Abstract
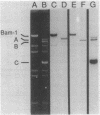
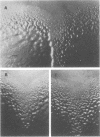
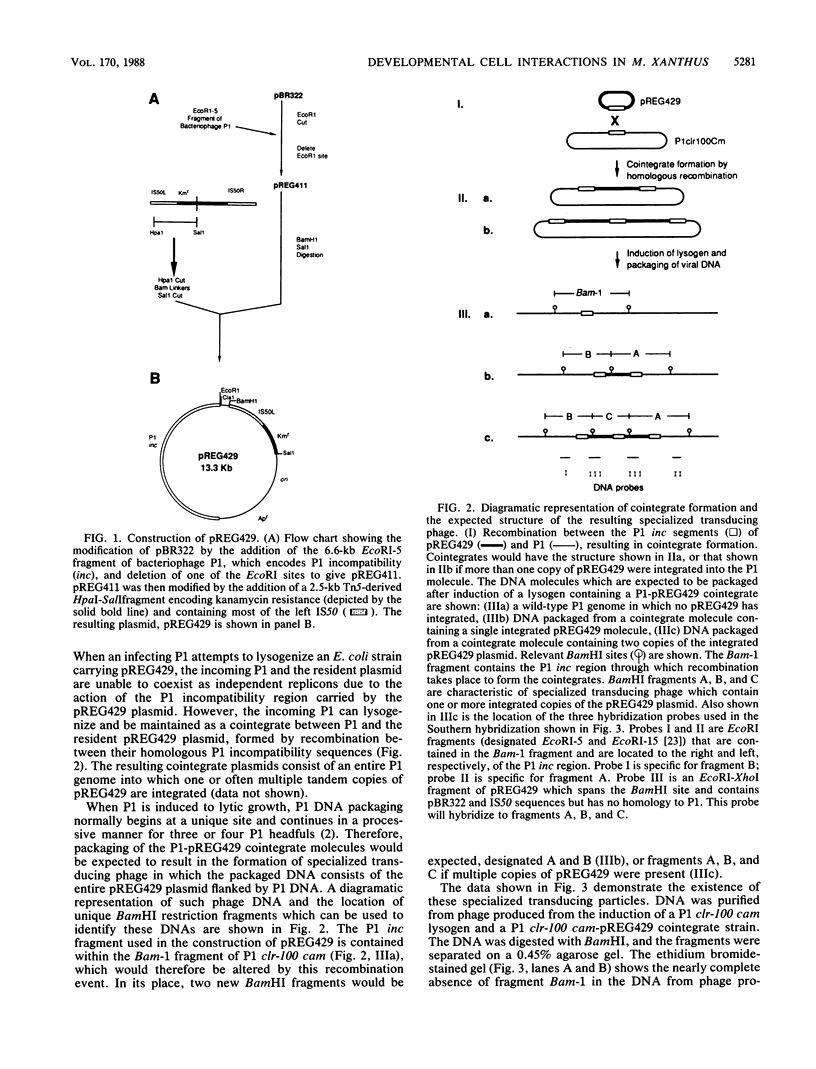
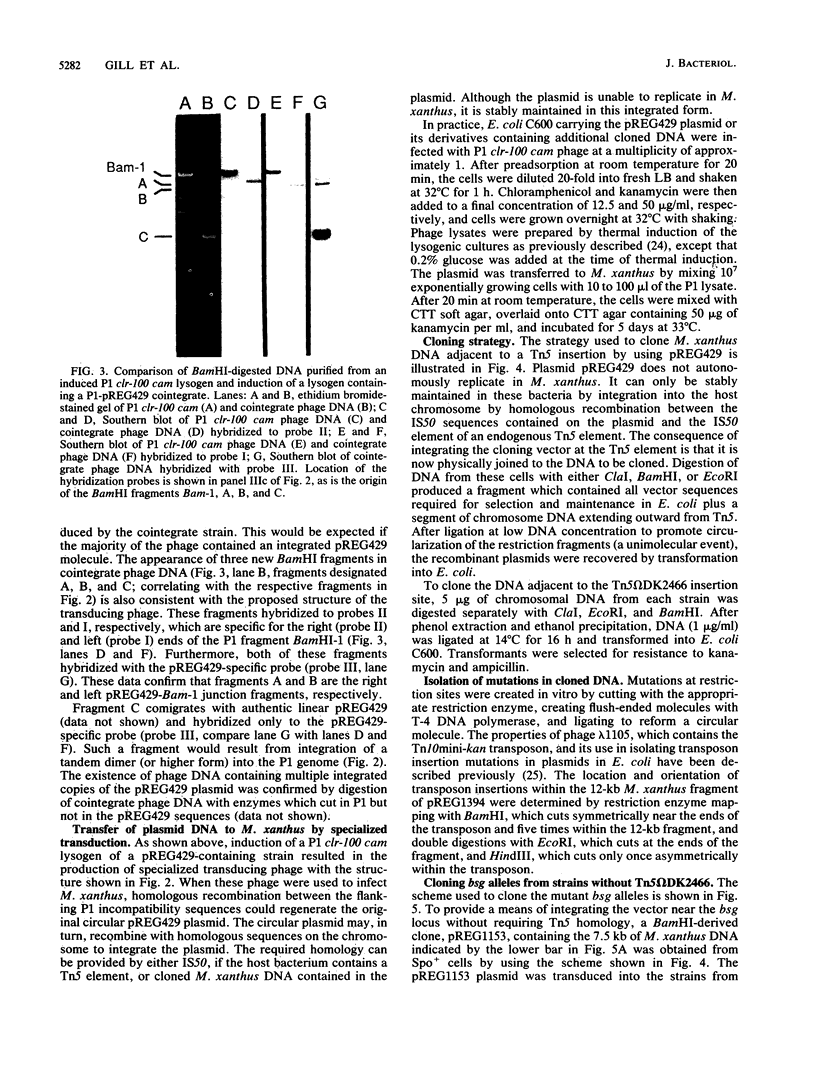
Developmental mutants of Myxococcus xanthus have been previously described which appear to be defective in required cell-cell interactions. These mutants fall into four phenotypic classes, Asg, Bsg, Csg, and Dsg, each of which is unable to differentiate into spores but can be rescued by extracellular complementation by wild-type cells or by mutants of a different class. We report the identification of one of the loci in which mutations result in a Bsg phenotype. The cloned locus was contained on a 12-kilobase EcoRI fragment and then localized by subcloning and a combination of in vitro and transposon mutagenesis. All mutations in this locus behave as a single complementation group, which we designate bsgA (formerly ssbA). Each of the bsgA mutations results in a nonsporulating phenotype, which can be rescued by extracellular complementation. Furthermore, we report that the bsgA mutants have a distinctive interaction with wild-type cells when vegetatively growing, swarming colonies converge.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avery L., Kaiser D. In situ transposon replacement and isolation of a spontaneous tandem genetic duplication. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):99–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00330896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Egner C., Hirschel B. J., Howard J., Johnsrud L., Jorgensen R. A., Tlsty T. D. Insertion, excision, and inversion of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):115–123. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi B., Arber W. Physical mapping of BglII, BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII and PstI restriction fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00431596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. E., Cull M. G. Control of developmental gene expression by cell-to-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Dworkin M. Cell-cell interactions in developmental lysis of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Introduction of transposon Tn5 into Myxococcus for analysis of developmental and other nonselectable mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):425–429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Sodergren E., Masuda T., Kaiser D. Systematic isolation of transducing phages for Myxococcus xanthus. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):44–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Coliphage P1-mediated transduction of cloned DNA from Escherichia coli to Myxococcus xanthus: use for complementation and recombinational analyses. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):317–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.317-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Control of morphogenesis in myxobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(3):195–227. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Gill R. E., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus and the spoC locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwag E., Fink J. M., Zissler J. Physical characterization of the genome of the Myxococcus xanthus bacteriophage MX-8. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):123–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00327521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Hoess R. The molecular genetics of bacteriophage P1. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:123–154. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. In vitro packaging of a lambda Dam vector containing EcoRI DNA fragments of Escherichia coli and phage P1. Gene. 1977 May;1(3-4):255–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]