Abstract
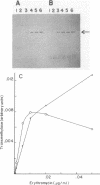
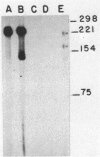
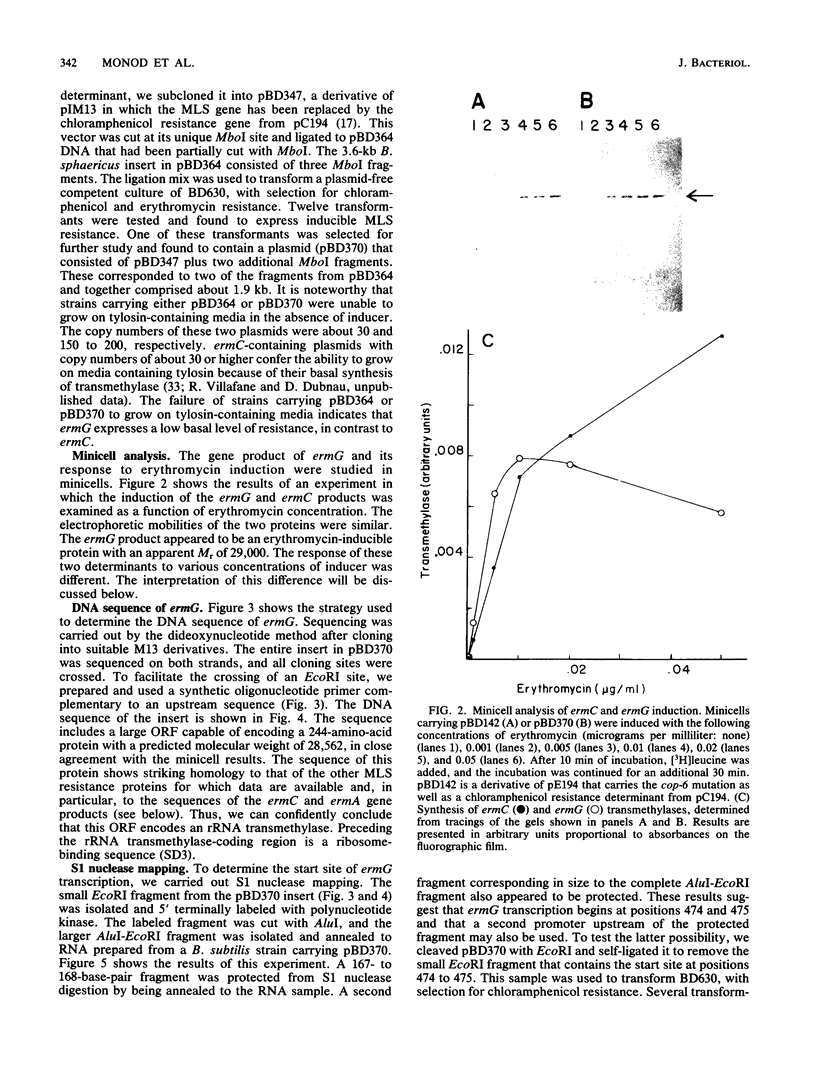
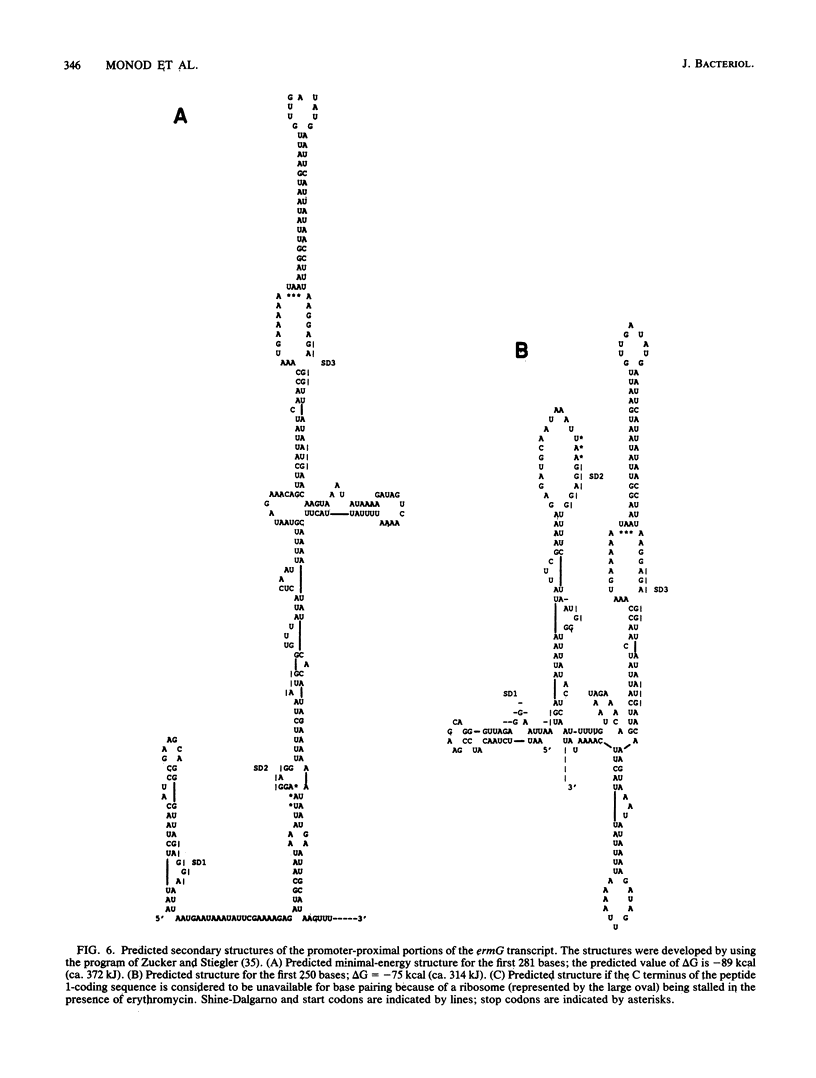
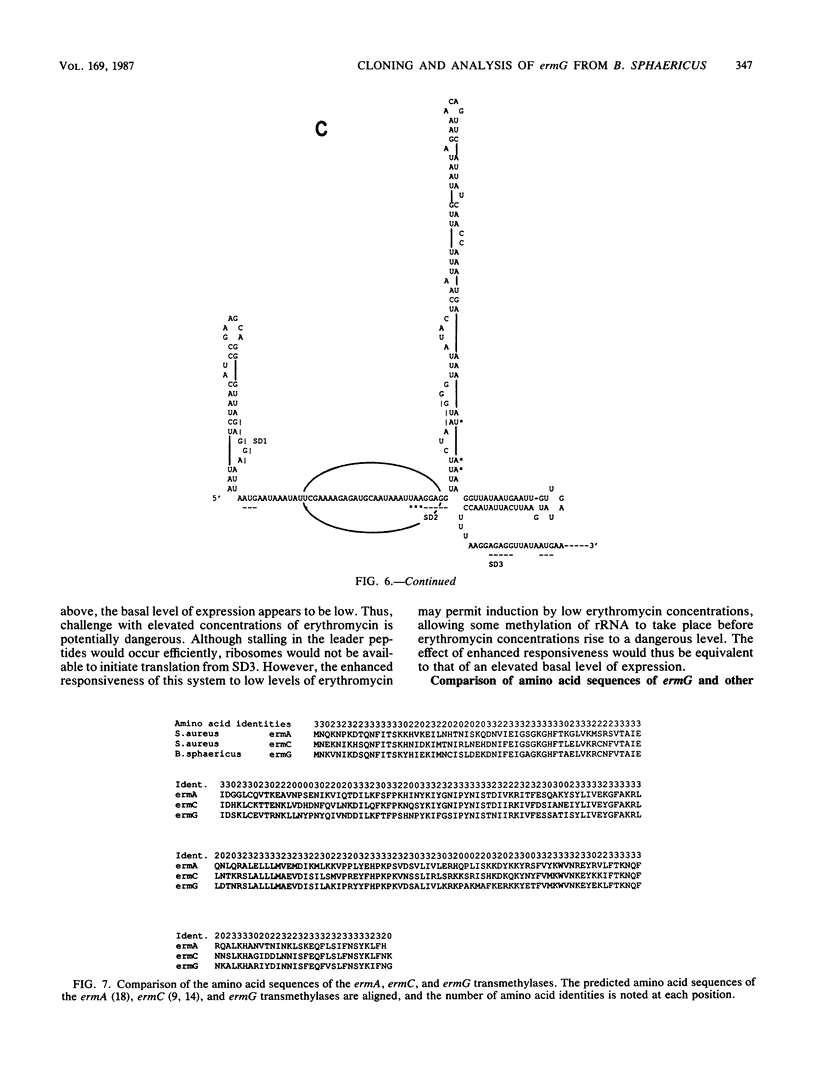
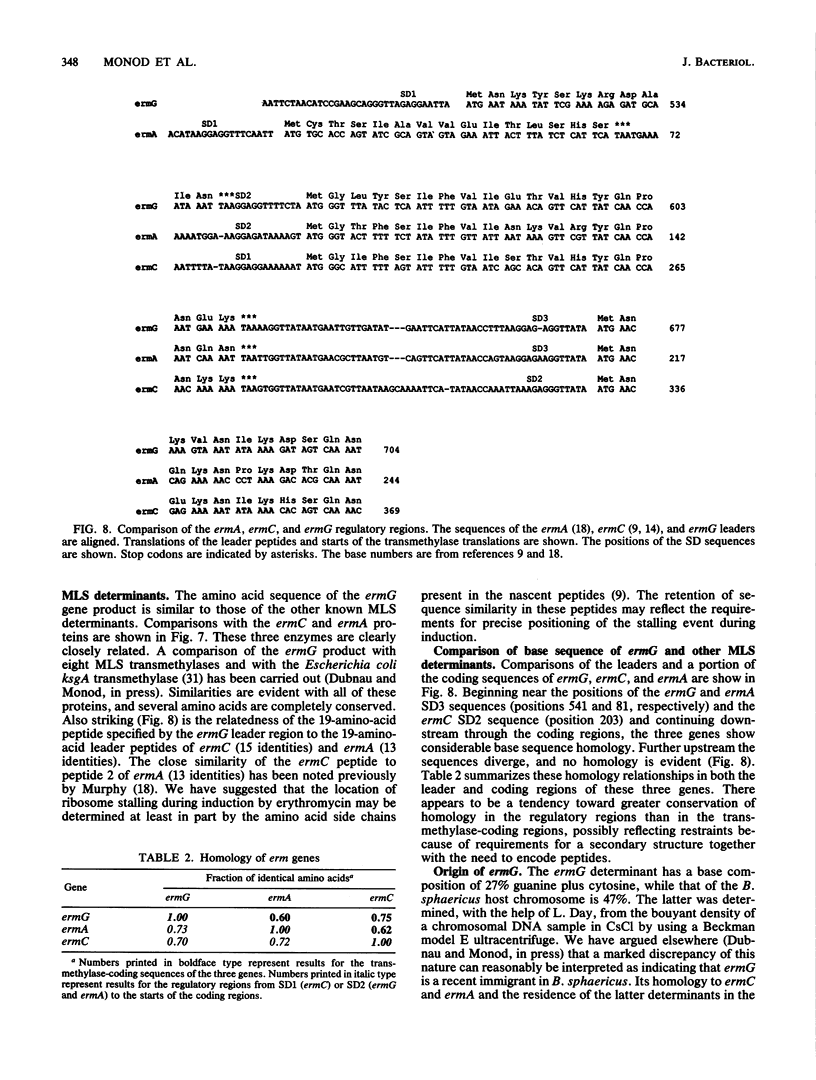
To analyze the regulation of a newly discovered macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance element (ermG) found in a soil isolate of Bacillus sphaericus, we cloned this determinant and obtained its DNA sequence. Minicell analysis revealed that ermG specifies a 29,000-dalton protein, the synthesis of which is induced by erythromycin. S1 nuclease mapping was used to identify the transcriptional start site. These experiments demonstrated the presence on the ermG mRNA of a 197 to 198-base leader. Within the leader are two small open reading frames (ORFs) capable of encoding 11- and 19-amino-acid peptides. Each ORF is preceded by a suitably spaced Shine-Dalgarno sequence. The ermG protein is encoded by a large ORF that encodes a 244-amino-acid protein, in agreement with the minicell results. This protein and the 19-amino-acid peptide are highly homologous to the equivalent products of ermC and ermA. We conclude, on the basis of this homology, that ermG encodes an rRNA transmethylase. The leader of ermG can be folded into a structure that sequesters the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and start codon for the large ORF (SD3). On the basis of these data and on the observed greater responsiveness of the ermG system than of the ermC system to low concentrations of erythromycin, we propose a model for the regulation of this gene in which the stalling of a ribosome under the influence of an inducer, while reading either peptide, suffices to uncover SD3 and allow translation of the rRNA transmethylase. The evolution of ermG is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of plasmid transformation in Bacillus subtilis: kinetic properties and the effect of DNA conformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 2;167(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00267416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Bechhofer D. H., Dubnau D. Translational autoregulation of ermC 23S rRNA methyltransferase expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1133–1141. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1133-1141.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Translational attenuation: the regulation of bacterial resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(2):103–132. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Grandi G., Hahn J., Grandi R., Dubnau D. Conformational alteration of mRNA structure and the posttranscriptional regulation of erythromycin-induced drug resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6081–6097. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T., Contente S., Dubnau D. Molecular cloning of heterologous chromosomal DNA by recombination between a plasmid vector and a homologous resident plasmid in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Feb;177(3):459–467. doi: 10.1007/BF00271485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T., Israeli-Reches M., Del Bue M., Dubnau D. DNA sequence and regulation of ermD, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance element from Bacillus licheniformis. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(3):349–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00425543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Grandi G., Gryczan T. J., Dubnau D. Translational attenuation of ermC: a deletion analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):204–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00331851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Byeon W. H., Weisblum B. A complex attenuator regulates inducible resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramin type B antibiotics in Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1252–1262. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1252-1262.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation: mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7079–7083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Weisblum B., Fahnestock S. R., Nomura M. Alteration of 23 S ribosomal RNA and erythromycin-induced resistance to lincomycin and spiramycin in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Denoya C., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of pIM13, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance plasmid from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):138–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.138-147.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. Nucleotide sequence of ermA, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B determinant in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.633-640.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan C. S., Dubnau D. Evidence for the translational attenuation model: ribosome-binding studies and structural analysis with an in vitro run-off transcript of ermC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7307–7326. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. L., Odelson D. A., Macrina F. L. Complete nucleotide sequence and transcription of ermF, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance determinant from Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):523–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.523-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. N., Mendelson N. H., Coyne S. I., Hallock L. L., Cole R. M. Minicells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):860–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.860-873.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. N., Hudson G. S., Brenner S. An erythromycin-resistance gene from an erythromycin-producing strain of Arthrobacter sp. Gene. 1985;35(3):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar A. G., Hahn J., Dubnau D. Studies on the synthesis of plasmid-coded proteins and their control in Bacillus subtilis minicells. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar A. G., Hahn J., Grandi G., Kozlov Y., Dubnau D. Posttranscriptional regulation of an erythromycin resistance protein specified by plasmic pE194. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner R., Cundliffe E., Schmidt F. J. Site of action of a ribosomal RNA methylase responsible for resistance to erythromycin and other antibiotics. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12702–12706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama H., Weisblum B. N-Methyl transferase of Streptomyces erythraeus that confers resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics: amino acid sequence and its homology to cognate R-factor enzymes from pathogenic bacilli and cocci. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Graham M. Y., Gryczan T., Dubnau D. Plasmid copy number control: isolation and characterization of high-copy-number mutants of plasmid pE194. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):635–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.635-643.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Siddhikol C., Lai C. J., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: requirements for induction. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):835–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.835-847.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buul C. P., van Knippenberg P. H. Nucleotide sequence of the ksgA gene of Escherichia coli: comparison of methyltransferases effecting dimethylation of adenosine in ribosomal RNA. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]