Abstract
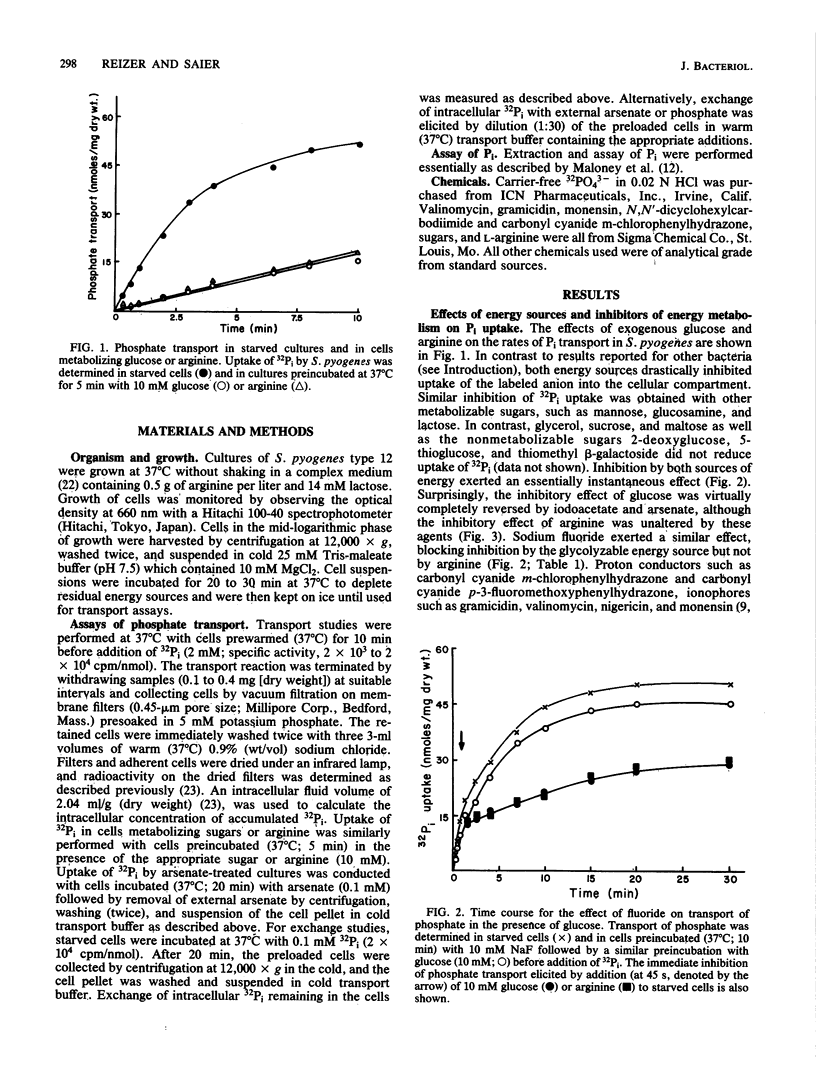
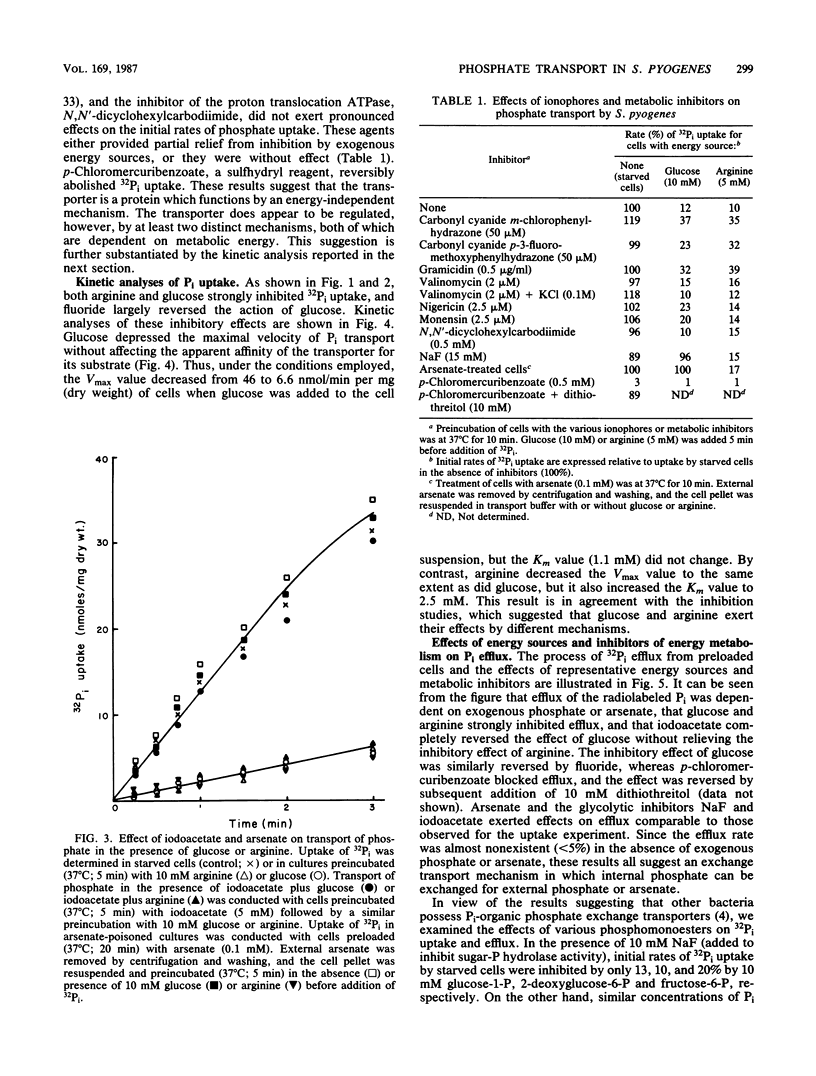
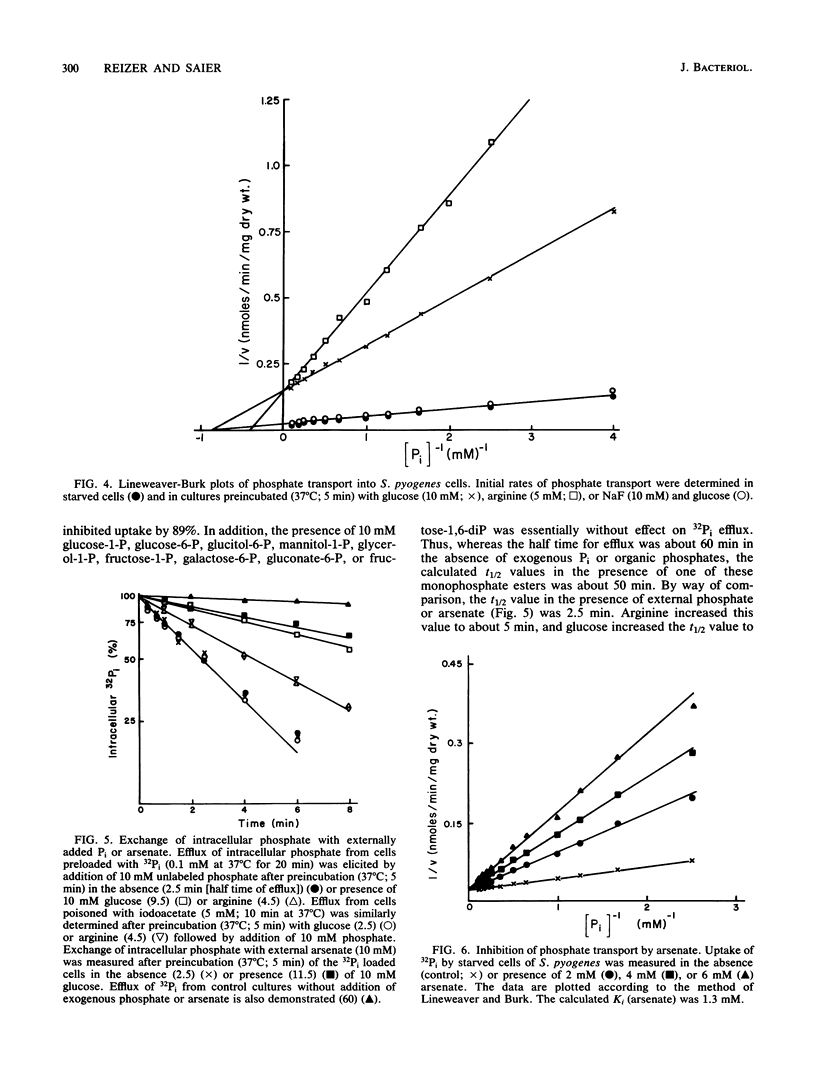
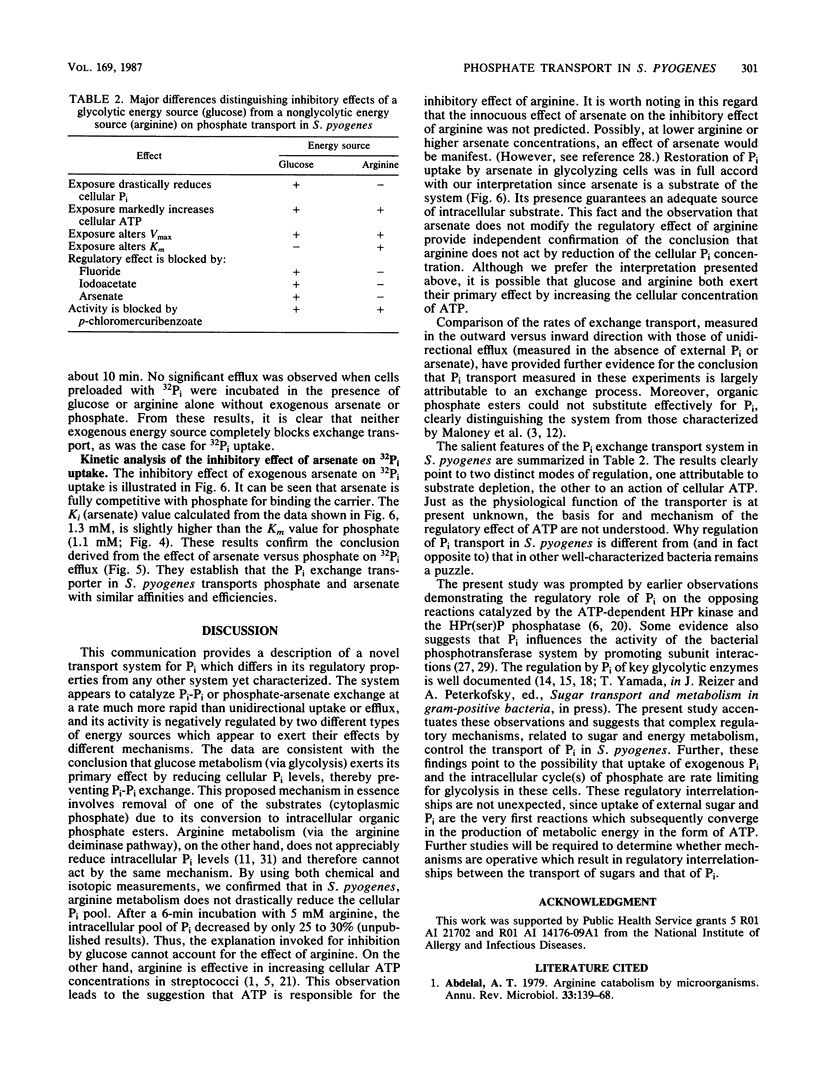
In contrast to results reported with other bacteria, uptake of 32Pi in Streptococcus pyogenes was found to occur rapidly in starved cultures and to be strongly and immediately inhibited by addition of exogenous glycolytic energy sources (such as glucose) and nonglycolytic sources of ATP (such as arginine). Preincubation of starved cells with NaF, iodoacetate, or arsenate eliminated the inhibiting effect of glucose but not that of arginine. In accordance with the hypothesis that transport was attributable to Pi-Pi exchange, uptake and efflux of 32Pi in the presence of trans unlabeled Pi exhibited similar characteristics and were largely eliminated by reduction of the trans Pi concentration. Neither process was inhibited appreciably by pretreatment of cells with ionophores or metabolic inhibitors, but both processes were abolished by exposure to p-chloromercuribenzoate. Inhibition by both exogenous energy sources resulted in a reduction in the maximal velocity of transport (Vmax). Whereas arginine also caused a shift in the apparent Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) to larger values, glucose did not alter the Km. On the basis of the results reported, we propose that the rate of Pi exchange is determined positively by the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of Pi and negatively by ATP or metabolites thereof. The mechanism of ATP action is unknown but could involve either covalent or noncovalent modification of the carrier protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdelal A. T. Arginine catabolism by microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:139–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfasi H., Friedberg D., Froedberg I. Phosphate transport in arsenate-resistant mutants of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):69–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.69-72.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar S. V., Maloney P. C. Characterization of phosphate:hexose 6-phosphate antiport in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12576–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar S. V., Sonna L. A., Maloney P. C. Variable stoichiometry of phosphate-linked anion exchange in Streptococcus lactis: implications for the mechanism of sugar phosphate transport by bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):280–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow V. L., Thomas T. D. Arginine metabolism in lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1024–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1024-1032.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher J., Kessler U., Hengstenberg W. Streptococcal phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system: purification and characterization of a phosphoprotein phosphatase which hydrolyzes the phosphoryl bond in seryl-phosphorylated histidine-containing protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1203-1209.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I. Phosphate transport in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAROLD F. M., HAROLD R. L., ABRAMS A. A MUTANT OF STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS DEFECTIVE IN PHOSPHATE UPTAKE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3145–3153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R. Gramicidin, valinomycin, and cation permeability of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):53–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.53-60.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R. Interaction of arsenate with phosphate-transport systems in wild- type and mutant Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2257–2262. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2257-2262.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Spitz E. Accumulation of arsenate, phosphate, and aspartate by Sreptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):266–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.266-277.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Transport of phosphate across the osmotic barrier of Micrococcus pyogenes; specificity and kinetics. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):73–82. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Ambudkar S. V., Thomas J., Schiller L. Phosphate/hexose 6-phosphate antiport in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.238-245.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Carbone D. P., Cushman R. A., Waggoner A. S. The importance of inorganic phosphate in regulation of energy metabolism of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Novotny M. J., Hengstenberg W., Saier M. H., Jr Properties of ATP-dependent protein kinase from Streptococcus pyogenes that phosphorylates a seryl residue in HPr, a phosphocarrier protein of the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.333-340.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Novotny M. J., Panos C., Saier M. H., Jr Mechanism of inducer expulsion in Streptococcus pyogenes: a two-step process activated by ATP. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):354–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.354-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Panos C. Regulation of beta-galactoside phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus pyogenes by an expulsion mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Panos C. Transport of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid by Streptococcus pyogenes and its derived L-form. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.211-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Medveczky N., La Nauze J. M. Phosphate transport in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D. The effect of fluoride on the arsenolysis of citrulline by soluble enzymes of streptococci. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Cox D. F., Feucht B. U., Novotny M. J. Evidence for the functional association of enzyme I and HPr of the phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase system with the membrane in sealed vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(2):231–238. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan M. M., Jacobson G. R. Subunit interactions of the Escherichia coli mannitol permease: correlation with enzymic activities. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4046–4051. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Krichevsky M. I., Keyes P. H. The coupling of phosphate accumulation to acid production by a non-growing streptococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):351–360. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Torchia D. A. Use of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 14C fluorography in studies of glycolysis and regulation of pyruvate kinase in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.791-800.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. PHO-regulon of Escherichia coli K12: a minireview. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C., Proulx M., Trahan L. Effect of gramicidin D on the acidogenic properties of oral streptococci and human dental plaque. J Dent Res. 1982 May;61(5):632–635. doi: 10.1177/00220345820610050201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H. Characterization of two genetically separable inorganic phosphate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):356–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.356-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



