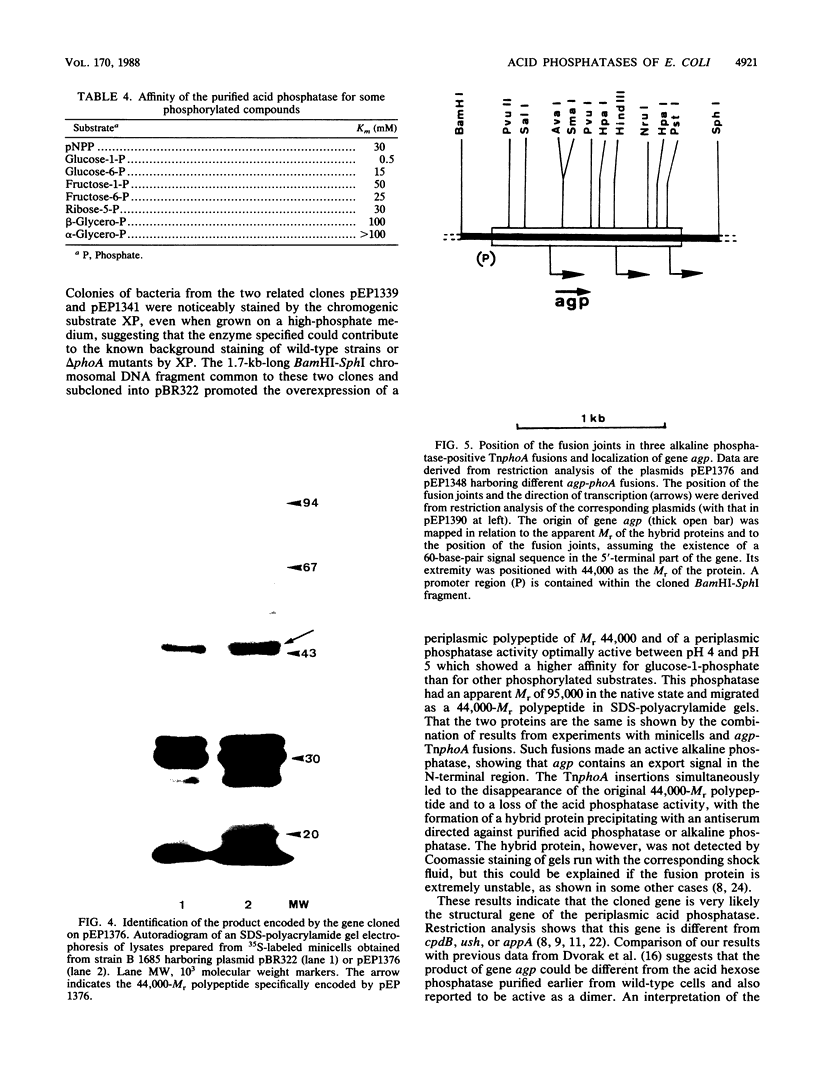
Several unknown Escherichia coli genes for different species of acid phosphatase were cloned in vivo with the plasmid Mu dII4042. When present in a multicopy state, each gene promoted hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl-phosphate at acidic pH. Among seven recombinant clones that encoded periplasmic acid phosphatase activities, five different genes could be distinguished by the pH optimum and substrate preference for the enzyme and by the restriction enzyme pattern. A 1.7-kilobase recombinant DNA fragment, common to two clones, was inserted into plasmid pBR322 and shown to contain a new gene, agp, which leads to the overexpression of the periplasmic acid glucose-1-phosphatase, a dimer of a 44-kilodalton polypeptide. Fusions of agp to gene phoA deprived of its own signal sequence conferred an alkaline phosphatase-positive phenotype to bacteria, showing the presence of an export signal on agp. The resulting hybrid proteins were characterized by immunoprecipitation with an antiserum directed against purified acid phosphatase or against alkaline phosphatase, showing that agp is the structural gene of the acid phosphatase. The beginning, the orientation, and the end of gene agp on the cloned DNA fragment were determined by the characteristics of such hybrid proteins.
Full text
PDF

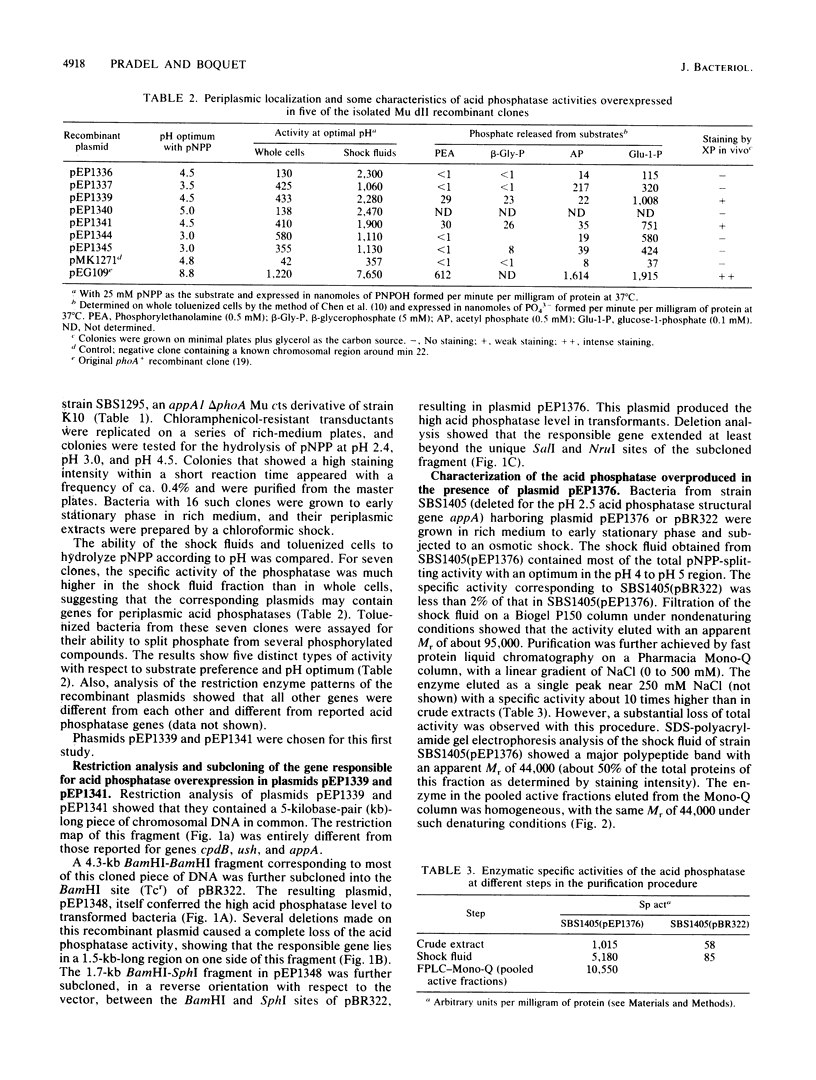
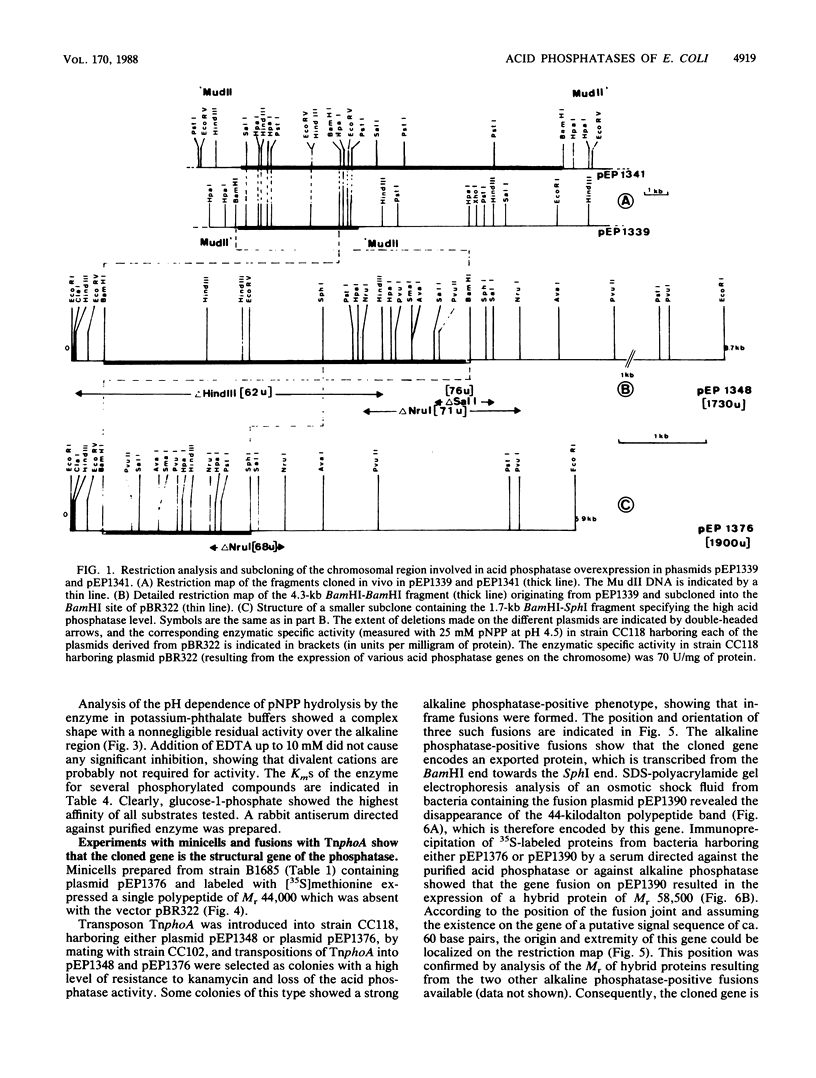


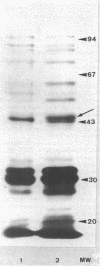
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANRAKU Y. A NEW CYCLIC PHOSPHODIESTERASE HAVING A 3'-NUCLEOTIDASE ACTIVITY FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI B. I. PURIFICATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3412–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANRAKU Y. A NEW CYCLIC PHOSPHODIESTERASE HAVING A 3'-NUCLEOTIDASE ACTIVITY FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI B. II. FURTHER STUDIES ON SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY AND MODE OF ACTION OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3420–3424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Prody C., Kustu S. Simple, rapid, and quantitative release of periplasmic proteins by chloroform. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1181–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1181-1183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R., Garrett S. Isolation of Escherichia coli mutants (cpdB) deficient in periplasmic 2':3'-cyclic phosphodiesterase and genetic mapping of the cpdB locus. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jul;119(1):31–34. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R. Periplasmic enzymes in gram-negative bacteria. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(11):877–883. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R., Yagil E. Genetic location of the gene (ush) specifying periplasmic uridine 5'-diphosphate glucose hydrolase (5'-nucleotidase) in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):487–489. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.487-489.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. L., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Use of TnphoA to detect genes for exported proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of the plasmid-encoded gene for a periplasmic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1663–1669. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1663-1669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. M., Abraham L. J., Beacham I. R. Characterization of the ush gene of Escherichia coli and its protein products. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A., Beacham I. R. Molecular cloning of the gene (ush) from Escherichia coli specifying periplasmic UDP-sugar hydrolase (5'-nucleotidase). Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. ExpA: a conditional mutation affecting the expression of a group of exported proteins in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(2):192–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00268426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Identification of the gene appA for the acid phosphatase (pH optimum 2.5) of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):68–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00383314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Cahu M., Desjoyaux-Cherel B., Boquet P. L. The acid phosphatase with optimum pH of 2.5 of Escherichia coli. Physiological and Biochemical study. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6669–6676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Brockman R. W., Heppel L. A. Purification and properties of two acid phosphatase fractions isolated from osmotic shock fluid of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1743–1751. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Curtiss R., 3rd Production, properties and utility of bacterial minicells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:1–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Castilho B. A., Casadaban M. J. In vivo DNA cloning and adjacent gene fusing with a mini-Mu-lac bacteriophage containing a plasmid replicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1480–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Burns D. M., Beacham I. R. Isolation and sequence analysis of the gene (cpdB) encoding periplasmic 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiesterase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):1002–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.1002-1010.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. The 5'-nucleotidase of Escherichia coli. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3896–3904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati E., Danchin A. The structure of the promoter and amino terminal region of the pH 2.5 acid phosphatase structural gene (appA) of E. coli: a negative control of transcription mediated by cyclic AMP. Biochimie. 1987 Mar;69(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von HOFSTEN, PORATH J. Purification and some properties of an acid phosphatase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;64:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90754-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]