Abstract
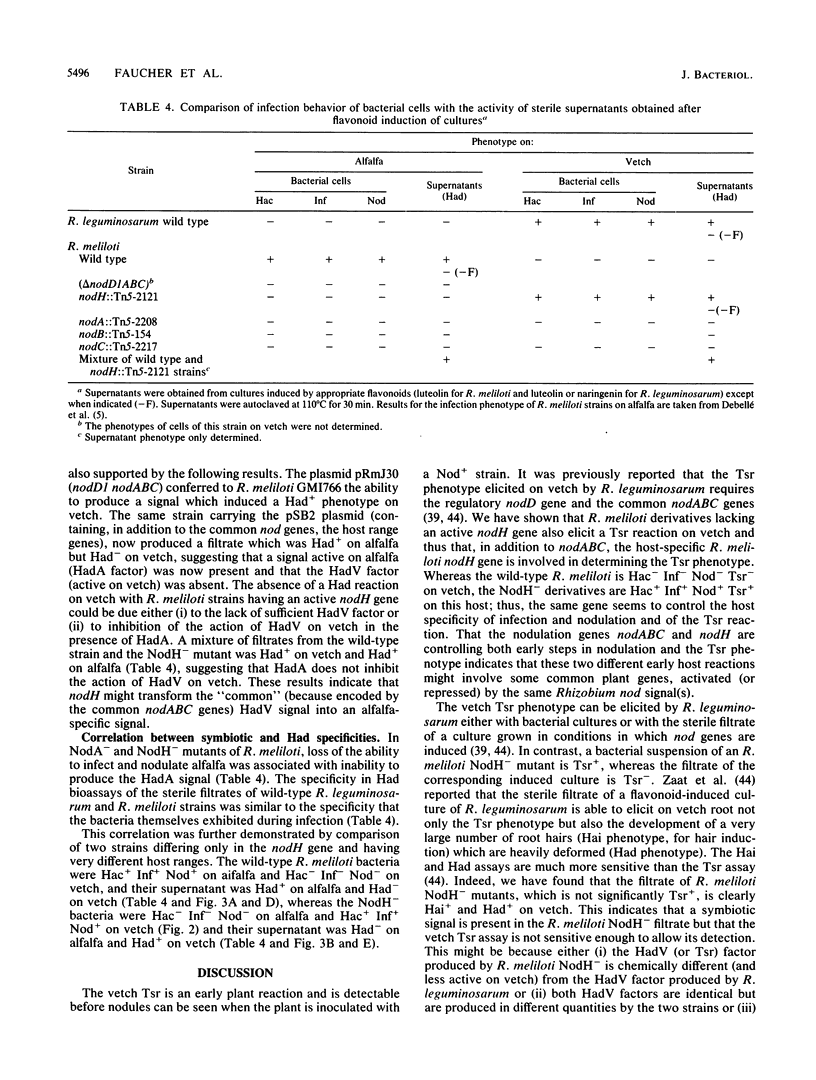
The Rhizobium meliloti nodH gene is involved in determining host range specificity. By comparison with the wild-type strain, NodH mutants exhibit a change in host specificity. That is, although NodH mutants lose the ability to elicit root hair curling (Hac-), infection threads (Inf-), and nodule meristem formation (Nod-) on the homologous host alfalfa, they gain the ability to be Hac+ Inf+ Nod+ on a nonhomologous host such as common vetch. Using root hair deformation (Had) bioassays on alfalfa and vetch, we have demonstrated that sterile supernatant solutions of R. meliloti cultures, in which the nod genes had been induced by the plant flavone luteolin, contained symbiotic extracellular signals. The wild-type strain produced at least one Had signal active on alfalfa (HadA). The NodH- mutants did not produce this signal but produced at least one factor active on vetch (HadV). Mutants altered in the common nodABC genes produced neither of the Had factors. This result suggests that the nodABC operon determines the production of a common symbiotic factor which is modified by the NodH product into an alfalfa-specific signal. An absolute correlation was observed between the specificity of the symbiotic behavior of rhizobial cells and the Had specificity of their sterile filtrates. This indicates that the R. meliloti nodH gene determines host range by helping to mediate the production of a specific extracellular signal.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Shaw E. J., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of an R factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1244-1249.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Maillet F., Vasse J., Rosenberg C., de Billy F., Truchet G., Dénarié J., Ausubel F. M. Interference between Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium trifolii nodulation genes: genetic basis of R. meliloti dominance. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5718–5727. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5718-5727.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Rosenberg C., Vasse J., Maillet F., Martinez E., Dénarié J., Truchet G. Assignment of symbiotic developmental phenotypes to common and specific nodulation (nod) genetic loci of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1075–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1075-1086.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Sharma S. B. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti RCR2011 genes involved in host specificity of nodulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7453–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervin S. E., Hubbell D. H. Root Hair Deformations Associated with Fractionated Extracts from Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.61-68.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHRAEUS G. The infection of clover root hairs by nodule bacteria studied by a simple glass slide technique. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Apr;16(2):374–381. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-2-374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Tu J. K., Long S. R. Conserved Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1432–1435. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1432-1435.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geremia R. A., Cavaignac S., Zorreguieta A., Toro N., Olivares J., Ugalde R. A. A Rhizobium meliloti mutant that forms ineffective pseudonodules in alfalfa produces exopolysaccharide but fails to form beta-(1----2) glucan. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.880-884.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M. A., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti has three functional copies of the nodD symbiotic regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8558–8562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Bachem C. W., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):841–848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Kondorosi E., John M., Schmidt J., Török I., Györgypal Z., Barabas I., Wieneke U., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Organization, structure and symbiotic function of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. W., Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Physical and genetic map of a Rhizobium meliloti nodulation gene region and nucleotide sequence of nodC. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.469-476.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. All nod genes of Rhizobium meliloti are involved in alfalfa nodulation by exo mutants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):1003–1006. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.1003-1006.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Reed J. W., Hanks J. F., Hirsch A. M., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to succinylate their calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide are defective in nodule invasion. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Signer E. R., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6231–6235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. O., Long S. R. Generalized transduction in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):125–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.125-129.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnoky P., Kondorosi A. Two gene clusters of Rhizobium meliloti code for early essential nodulation functions and a third influences nodulation efficiency. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):881–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.881-887.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Boistard P., Dénarié J., Casse-Delbart F. Genes controlling early and late functions in symbiosis are located on a megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):326–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00272926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. A., Tu J. K., Ogawa J., Sanga R., Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. I. Phenotypes of Tn5 Insertion Mutants. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):181–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truchet G., Debellé F., Vasse J., Terzaghi B., Garnerone A. M., Rosenberg C., Batut J., Maillet F., Dénarié J. Identification of a Rhizobium meliloti pSym2011 region controlling the host specificity of root hair curling and nodulation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1200-1210.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truchet G., Rosenberg C., Vasse J., Julliot J. S., Camut S., Denarie J. Transfer of Rhizobium meliloti pSym genes into Agrobacterium tumefaciens: host-specific nodulation by atypical infection. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.134-142.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Brussel A. A., Zaat S. A., Cremers H. C., Wijffelman C. A., Pees E., Tak T., Lugtenberg B. J. Role of plant root exudate and Sym plasmid-localized nodulation genes in the synthesis by Rhizobium leguminosarum of Tsr factor, which causes thick and short roots on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.517-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., van Brussel A. A., Tak T., Pees E., Lugtenberg B. J. Flavonoids induce Rhizobium leguminosarum to produce nodDABC gene-related factors that cause thick, short roots and root hair responses on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3388–3391. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3388-3391.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





