Abstract
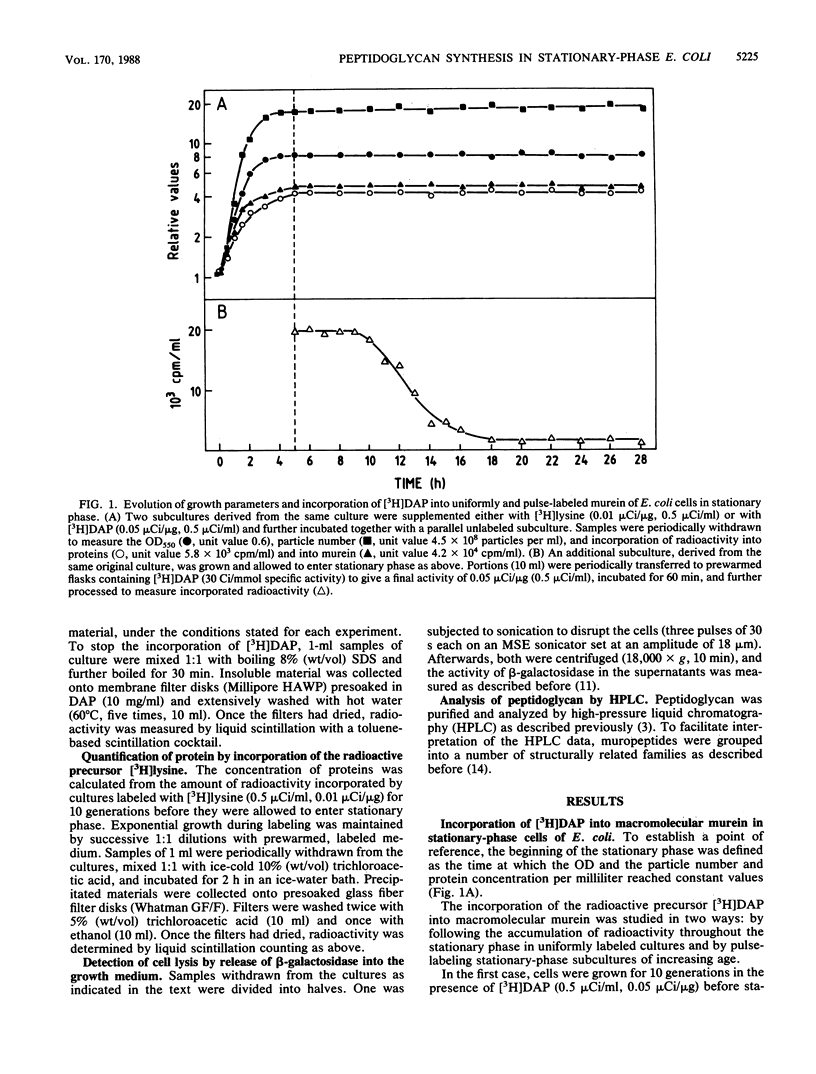
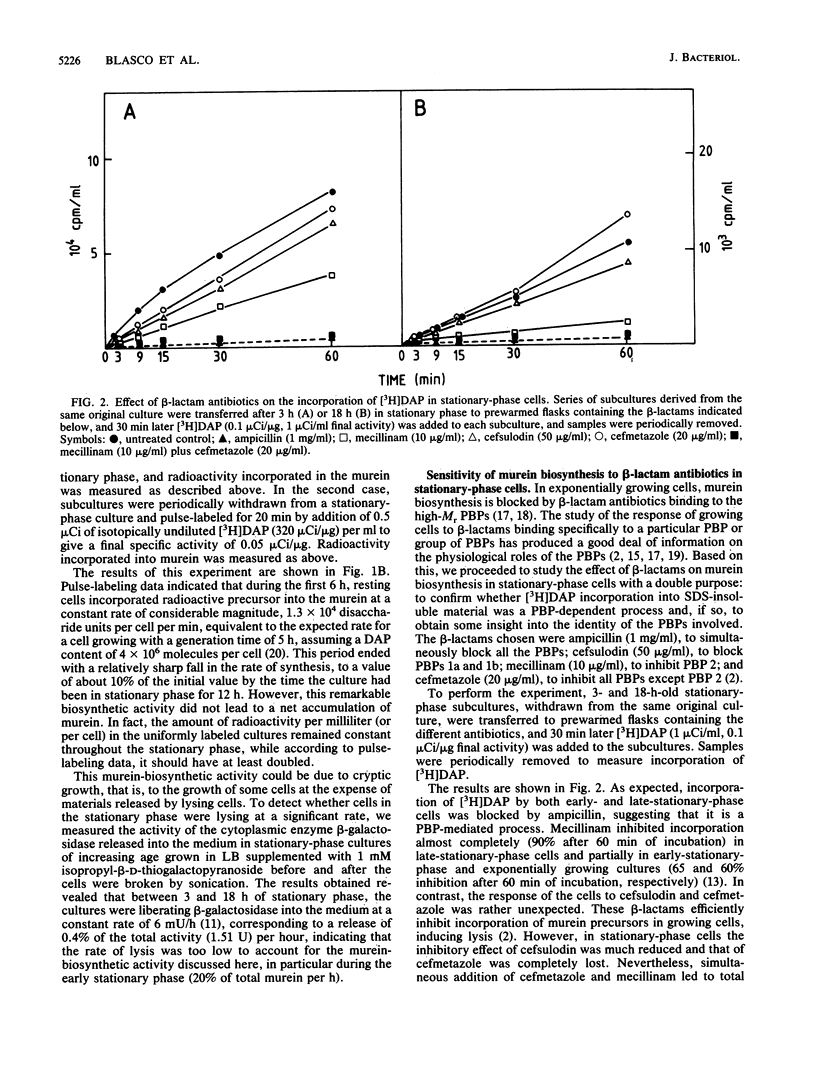
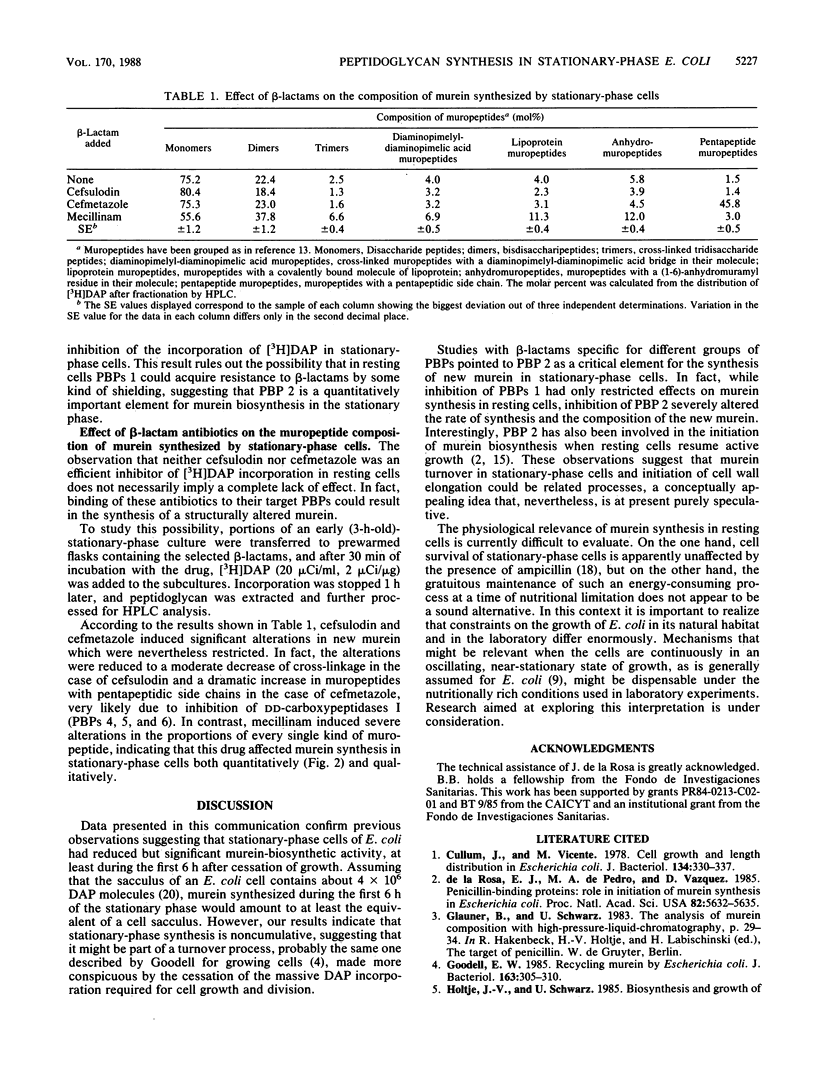
The ability of stationary-phase cells of Escherichia coli W7 to incorporate radioactive precursors into macromolecular murein has been studied. During the initial 6 h of the stationary phase, resting cells incorporated meso-[3H]diaminopimelic acid at a rate corresponding to the insertion of 1.3 X 10(4) disaccharide units min-1 cell-1. Afterwards, the rate of incorporation dropped drastically (90%) to a low but still detectable level. Incorporation during stationary phase did not result in an increased amount of total murein in the culture, suggesting that it was related to a turnover process. Analysis of the effects of a number of beta-lactam antibiotics indicated that incorporation of murein precursors in stationary-phase cells was mediated by penicillin-binding proteins, suggesting that the activity of penicillin-binding protein 2 was particularly relevant to this process.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cullum J., Vicente M. Cell growth and length distribution in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):330–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.330-337.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W. Recycling of murein by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):305–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.305-310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Ramey W. D. Stringent control of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1119–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1119-1126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusser W., Ishiguro E. E. Temperature sensitivity of the penicillin-induced autolysis mechanism in nongrowing cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2310–2312. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2310-2312.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason T. G., Richardson G. Escherichia coli and the human gut: some ecological considerations. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;51(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengin-Lecreulx D., van Heijenoort J. Effect of growth conditions on peptidoglycan content and cytoplasmic steps of its biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):208–212. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.208-212.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olijhoek A. J., Klencke S., Pas E., Nanninga N., Schwarz U. Volume growth, murein synthesis, and murein cross-linkage during the division cycle of Escherichia coli PA3092. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1248–1254. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1248-1254.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. T., Burman L. FL-1060: a new penicillin with a unique mode of action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):863–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisabarro A. G., de Pedro M. A., Vázquez D. Structural modifications in the peptidoglycan of Escherichia coli associated with changes in the state of growth of the culture. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):238–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.238-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Hirota Y., Schwarz U. Process of cellular division in Escherichia coli growth pattern of E. coli murein. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;78(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Cozens R., Tosch W., Zak O., Tomasz A. The rate of killing of Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics is strictly proportional to the rate of bacterial growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1297–1304. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes F. B., Pas E., Taschner P. E., Woldringh C. L. Kinetics of uptake and incorporation of meso-diaminopimelic acid in different Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):331–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.331-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa E. J., de Pedro M. A., Vázquez D. Penicillin binding proteins: role in initiation of murein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5632–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



