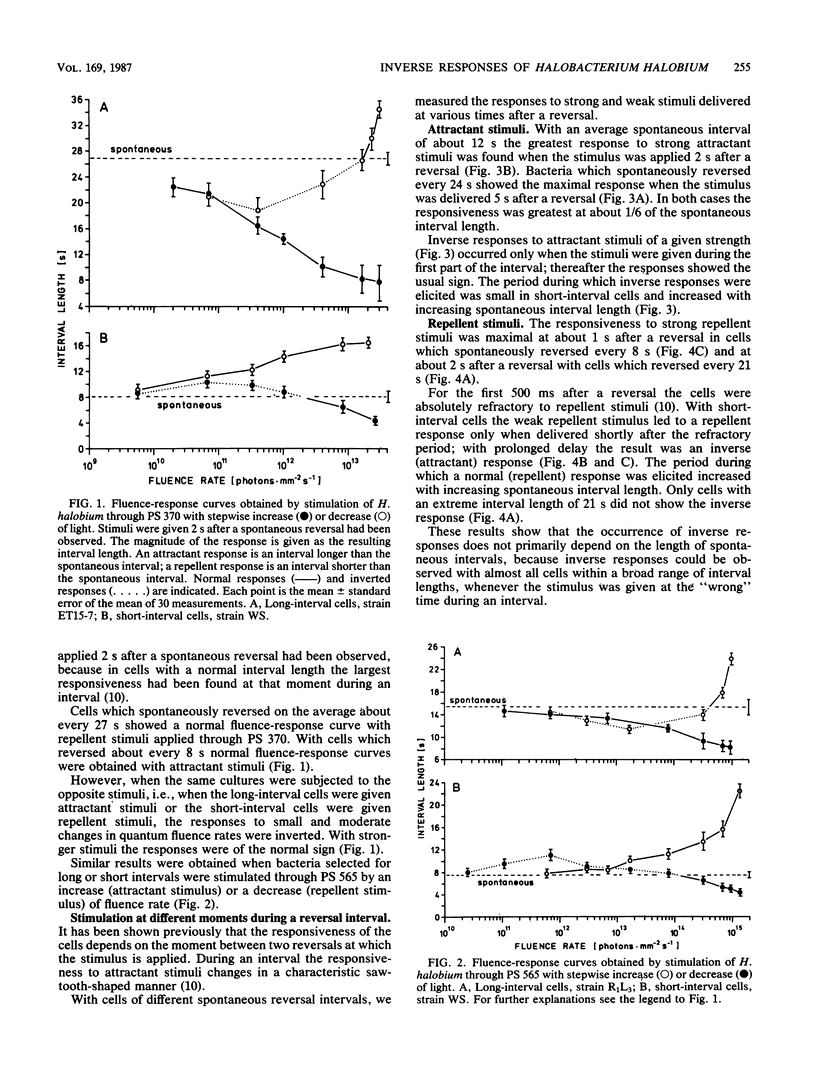
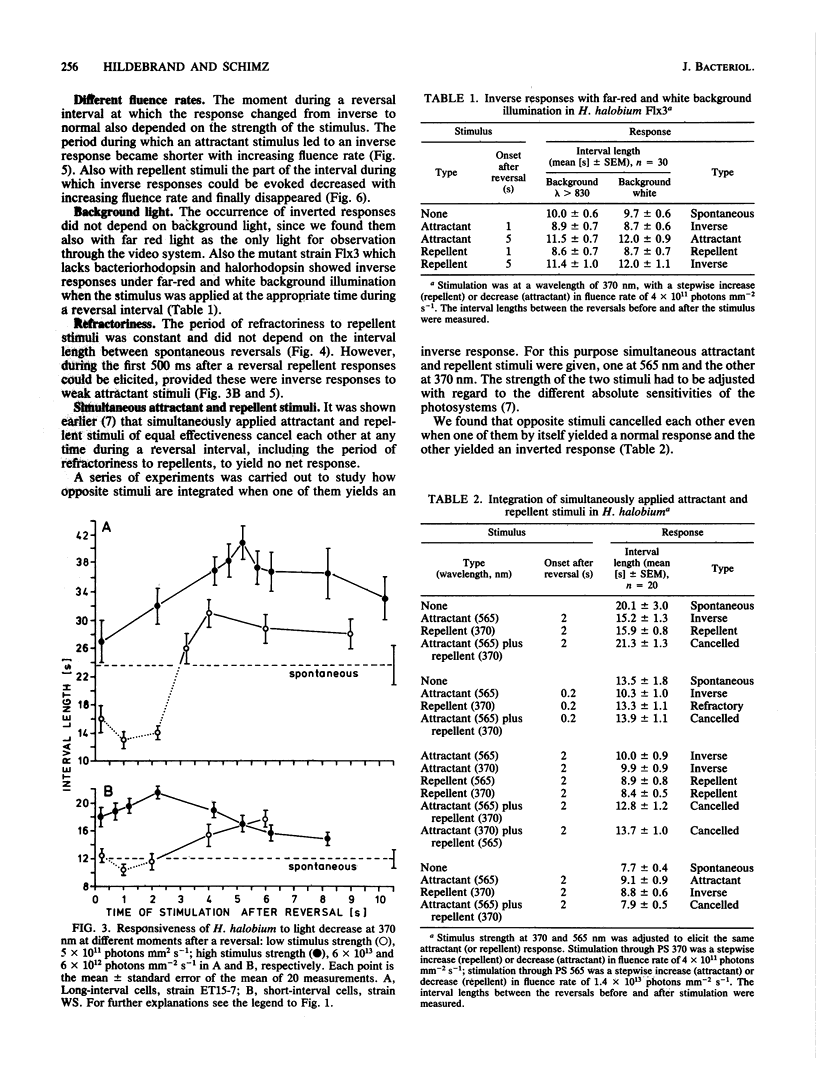
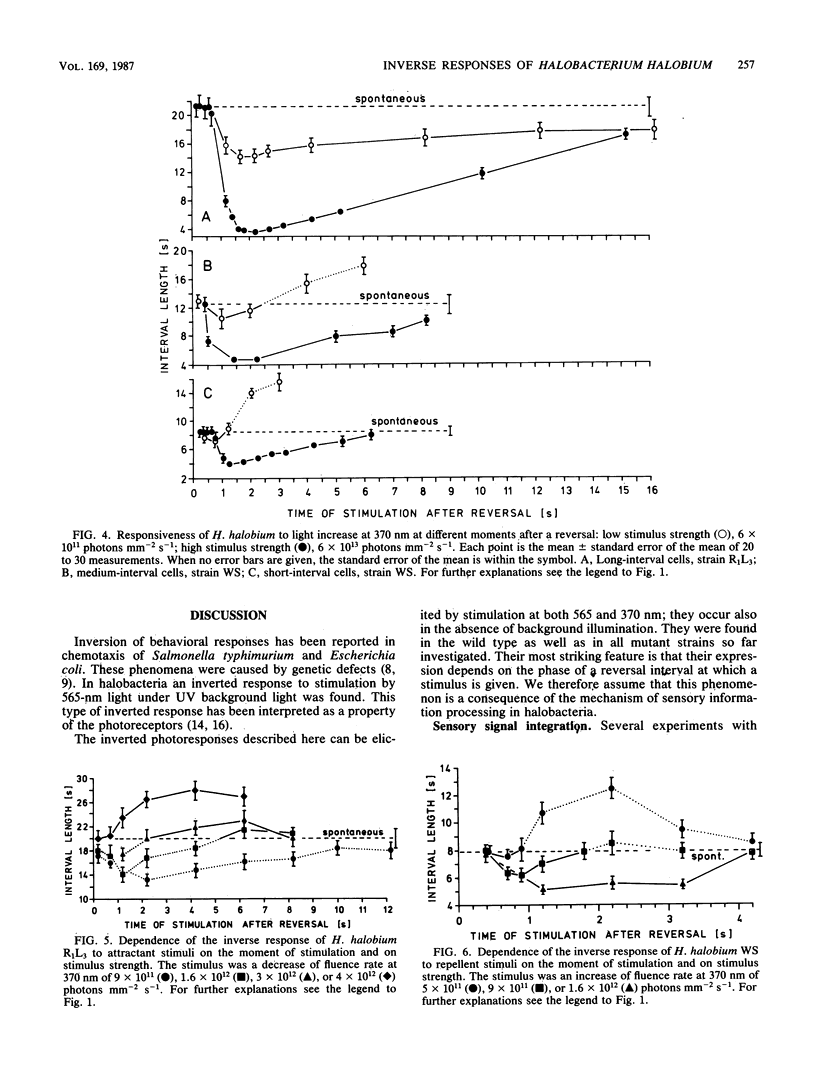
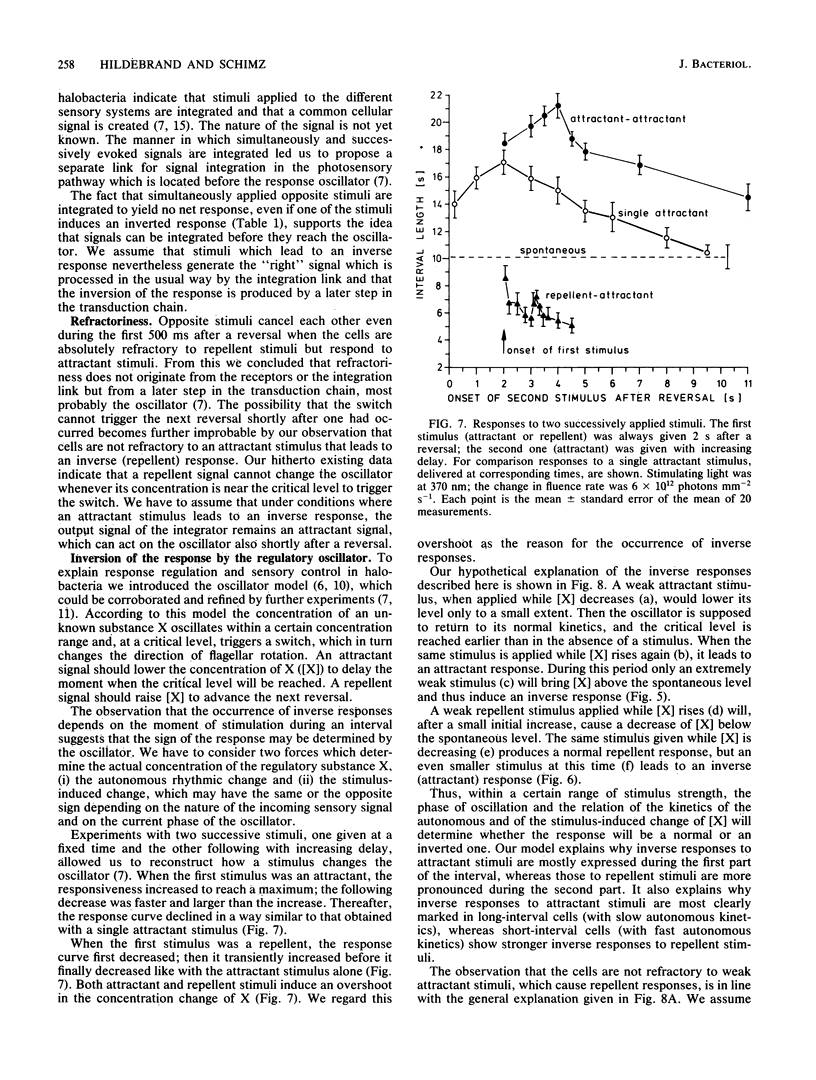
Abstract
Under certain conditions Halobacterium halobium organisms respond to a weak attractant light stimulus with a repellent response and to a weak repellent stimulus with an attractant response. The appearance of inverse responses depends on the stimulus strength, on the interval length between spontaneous reversals, and on the moment of stimulation during the interval. Although the cells are absolutely refractory to repellent stimuli for 500 ms after a reversal, repellent responses can be evoked even during that period if they are inverse responses to weak attractant stimuli. Simultaneous attractant and repellent stimuli cancel each other even when one of them leads to an inverse response, indicating that normal cellular signals occur at the site of signal integration. We postulate that the inverse responses are caused by certain properties of a cellular oscillator for which we previously postulated a role in response regulation and sensory control in halobacteria (A. Schimz and E. Hildebrand, Nature [London] 317:641-643, 1985).
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Hildebrand E. Sensory transduction in Halobacterium halobium: retinal protein pigment controls UV-induced behavioral response. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 Sep-Oct;34(9-10):841–847. doi: 10.1515/znc-1979-9-1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Dencher N. Two photosystems controlling behavioural responses of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):46–48. doi: 10.1038/257046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Schimz A. Integration of photosensory signals in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):305–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.305-311.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M., DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Inversion of a behavioral response in bacterial chemotaxis: explanation at the molecular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4150–4154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Kort E. N., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Attraction by repellents: an error in sensory information processing by bacterial mutants. Science. 1978 Jul 7;201(4350):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.351803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimz A., Hildebrand E. Entrainment and temperature dependence of the response oscillator in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):689–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.689-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling W., Schimz A. Photosensory retinal pigments in Halobacterium halobium. Biophys Struct Mech. 1980;6(2):165–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00535752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Control of transmembrane ion fluxes to select halorhodopsin-deficient and other energy-transduction mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Mochizuki Y., Kamo N., Kobatake Y. Evidence that the long-lifetime photointermediate of s-rhodopsin is a receptor for negative phototaxis in Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



