Abstract
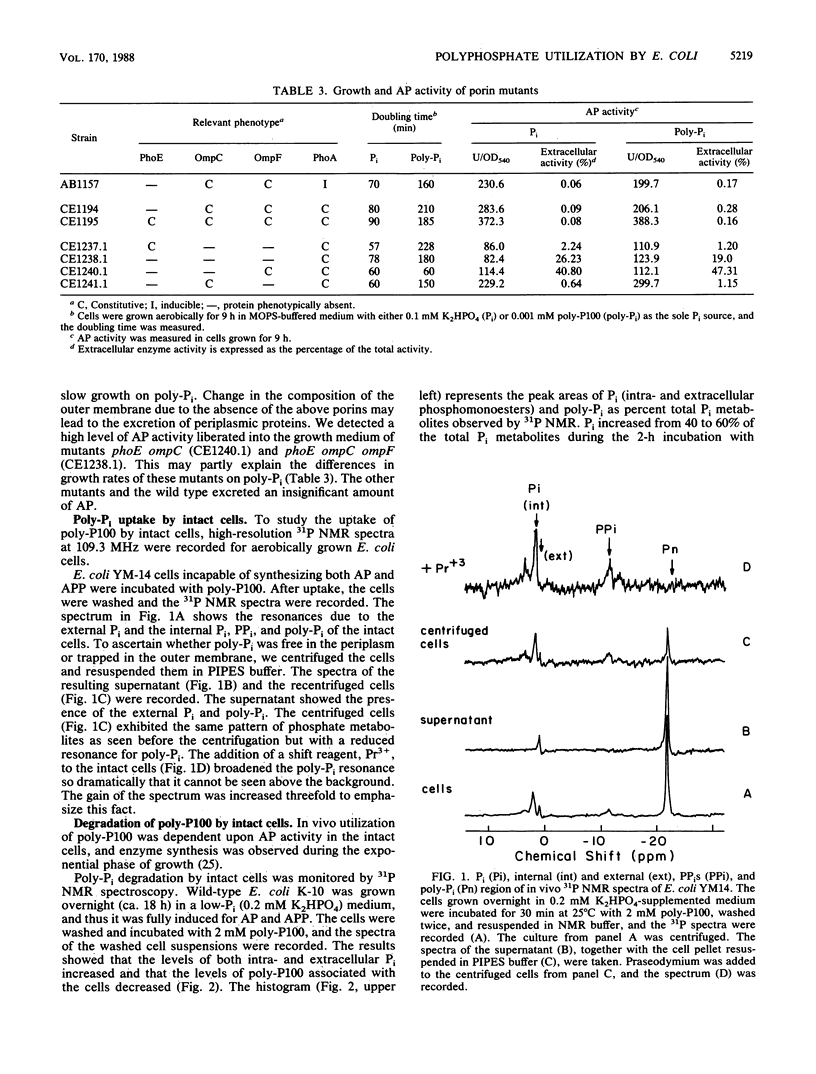
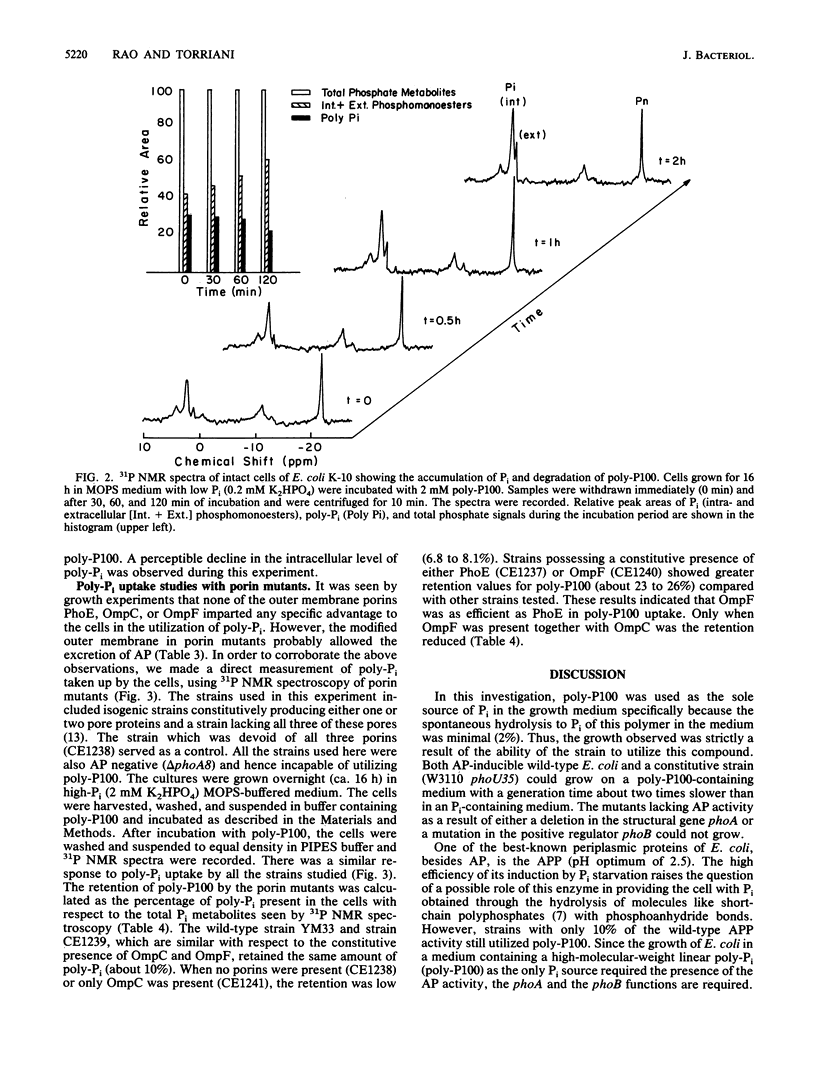
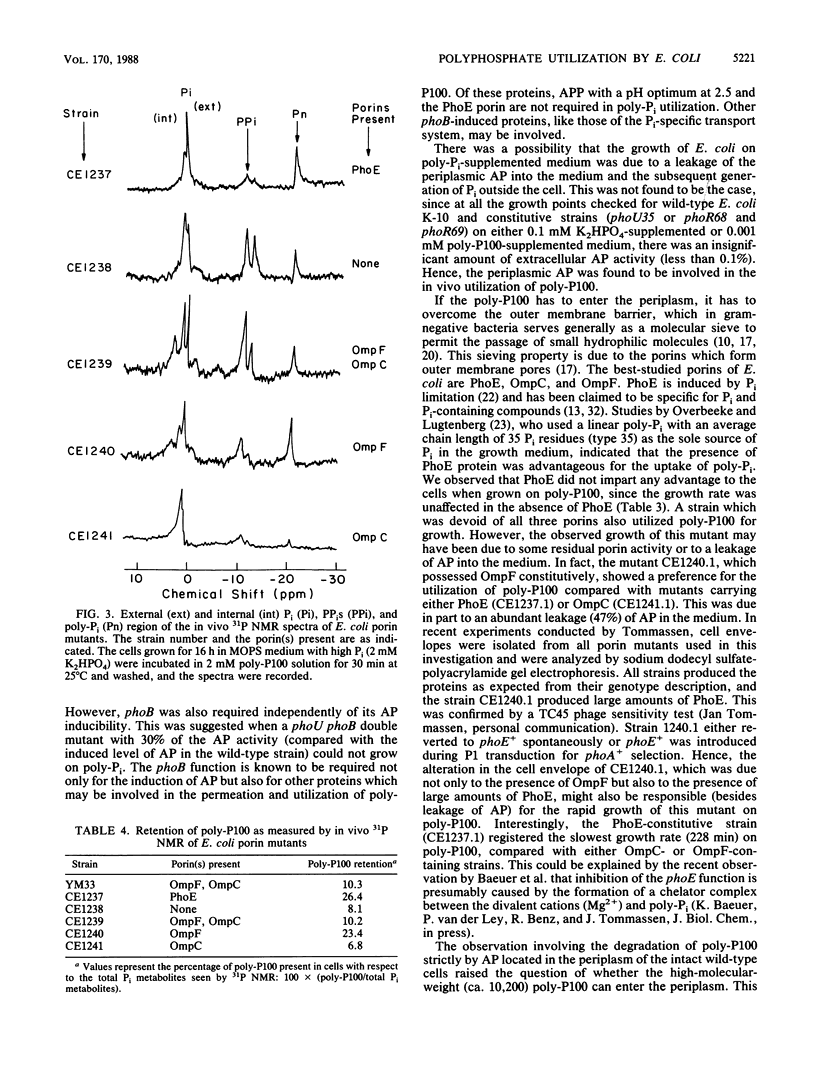
We observed that wild-type Escherichia coli utilized a linear polyphosphate with a chain length of 100 phosphate residues (poly-P100) as the sole source of phosphate in growth medium. A mutation in the gene phoA of alkaline phosphatase or phoB, the positive regulatory gene, prevented growth in this medium. Since no alkaline phosphatase activity was detected outside the wild-type cells, the periplasmic presence of the enzyme was necessary for the degradation of polyphosphate. A 90% reduction in the activity of periplasmic acid phosphatase with a pH optimum of 2.5 (delta appA mutants) did not affect polyphosphate utilization. Of the porins analyzed (OmpC, OmpF, and PhoE), the phoB-inducible porin PhoE was not essential since its absence did not prevent growth. To study how poly-P100 diffused into the cells, we used high-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (31P NMR) spectroscopy. The results suggest that poly-P100 entered the periplasm and remained in equilibrium between the periplasm and the medium. When present individually, porins PhoE and OmpF facilitated a higher permeability for poly-P100 than porin OmpC did. The degradation of polyphosphate by intact cells of E. coli observed by 31P NMR showed a time-dependent increase in cellular phosphate and a decrease in polyphosphate concentration.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban R. S. The application of nuclear magnetic resonance to the study of cellular physiology. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):C10–C19. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.1.C10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Porin from bacterial and mitochondrial outer membranes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):145–190. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P. L., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Use of TnphoA to detect genes for exported proteins in Escherichia coli: identification of the plasmid-encoded gene for a periplasmic acid phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1663–1669. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1663-1669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Is the acid phosphatase of Escherichia coli with pH optimum of 2.5 A polyphosphate depolymerase? FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Tetu C., Boquet P. L. Identification of the acid phosphatase (optimum pH 2.5) of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80608-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECHOLS H., GAREN A., GAREN S., TORRIANI A. Genetic control of repression of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:425–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Role of porins in outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):929–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.929-933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korteland J., Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. PhoE protein pore of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12 is a particularly efficient channel for organic and inorganic phosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 9;690(2):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaev I. S., Vagabov V. M. Polyphosphate metabolism in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:83–171. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludtke D., Bernstein J., Hamilton C., Torriani A. Identification of the phoM gene product and its regulation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.19-25.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUHAMMED A., RODGERS A., HUGHES D. E. Purification and properties of a polymetaphosphatase from Corynebacterium xerosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):482–495. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Identification of the outer membrane protein of E. coli that produces transmembrane channels in reconstituted vesicle membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90913-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Lugtenberg B. Expression of outer membrane protein e of Escherichia coli K12 by phosphate limitation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 7;112(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Lugtenberg B. Recognition site for phosphorus-containing compounds and other negatively charged solutes on the PhoE protein pore of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. N., Roberts M. F., Torriani A. Amount and chain length of polyphosphates in Escherichia coli depend on cell growth conditions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):242–247. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.242-247.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Yamane T., Shulman R. G., Ogawa S. High resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of intact yeast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetu C., Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Unusual pattern of nucleoside polyphosphate hydrolysis by the acid phosphatase (optimum pH = 2.5) of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):314–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Torchia D. A. Use of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 14C fluorography in studies of glycolysis and regulation of pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.791-800.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijssen J. P., Van Steveninck J. Detection of a yeast polyphosphate fraction localized outside the plasma membrane by the method of phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 15;119(2):447–451. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. Outer membrane protein e of Escherichia coli K-12 is co-regulated with alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):151–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.151-157.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckier G., Torriani A. Genetic and physiological tests of three phosphate-specific transport mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1249–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1249-1256.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



