Abstract
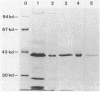
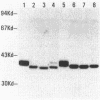
The pigmented enterobacterium Serratia marcescens, an opportunistic pathogen, shows a striking variation of its red color. Different strains differ greatly both in color and in the frequency with which they produce color variants. Within a strain, the variations occur at constant rates and are reversible. During an investigation of this phenomenon we observed that variation of a 39-kilodalton protein in S. marcescens 274 is closely associated with color variation. Using antibodies to this protein we identified it as being a component of the bacterial flagella. Variation of surface proteins often provides an organism with alternate offense-defense strategies for survival in a challenging environment. The pigment, in association with flagella, may provide such a function for S. marcescens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunting M. I., Robinow C. F., Bunting H. FACTORS AFFECTING THE ELABORATION OF PIGMENT AND POLYSACCHARIDE BY SERRATIA MARCESCENS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Jul;58(1):114–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauenhauer S. A., Hull R. A., Williams R. P. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Serratia marcescens genes encoding prodigiosin biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1128-1132.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Chien Y. H., Gascoigne N. R., Hedrick S. M. A murine T cell receptor gene complex: isolation, structure and rearrangement. Immunol Rev. 1984 Oct;81:235–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt M. C., Williams R. P. Thiamine-induced formation of the monopyrrole moiety of prodigiosin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.609-616.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics of structure and function of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:161–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata A. Use of endo- and exoglycosidases for structural studies of glycoconjugates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Bacteriophage receptors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:205–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Prodigiosin synthesis in mutants of Serratia marcesens. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1599-1604.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURKAYASTHA M., WILLIAMS R. P. Association of pigment with the cell envelope of Serratia marcescens (Chromobacterium prodigiosum). Nature. 1960 Jul 23;187:349–350. doi: 10.1038/187349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. A., Mehta A. M., Dave P. J. Prodigiosin, a component of kappa phage receptor complex in Serratia marcescens. Microbios. 1982;34(137-38):153–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. S., Hubert E. G., Montgomerie J. Z., Kalmanson G. M., Guze L. B. Defects in prodigiosin formation by L-forms of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1343–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1343-1345.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. P., GOLDSCHMIDT M. E., GOTT C. L. INHIBITION BY TEMPERATURE OF THE TERMINAL STEP IN BIOSYNTHESIS OF PRODIGIOSIN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 9;19:177–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90500-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA S. A study of a water-soluble complex of prodigiosin produced by a strain of Serratia marcescens. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Aug;40:1019–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]