Abstract
When faced with a variable environment, organisms may switch between different strategies according to some probabilistic rule. In an infinite population, evolution is expected to favor the rule that maximizes geometric mean fitness. If some environments are encountered only rarely, selection may not be strong enough for optimal switching probabilities to evolve. Here we calculate the evolution of switching probabilities in a finite population by analyzing fixation probabilities of alleles specifying switching rules. We calculate the conditions required for the evolution of phenotypic switching as a form of bet-hedging as a function of the population size N, the rateθ at which a rare environment is encountered, and the selective advantage s associated with switching in the rare environment. We consider a simplified model in which environmental switching and phenotypic switching are one-way processes, and mutation is symmetric and rare with respect to the timescale of fixation events. In this case, the approximate requirements for bet-hedging to be favored by a ratio of at least R are that sN > log(R) and .
Keywords: population genetics, Moran model, fluctuating environment, phenotypic plasticity, evolutionarily stable strategy, frequency-dependent selection, extinction, evolutionary capacitance, evolvability
Bet-hedging organisms decrease their risk in an unpredictable environment by producing offspring of different phenotypes according to some probabilistic rule (Seger and Brockman, 1987). Bet-hedging theory was originally developed to describe an annual plant’s tradeoff between germinating seeds immediately versus germinating them over a larger number of years (Cohen, 1966). When only two different environments are encountered, one good and one bad, and the number of seeds produced is large, the predicted optimal strategy is to germinate a proportion of seeds each year approximately equal to the probability that a seed will encounter a good environment that year (Cohen, 1966).
Bet-hedging theory has been applied in many traditional ecological settings, including the resistance of weeds to eradication (Roberts and Feast, 1972; Swanton and Weise, 1991), invertebrate silk ballooning dispersal (Bell et al., 2005), the perennial life cycle of plants (Tuljapurkar, 1990), variable diapause in such diverse animals as crustaceans (Hairston and Munns, 1984), mosquitoes (Andreadis, 1990), sponges (Fell, 1995) and fish (Martin, 1999), and variable offspring size in frogs (Crump, 1981). There has also been much interest recently in phenotypic switching behaviors in microbes as a form of bet-hedging against novel and hostile environments (Avery, 2006; Kussell et al., 2005; Kussell and Leibler, 2005; Stumpf et al., 2002; Thattai and van Oudenaarden, 2004; Wolf et al., 2005). Examples of bet-hedging in the form of phenotypic switching or phase variation include pili expression in bacteria (Abraham et al., 1985), phage growth limitation machinery (Sumby and Smith, 2003), bacterial persistence (Balaban et al., 2004; Kussell et al., 2005; Kussell and Leibler, 2005), the yeast prion [PSI+] (Masel, 2005; Masel and Bergman, 2003; True and Lindquist, 2000), viral latency (Stumpf et al., 2002), as well as many other examples (Avery, 2006; Hallet, 2001; Henderson et al., 1999).
In the study of bet-hedging strategies, optimality is usually defined according to the maximization of expected geometric mean fitness over time, even at the expense of a decrease in arithmetic mean fitness (Seger and Brockman, 1987). If one phenotype is very strongly adaptive, but only on very rare occasions whose frequency isθ, then geometric mean fitness calculations predict that the phenotype will be optimally expressed with probabilityθ. This geometric mean fitness approach to bet-hedging has recently been exploited to explain phenotypic switching phenomena in microbes (Kussell et al., 2005; Kussell and Leibler, 2005; Stumpf et al., 2002; Thattai and van Oudenaarden, 2004; Wolf et al., 2005).
Unfortunately, geometric mean fitness calculations invoke infinitely large populations, and hence cannot capture the dynamics of weak selection. It has been suggested that selection for optimal bet-hedging in real populations may be weak, and that true optimality is not always achieved (Philippi, 1993). There are two scenarios of weak selection. First, selection for bet-hedging may be of recent origin, with insufficient time for optimal strategies to evolve. Second, selection for bet-hedging may be infrequent. In this case, even if an allele that hedges against rare catastrophic events has maximal geometric mean fitness, short-term selection against this allele may drive it extinct before the next catastrophic event occurs. This second limitation relating to the “myopic” nature of natural selection has largely been considered with regards to the evolution of evolvability (e.g, Sniegowski and Murphy (2006)), but also applies to the evolution of all bet-hedging strategies against rare events.
One way to study the limitations posed by weak selection of this kind is to focus on fixation probabilities rather than geometric mean fitness, thus explicitly capturing extinction dynamics (Masel, 2005; Masel and Bergman, 2003; Nowak et al., 2004; Proulx and Day, 2001). Here the fixation probability of a bet-hedging strategy is the probability that it replaces the resident strategy in a population, when it is originally held by a single individual. In this setting, optimality, rather than maximizing some explicit fitness function, becomes a game-theoretic notion. For example, in the formulation of Masel (2005), a strategy S is called optimal if, for every strategy T, the fixation probability of S in a resident population of T is at least as large as the fixation probability of T in a resident population of S.
The optimal strategy was computed according to this definition by Masel (2005), using a simplified model of a fluctuating environment and various approximations for computing fixation probabilities. Counterintuitively, as the population size increased, the optimal strategy diverged from the expected result of phenotype expression with probability equal to that of the environment making the phenotype useful. This discrepancy at large population sizes is puzzling in the light of the fact that the expected result was derived for an infinite population (Kussell et al., 2005). Here we revisit the Masel (2005) model, and describe improved analytical and computational methods for estimating fixation probabilities, which we validate using Monte Carlo simulations. This leads to qualitatively and quantitatively different results to those of the earlier study (Masel, 2005), including the elimination of this puzzling discrepancy.
2. MATHEMATICAL MODEL
We consider individuals having two phenotypes, A and B. These phenotypes are heritable, but subject to random switching: with probability m an offspring of a type A individual will be of type B, and with probability m′ an offspring of a type B individual will be of type A. Here the probabilities m and m′, which completely characterize the bet-hedging strategy, are assumed to be governed by some heritable modifier allele M.
We also consider two environments, E and F, with stochastic switching between the environments. The waiting times until environmental changes are modeled as being exponentially distributed, with rateθ from E to F and rateθ ′ from F to E. Here the units of time are generations, so for example when starting in environment E, the probability that a change to F happens within t generations is given by 1 − e −θt. In environment E, type A individuals have fitness fAE and type B individuals have fitness fBE. In environment F, type A individuals have fitness fAF and type B individuals have fitness fBF.
Note that our assumption of discrete and heritable phenotypes has been most frequently studied in microbial contexts, but also applies to any epigenetically inherited state. Similarly, the highly autocorrelated environments that we model are most frequently assumed in microbial contexts in which environmental change is rare relative to generation time, but our model also applies to exceptionally rare events in the context of organisms with longer generation times. Note that our model describes bet-hedging against aggregate rather than idiosyncratic risk (Robson et al., 1999).
We are concerned with the following two main problems:
Given two genotypes that differ only in modifiers controlling their phenotypic switching probabilities m and m′, what is the probability that a single individual with one genotype replaces a resident population with the other genotype?
What are the “optimal” switching probabilities m and m′, for some suitable definition of optimality? (For this question to be interesting, A individuals should be more fit than B individuals in one of the two environments, and less fit in the other.)
2.1 Full model
To address these questions we consider a haploid population of constant size N consisting of four types of individuals, A1, A2, B1, B2, where A and B indicate the phenotypes, and the subscript indexes the modifier allele --- subscript 1 for modifier allele M1, which has switching probabilities (m1, m1′ ), and subscript 2 for modifier allele M2, which has switching probabilities (m2, m2′ ).
We use a Moran model for the evolutionary process: at each step one individual is chosen uniformly at random to die, and one individual (possibly the same) is chosen to reproduce with probability proportional to its fitness in the current environment. The newly-born individual immediately switches phenotype with probability m1, m2, m1′, or m2′, according to its type. Before taking each step, the environment has an opportunity to change: if the environment is currently E, it switches to F with probability T1,2, and if the environment is currently F, it switches to E with probability T2,1, where T = exp(R) is the rate matrix . Note that N birth-death rounds in the Moral model correspond to one generation for the population, and that when θ′ = 0 we have .
Eventually one of the two modifier alleles will be lost, and the population will consist entirely of type A1 and B1 individuals, or entirely of type A2 and B2 individuals. Under this model, the evolution of the population and environment are jointly Markovian, so by standard Markov chain theory it is in principle possible to compute the probabilities of each of these two outcomes by solving a particular system of linear equations --- see, for example, section 1.3 of Norris (1998).
The number of equations in this system is equal to the size of the state space (≈ N 3/3; see Appendix A). The system of equations is quite sparse, as each state can move in one step to at most 13 other states. By ordering the states appropriately, one can structure the system of equations to be band-diagonal with upper- and lower- bandwidth of order N 2, but no smaller (even for a single environment), as described in Appendix A. Solving this system directly with a band-diagonal solver would then have space requirements of order N5 and time requirements of order N 7 (see e.g. section 4.3 of Golub and Van Loan, (1996)), making it currently impractical for N above 100 or so. It may be possible to bring the time and space requirements closer to order N 3 by using a direct method that exploits the sparseness via a different strategy, or by using an iterative method such as conjugate gradients, but we do not pursue these direction here. Rather, we make several simplifying assumptions, and use several approximations, to arrive at an algorithm for computing approximate fixation probabilities in order N time and space. This is suitable for population sizes up to at least 10 million.
2.2 Simplifications and approximations
To simplify the problem, we assume that different evolutionary processes occur on sufficiently different time scales such that they can be separated (Gillespie, 1983). In particular, we assume that environmental change events are rare relative to the time scales of phenotypic switching and of fixation at the modifier locus. Rare environmental change events mean that we can study switching from environment E to F and associated adaptive phenotypic switching from A to B separately from switching in the reverse direction. Without loss of generality, we consider environmental switching in a single direction only, and set θ ′ to zero.
The next simplifying assumption is that phenotype B has fitness 0 in environment E, i.e., that fBE = 0. This is a conservative assumption, simplifying the mathematics while increasing the cost of phenotypic switching and hence making it harder for bet-hedging to evolve. As only the relative fitnesses within each environment matter, we may assume without loss of generality that fAE = 1 and fAF = 1, and we will write fBF = 1 + s.
Since we are studying evolutionary processes associated only with switching from E to F, we begin in environment E as our initial condition. Since phenotype B has fitness 0 in environment E, we initialize the population with phenotype A only. Phenotypic switching from B to A now has no opportunity to occur in environment E, and in F it is both rare and disadvantageous, so we approximate m′ as zero.
Again employing the “weak mutation” separation of timescales approximation (Gillespie, 1983), we assume that mutations at the switching modifier locus are rare relative to other processes. We therefore consider events occurring after each such mutation, and begin with N – 1 individuals of type A1 and a single individual of type A2. We define pfix(m1, m2) to be the probability that modifier allele M2 with switching probability m2 ultimately fixes, i.e. that the population eventually consists entirely of type A2 and B2 individuals. We will sometimes write pfix (m1, m2) as pfix(m1, m2, N, θ, s) to emphasize its dependence on N, θ, and s.
These same simplifying assumptions were used in Masel (2005), and in what follows we mostly use the same notation as in that study, except that here we denote fixation probabilities by pfix rather than pinvasion, and we use hats to denote approximate values e.g., p̂fix
With these simplifications, we can approximate the population in environment E as consisting of two types of individuals, A1 and A2, having fitnesses 1 – m1 and 1 – m2, respectively. This approximation becomes exact if we change the rules of the Moran model in environment E slightly, so that new-born individuals of type B, which have fitness 0, are replaced immediately. This effectively reduces the state space of the Markov chain to size N + 1, and allows us to compute the probability q(1, i) that there are exactly i individuals of type A2 at the time of the first environmental change to F, given that there was initially just one. Details are given in section 2.4.
In environment F, we again explicitly track only the numbers of types A1 and A2 individuals, but here we introduce “jump” moves --- each time a new type B individual appears by phenotypic switching, we estimate the probability that it and its descendents eventually take over the population, treating this as a single step in the Markov chain. Using this chain we compute the approximate probability p(i) of a modifier allele with switching probability m2 fixing, given that there are exactly i individuals of type A2 at the time of the environmental change. Details are given in section 2.5.
Our approximation p̂fix(m1, m2) to pfix(m1, m2) is then computed as
| (1.) |
The values q(1, i) for i = 0, …, N can be computed numerically by solving a single system of N + 1 linear equations, as can the values of p(i) for i = 0, …, N. In both cases the systems of equations are tridiagonal, so can be solved in time and space of order N ---see, e.g., Golub and van Loan (1996). These systems can be solved in memory for N up to about 10 million on a computer with 1GB of RAM.
2.3 Optimality
To address problem (2) above, we need a definition of optimality. As in Masel (2005), we will say that the switching probability m1 is optimal (for given N, θ, and s) if pfix(m1, m2, N, θ, s) ≥ pfix(m2, m1, N, θ, s) for all switching probabilities m2. (Here we are still assuming that θ ′ = 0 and m′ =0, although the above definition of optimality readily extends to the more general case.) The two-way comparisons used to define optimality are equivalent to asking which of two possible alleles will be more prevalent if mutation rates are symmetric and mutations are rare relative to fixation time --- see section 4.1.
With this definition, for any given parameters N, θ, and s we can ask whether an optimal switching probability exists and whether it is unique. While we do not presently have a formal answer to either of these questions for this model, both appear to hold numerically for all of the parameter values we have tried. Moreover, for this particular model it appears, from Fig. 3A and other numerics, to be sufficient to check optimality locally, i.e., that if pfix (m2, m1) ≥ pfix (m1, m2) holds for all m2 in a small interval [m1 −ε, m1 +ε] around m1 (with ε> 0), then it also holds for all m2 in the entire interval [0, 1]. This makes numerical search algorithms for mopt straightforward, while allowing all values of mopt returned by the algorithm to be subsequently checked for global optimality.
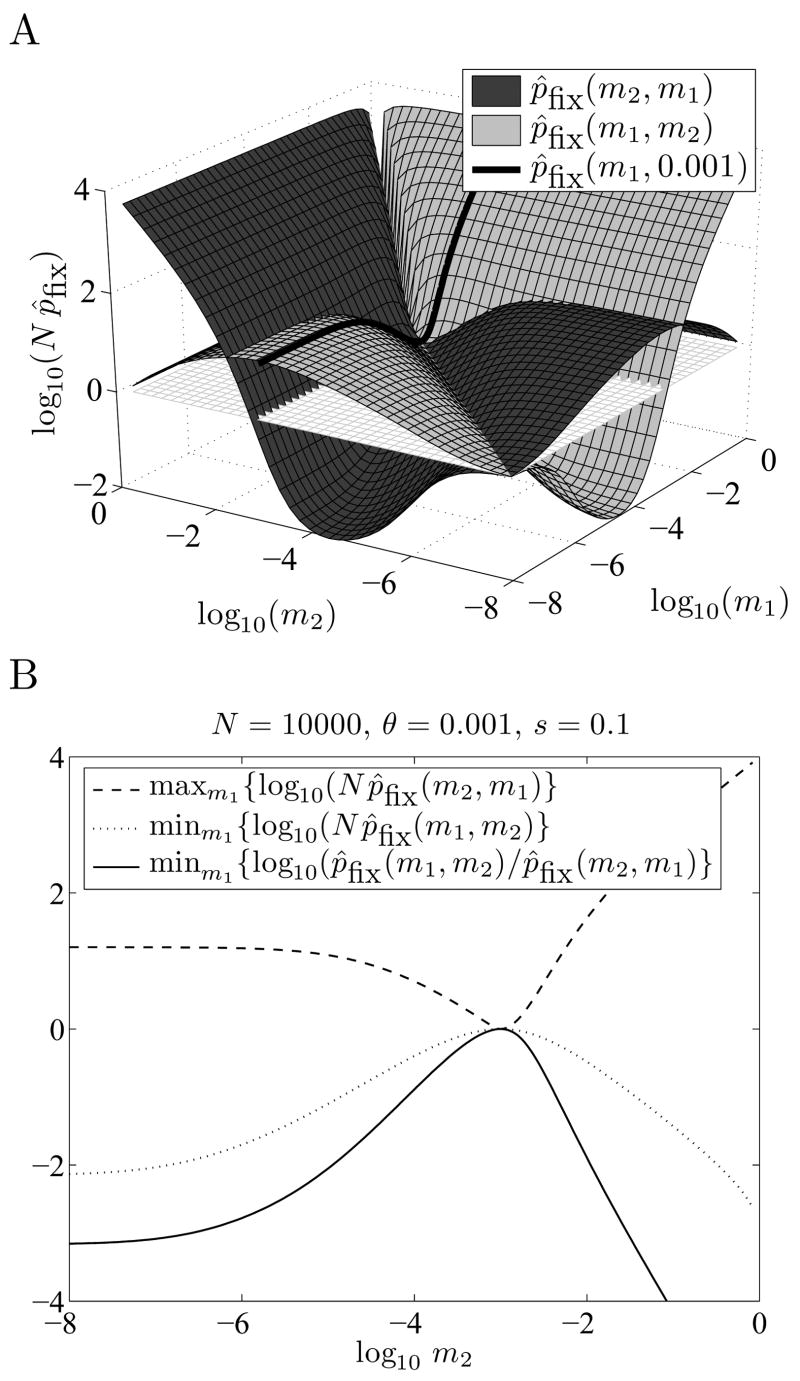
Figure 3.
The optimal switching probability is unique. Part A shows the surfaces of estimated fixation probabilities p̂fix(m1,m2) and p̂fix(m2, m1). Here m̂opt ≈ θ = 0.001 --- note that p̂fix (m1,0.001) ≥ p̂fix (0.001,m1) for all m1 in the interval [0, 1]. Part B shows that there is a unique optimal value: m̂opt ≈ = 0.001 is the only m2 for which p̂fix(m1, m2) ≥ p̂fix(m2, m1) for all m1 (solid line). It is also the only m2 for which p̂fix(m1, m2) ≥ 1/N for all m1 (dotted line), and the only m2 for which p̂fix (m2, m1) ≤ 1/ N for all m1 (dashed line).
2.4 Model preceding environmental change
Suppose we are in environment E, and that a population currently consists of i individuals of type A= and N – i individuals of type A1. The number of type A2 individuals increases to i + 1 after one step of the Moran model if a type A2 individual is chosen to reproduce and a type A1 individual is chosen to die. The probability that both these events happen is given by
The probability that the number of type A2 individuals decreases from i to i – 1 is given by the probability that a type A1 individual is chosen to reproduce and a type A2 individual is chosen to die:
Let q(i, j) be the probability that there are exactly j individuals of type A2 at the time of the next environmental change event, given there are initially i individuals of type A2. To evaluate Equation 1, only the values q(1, j) for j = 1, …, N are needed. (The value q(1,0) is not needed since p(0) = 0.) The values q(1, j) for j = 1, …, N –1 can be found by solving the single tridiagonal system of linear equations
and q(1,N) --- the probability that a single m2 individual fixes by drift before an environmental change --- is given by . The derivation of the single tridiagonal system of linear equations is given in Appendix B: this is the key mathematical observation of the current work, as it reduces a calculation that appears to be of order N2 to a far more tractable order N. This allows us to compute the values q(1, j) directly, avoiding several of the approximations used in Masel (2005).
2.5 Model after environmental change
Suppose now we are in environment F. If the population consists of i individuals of type B (which have fitness 1 + s) and N – i individuals of type A (which have fitness 1), and if we neglect further phenotypic switching, then following Ewens (2004) Eq. 2.158, the probability π(i) that type B fixes is given by
| (2.) |
In what follows we set y = π (1) --- the probability that a single B replaces a resident population of type A. Suppose that at the time of the change to environment F, there are i individuals of type A2 and N – i individuals of type A1. We wish to compute p(i), the probability that the m2 allele fixes --- this includes both the possibility of adaptive B2 individuals sweeping the population, and the possibility of A2 individuals taking over by drift.
To avoid explicitly tracking four types of individuals, we instead consider a population consisting only of type A individuals, say i of type A2 and N – i of type A1. This is always the case in environment E, since we have assumed that type B individuals have fitness zero there, and are replaced immediately. This population evolves by neutral drift until it reaches an absorbing state i = 0 or i = N, but with the following modification:
Each time an A2 is born, with probability m2 it switches to B2. In this case with probability y we jump immediately to state i = N; this jump corresponds to the new-born B2 variant being destined for fixation. With probability 1 – y this variant does not become fixed, and is eliminated from future consideration: this reduces the number of A1 and A2 individuals to N –1. To keep the size of the population we are tracking constant, we replace the B2 by an A1 with probability (N – i)/(N – 1) and by an A2 with probability (i –1)/(N – 1). (Note that these replacement individuals are not given the opportunity to switch phenotype, but such two-in-a-row switching should happen with probability of order m2.)
Similarly, each time an A1 is born, with probability m1 it switches to B1. In this case with probability y we jump immediately to state i = 0; otherwise the B1 is replaced by an A1 with probability (N − 1 − i)/(N − 1) and by an A2 with probability i/(N − 1).
Under this approximation, the values p(i) satisfy the following tridiagonal system of linear equations:
where
This formulation differs from that in Masel (2005) in several regards, and has the advantages that it becomes exact when y = 1, and gives p(i) = i/N when m1 = m2.
Note that, for s > 0, if there is more than one type B variant, then y overestimates the probability that any particular one of these type B variants eventually takes over the population. (For example, when s = 0.2 and N is large, y is roughly 1/6; if there are ten type B variants they certainly cannot each have probability more than 1/10 of taking over the population.) In some cases the population may become pure B while it is still comprised of a mixture of B variants with independent origins. This is known as a “soft sweep”, as opposed to the traditional scenario considered by population genetics of a “hard sweep” in which a single adaptive variants is selected to the point of fixation (Hermisson and Pennings, 2005). In practice, however, our approximation works well for a wide range of parameters, as analyzed in Appendix C and assessed with Monte Carlo simulations in Appendix D.
2.6 The accuracy and biological significance of m̂opt
For fixed N, θ, and s, if the curves for pfix(mopt, m, N, θ, s) and pfix(m, mopt, N, θ, s), as functions of m, are flat for m close to mopt, then even if our approximate fixation probabilities are accurate, our approximation m̂opt may be less accurate. In such cases the accuracy of m̂opt can be difficult to assess with Monte Carlo simulations, because small differences in probabilities require many simulation runs to resolve. In addition, when these curves are flat then the theoretical superiority of m̂opt relative to close values of m does not reflect a significant biological advantage.
To give a sense of the flatness of the curves, after computing m̂opt, we found the range of m surrounding m̂opt for which p̂fix (m,m̂opt)/p̂fix (m̂opt ,m)< R , for several thresholds R > 1. (By the definition of m̂opt, this ratio is at least 1.) For mild inaccuracies in computing fixation probabilities, these intervals should contain the true value of mopt. Under certain assumptions the ratio pfix (m, mopt )/pfix (mopt ,m) is also approximately equal to the ratio of times for which a population is homogeneous for mopt versus m alleles (Proulx and Day, 2001) --- see section 4.1. For this reason, the magnitude of R can be interpreted as a measure of the extent to which mopt is superior.
3. RESULTS
In Figure 1A we show the estimated optimal probability of phenotypic switching, m̂opt, as a function of the three parameters of the model, N, θ and s. For N larger than some critical cutoff, we get m̂opt ≈ θ. (Note that since θ can be arbitrarily large but m can be at most 1, this relationship breaks down for largeθ; it is more accurately given by m̂opt ≈ 1−e−θ = θ− θ2/2! + θ3/3!-..., where 1−e−θ is the probability that the environment changes within one generation. The difference between θ and 1 − e−θis barely noticeable in the curve for θ = 0.1 in Figure 1A (where 1 − e−θ= 0.095), and is negligible for smaller θ.) This result agrees with the classical result (Cohen, 1966) confirmed for phenotypic switching through geometric mean fitness calculations (Kussell et al., 2005), namely that the optimum probability of expressing a trait is approximately equal to the probability that the trait is adaptive.
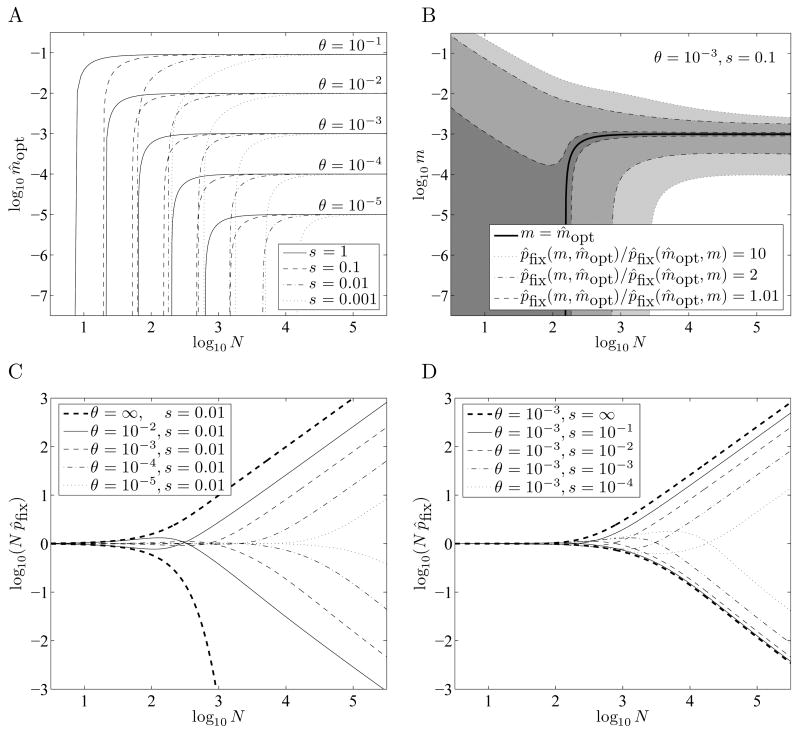
Figure 1.
Optimal switching probabilities and the extent to which they are favored. A: The estimated optimal switching probability m̂opt is approximately θ for N larger than a threshold that increases as s decreases. Note that on the curves for θ = 0.1, m̂opt is slightly less than 0.1 even for large N, but is approximately equal to 1 − e−0.1 = 0.095. B: A broad range of switching probabilities m are only slightly disfavored relative to m̂opt when N is less than the threshold for which m̂opt ≈ θ. C and D: These graphs compare p̂fix (0, θ, N, θ, s) and p̂fix (θ, 0, N, θ, s) for a variety of s, N, and θ. For small N the switching probability m = 0 has an advantage over the switching probability m = θ, but the latter dominates for large N. (In C, the fixation probabilities for θ = ∞ were computed as π(1) and 1 – π(N – 1): the fixation probabilities of type B and type A alleles in environment F, in which they have fitness 1 + s and 1, respectively.)
With smaller population sizes, bet-hedging alleles are not favored by natural selection. The minimum cutoff value of N depends on the parameters s andθ; the cutoff increases as s decreases and as θ decreases. Below this cutoff value of N, bet-hedging alleles are only mildly disfavored, however. In Figure 1B we show envelopes around m̂opt consisting of those m for which p̂fix (m, m̂opt) / p̂fix (m̂opt ,m)<R , for R = 1.01, 2, and 10, where R is a good measure of the extent to which one allele is favored over another, as described in Sections 2.6 and 4.1. These envelopes are rather broad for small N, and narrow as N increases. When m = 0, we refer to the ratio R =p̂fix (0,mopt ) / pfix (mopt ,0) as the “advantage of bet-hedging.”
In Figures 1C and 1D we compare the fixation probabilities for m = 0 and m =θ alleles, for a variety of parameters N, s, and θ. For small N, m = 0 is favored over m =θ, although only slightly. As N increases, m = θ becomes favored over m = 0 (provided s > 0 and θ> 0). Note in Figure 1C that for small sN, the switching probability m =θ can be disfavored relative to no switching. This approximate result is confirmed in Figures 4F and 4I. When sN is very small, switching phenotypes gives only a negligible advantage in environment F. But it gives a disadvantage in environment E that depends on mN, which can be larger. So the switching probability m =θ can be worse than m = 0 when sN is small. Of course, in such cases sufficiently small positive switching probabilities m < θ will be approximately neutral.
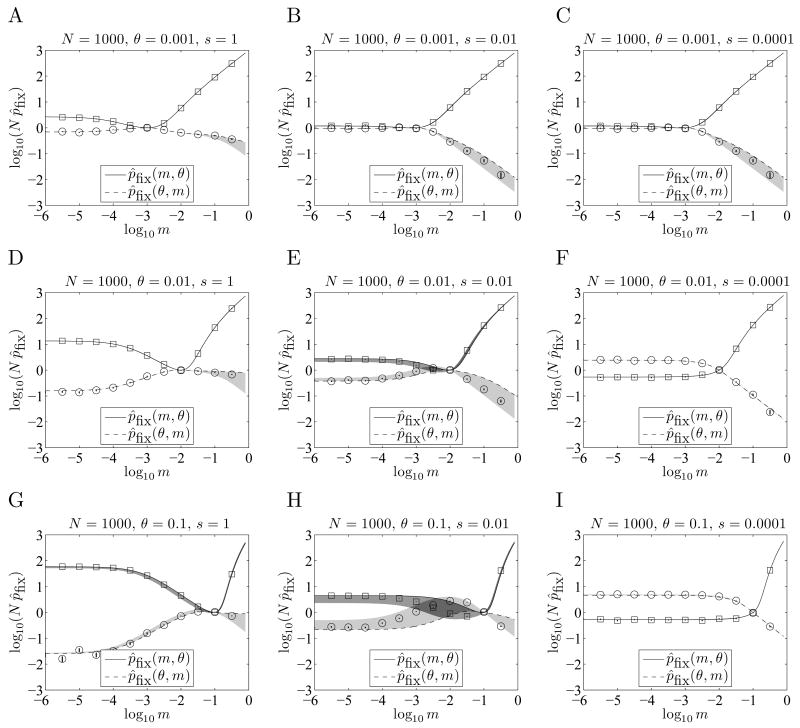
Figure 4.
Accuracy of fixation probability formula. Here we compare the approximate fixation probabilities computed with Equation 1 to Monte Carlo (MC) simulations for N = 1000. In parts A - I, θ varies by row, and s by column. The MC estimates for pfix (m, θ) and pfix (θ, m) are indicated by squares and circles respectively, and the vertical bars through these symbols indicate the standard error based on 106 trials. Equation 1 sometimes becomes inaccurate when θ and m are large, particularly for intermediate values of sN ≈ 10, for which selection is important but fairly slow. This is most noticeable in part H. Note that m̂opt ≈ θ for s = 1, but switching probabilities smaller than θ are favored for s = 0.0001. The gray shaded areas indicate the regions between p̂fix from Equation 1 and the heuristic bound for pfix described in Appendix C. The heuristic bound for pfix (m1, m2) is typically a lower-bound when m1 < m2 and an upper-bound when m2 < m1. (The shaded areas are often too narrow to be seen.)
In Appendix E we look at the minimum value of N more carefully as a function of θ and s, showing that the smallest value of N for which m̂opt > 0 is around
| (3.) |
But we are more interested in knowing for which parameters bet-hedging is strongly favored, say p̂fix (0,m̂opt, N,θ, s) / p̂fix (m̂opt,0, N,θ, s)>R for R = 10 or R = 100. We first consider the case of large θ, then the case of large s.
For fixed N and s > 0,p̂fix (0, m̂opt , N, θ, s) / p̂fix(m̂opt ,0, N, θ, s) increases as θ increases; it is bounded above by the ratio of the fixation probabilities of type B to type A alleles in environment F, which is given by π(1)/(1 – π (N – 1)), with π (i) as defined in Equation 2. This ratio simplifies to (1 + s) N – 1, providing the bound R≤(1 + s) N – 1 < (1 + s) N. Rearranging this inequality gives the bound N > log(R)/log(1 + s), and the bound
| (4.) |
The approximation (1 + s)N≈esN is good for large N when sN is not too large. It is accurate to within about two percent when N > 104 and sN < 20, so for N >104 and R up to about 109 we can use the simpler approximate bound
| (5.) |
Next we consider the case of large s. Let θmin (R, N, s) denote the minimum θ required for bet-hedging to have advantage R, as a function of N and s. We can numerically compute a lower-bound θmin (R, N, s) by setting y = 1 in our formula for p(i), corresponding toθmin (R, N,∞). It appears that
| (6.) |
gives a good approximation to θmin (N, R, ∞) for R between roughly 1 + 10 log(N)2/N and N 2 /100. Figures 2A and 2B show target ratios R plotted against the computed ratios p̂fix (0,m, N, θ, s) /p̂fix (m,0, N, θ, s), where, θ is given by Equation 6, s = ∞, and m = 1 – e−θ≈ mopt. Note that θ in Equation 6 is roughly proportional to R1/2 in Figure 2A, and to (R–1)1/2 in Figure 2B (using the approximation log(1 + x) ≈ x for small x), and that the advantage of bet-hedging is sensitive to θ in the ranges shown --- θ has not saturated, so no significantly smaller θ would allow as large an advantage. This range of R shown in Figures 2A and 2B corresponds to a range of θ from ~30log(N)/N 2 to ~0.1. Note also that although the condition y = 1 corresponds strictly to s = ∞, the computed ratios change very little for s down to about 10.
Figure 2.
Minimum conditions for bet-hedging to evolve in a finite population. R = p̂fix (0, m̂opt, N, θ, s) / p̂fix (m̂,0, N, θ, s) denotes the estimated advantage provided by using the optimal bet-hedging strategy over using no bet-hedging. A and B: When (from Equation 6), s = ∞, and m−1−e−θ ≈ m̂opt, the ratio p̂fix (0, m̂opt, N, θ, s) / p̂fix(m̂opt, 0, N, θ, s) , shown on the vertical axis, is approximately R. Curves in A are shown for R < N2/100, and in B for R > 1 + 10 log(N)2/N, roughly the range for which the approximation is accurate. (Note that B covers the range from R = 1.001 to R = 2.) C: Rectangular regions in which s and θ must fall to allow for a given advantage R; these are necessary but not sufficient conditions. For smaller R these rectangles are encroached on by the approximate equation for Nmin Computed estimates are shown for θ ≤ s. D: Estimated parameters θ and s for which R = 100, given as hyperbolas in log (s) and log(θ). Our computed estimates become less accurate for small sN and large θ, and are shown only for sN > 10. The curve for N = 108 is extrapolated using Equation 7.
Thus for bet-hedging to have an advantage of at least R, the parameters s and θ should satisfy Inequality 4 (or s > log(R)/N, for appropriate R and N) and θ>θ min (N, R, ∞), which can be approximated by Equation 6 when R is between 1 + 10 log(N)2/N and N2/100. They should also satisfy the inequality sθ> 2/N 2, although this provides no additional restriction when R is greater than about log(N)2. Figure 2C shows the regions of parameter space defined by these inequalities for various R, with N = 106. In Figure 2D we attempt to make these regions more precise for R = 100 and various N, by numerically computing estimates of θmin (N, R, s) for finite s.
The minimum rate of environmental change θ increases gradually as s decreases down to about 100/N, and increases sharply for smaller s. Our computed values p̂fix (m1, m2 , N, θ, s) can become noticeably inaccurate for sN < 10 when θ is large (see Fig. 4H). Because of this, we have limited these curves to s > 10/N and approximated the entire range for s > log(R)/N by a hyperbola in log(s) and log(θ) having asymptotes at s = log(R)/N and at θ given by Equation 6. Such a hyperbola is given generically by
| (7.) |
where the adjustable parameter g(N,R) was fit by eye as 0.12 log(N) for R = 100; we did not explore the dependence of g(N,R) on N or R in detail, but this simple estimate allows us to roughly extrapolate a curve for N = 108. This covers the range of the estimated effective population size Ne ≈ 107–108 for Saccharomyces, and is at the lower-end of the estimated effective population sizes for prokaryotes (Lynch and Conery, 2003; Wagner, 2005).
For bet-hedging to provide an organism with a 100-fold advantage in a population of effective size Ne = 108, necessary conditions are s > 4.6×10−8 (from Inequality 5) and θ> 3.5×10−8 (from Equation 6). From the approximations in Figure 2D it appears that a conservative sufficient condition is for both s > 10−6 and θ> 10−6 to hold, as the rectangle described by these two inequalities lies completely above the curve for N = 108.
Note that the persistent nature of both the environment and heritable phenotypes are important to our results. Consider the case of non-persistent switching in environment F: If each individual chooses phenotype B with probability θ, independently in each round of the Moran model, then the selective advantage of switching would scale as s θ The value of sθN required for switching to be favored by a ratio R would then scale as log(R) in environment F --- a much more stringent requirement than given above. This condition is relaxed somewhat if phenotype B persists for the duration of an individual’s life, and is further relaxed if phenotype B is heritable, which is the framework we consider. The example above corresponds to the case where a persistent change to environment F has been made. The results would again be different if environmental changes were nonpersistent, so that F occurred independently with probability θ each generation.
Note also that we do not claim that m2 = mopt is the optimal response to all switching probabilities m1, in the sense of maximizing pfix (m1,m2 ) / pfix (m2 ,m1 ) simultaneously for all m1 in the interval [0, 1]; In particular, we do not claim that m2 = mopt maximizes this ratio when m1 = 0. Based on computations using Equation 1, and Monte Carlo simulations, it appears that when m1 = 0 this ratio can be maximized for m2 much smaller than mopt --- decreasing m2 can lead to a modest decrease in pfix(0,m2) that is more than compensated for by a large decrease in pfix(m2,0). It should therefore be emphasized that the minimality of θ in Equation 6, and the curves in Figure 2C and 2D --- apply to the case of m2 = mopt and m1 = 0. An advantage R over no switching (m1 = 0) may be attainable for θ< θ min (R, N, s) by a suboptimal switching probability m2 < mopt. But such a switching probability m2 would be disfavored relative to mopt.
In Figure 2D, for the points calculated along the curves for N =105–107 we have m̂opt≈0.9θ when sN = 10, and θ > m̂opt>0.99θ when sN > 100. In Figure 1A, we see that for fixed s and N,m̂opt approaches θ sooner for larger θ. Thus we expect that mopt is very nearly θ (or 1 – e−θ when θ> 0.1) within the entire region satisfying s > 10−6 and θ> 10−6 described above for N = 108.
In Figure 3A, we show the surfaces defined by p̂fix (m1,m2) and p̂fix(m1,m2) for all m1 and m2, for N = 10000, θ = 0.001, and s = 0.1. In Figure 3B we show that for these parameters there is a unique m̂opt for which p̂fix (m,m̂opt )/ p̂fix (m̂opt ,m)≥1 for all m. Note that Figure 3A and other numerical computations suggest that for this particular model it may be sufficient to check optimality locally, i.e., if pfix (m2, m1)≥pfix (m1, m2) holds for all m2 in a small interval [m1 –ε, m1 + ε] around m1 (with ε > 0), then it also holds for all m2 in the entire interval [0, 1].
In Appendix D and Figure 4 we assess the accuracy of our approximations for pfix (m1, m2) , and the tightness of our heuristic bounds, using Monte Carlo simulations of the Moran model, and find good agreement for a wide range of parameters.
4. DISCUSSION
Using a finite population, we have confirmed the classical bet-hedging prediction that the optimum probability for employing a strategy is approximately equal to the probability that the strategy will be useful, provided the population size N is sufficiently large.
When bet-hedging appears not to be favored, or to be favored so weakly that it can barely be detected numerically. The approximate requirements for bet-hedging to be favored by a ratio of at least R (where R is between 2 and N 2/100), are that N > log(R)/ log(1+s) and . (Note that the former condition is roughly equivalent to N > log(R)/s when s < 0.1, and that the latter condition is obtained by rearranging Equation 6 and ignoring lower-order terms.) A general pattern in population genetics is that the balance between selection and drift is determined by the product sN, with values close to 1 being critical. For bet-hedging in finite populations, we have obtained two conditions relating to two such products, θN and sN, corresponding to the frequency of selection as well as its intensity when it does occur.
Our results differ both quantitatively and qualitatively from earlier work (Masel, 2005) that addressed the same problem using different approximations. In Masel (2005) the expectations of functions of certain random variables were approximated by functions of the expectations of the random variables (e.g., Equation A4 of Masel (2005)). Also, given that an environmental change occurs before fixation or loss of a B allele, the probability of having exactly i type B individuals at the time of the environmental change was assumed to be proportional to τ̄1i--- the expected time spent in state i before loss or fixation in a static environment. These approximations introduced several artifacts, such as p̂fix (m 1, m 2, N, θ, s) sometimes differing markedly from 1/N when m1 = m2 (e.g., in Fig 3C of Masel (2005)), and m̂opt decreasing from θ to 1/N as N increases (e.g., in Fig 2A of Masel (2005)). Our present formulation avoids these artifacts. Moreover we have confirmed the accuracy of our approximations for a broad range of parameters using Monte Carlo simulations.
Note that we have described a switch from environment E to environment F in the short term. Over the long term, the model could switch back-and-forth between these two environments, and so the scenario we analyze could arise repeatedly. Alternatively, it could be interpreted as a continued progression to novel environments: i.e., after the dynamics of the switch are complete, environment F can be renamed environment E, and some totally novel environment G plays the role of environment F. In this context, switching can be between suppressing and revealing variation (evolutionary capacitance), rather than between two distinct phenotypes, each of which has been honed by natural selection in an environment that the population has encountered many times before.
An ideal model for bet-hedging scenarios other than evolutionary capacitance would allow the environment to switch in both directions. We have considered an approximation in which environmental change events are sufficiently rare to be treated according to a separation of timescales, and hence switching in each of the two directions can be treated separately. Our conditions on θ, N and s indicate the likely parameter range under which bet-hedging can evolve, and provide a finite-population complement to infinite-population approximations of other bet-hedging scenarios. Our approach relies on several approximations, most critically that both the appearance of new alleles and changes in the environment are rare relative to all other processes. The sensitivity of our conclusions to these assumptions remains to be explored.
4.1 Fixation probabilities and evolutionary dynamics
The overall evolutionary dynamics are governed not just by fixation probabilities, but also by the rates with which different alleles appear by mutation or migration, and the speed with which different alleles replace the resident population. Suppose there are just two alleles, with switching probabilities m1 and m2, that the rates at which these appear are equal, and that the rates at which they appear and fix are small relative to the fixation time. Then the proportion of the time for which m2 alleles are fixed is approximately pfix(m1, m2)/( pfix(m1, m2) + pfix(m2, m1)) (see, e.g., Proulx and Day (2001)). But if m1 alleles appear much more often than m2 alleles, this can give m1 alleles an advantage over m2 alleles even when pfix (m2, m1) < pfix (m1, m2) --- the proportion of the time for which m2 alleles are fixed is given more generally by approximately
where r(mi, mj) is the rate of mutation from mj to mi. One might expect, for example, that alleles with m1 = 0, corresponding to loss of function of the modifier allele, could appear by mutation more often than alleles with m2 = mopt. The extreme scenario of unidirectional mutational degradation is examined in Masel et al. (2007), although under a somewhat different framework that includes environmental-dependent fitness but does not explicitly model stochastic switching.
In the more general case, if there is a discrete number K of known allele types and the probabilities associated with all mutational transitions can be estimated, then we can find the equilibrium solution of the corresponding system of K equations derived from the values of r(mj ,mi ) pfix (mi, mj ) . The solution yields the long-term behavior according to the stationary probability distribution of the system (Claussen and Traulsen, 2005; Fudenberg and Imhof, 2006; Fudenberg et al., 2006), including the long-term mean value of m. Note that this approach depends on the assumption that fixation events are rare relative to fixation times.
4.2 Evolutionary optimality in finite populations
Evolutionary theory includes many metrics that attempt to predict what will and will not evolve. The oldest is reproductive fitness (Haldane, 1932), normally defined as the expected number of offspring. The concept of inclusive fitness expands this to include the reproductive fitness of other individuals with similar genotypes (Hamilton, 1964). Bet-hedging theory shows that in a variable environment, geometric mean fitness is a better metric than arithmetic mean fitness (Seger and Brockman, 1987).
Both arithmetic and geometric mean fitnesses may vary according to allele frequency, for example when individuals interact, and hence break down as a clear metric. The concept of an evolutionary stable strategy addresses the problem of frequency-dependence by focusing only on the fitness of rare mutants. An ESS was originally defined as a strategy that once established, has higher fitness than any rare mutant (Maynard Smith and Price, 1973). To avoid reference to a particular definition of fitness, an ESS is often defined instead as a strategy that, once established, cannot be invaded by a rare mutant, where “invasion” means that the mutant will increase in frequency (Maynard Smith, 1982). The ESS approach has also been applied to variable environments, where invasion is predicted using a Lyapunov exponent as a refinement of geometric mean fitness when rare (Benton and Grant, 2000; Kussell et al., 2005; Metz et al., 1992; Rand et al., 1994; Tuljapurkar, 1982).
Unfortunately, the invasion-based definition of an ESS breaks down for finite populations, which can always be invaded at some (possibly very low) stochastic rate. This problem is not just theoretical: ESSs have been shown to fail to predict the behavior of finite populations (Fogel et al., 1998; Imhof et al., 2005). Attempts have been made to broaden metrics of environment-dependent (Masel, 2005) and frequency-dependent (Nowak et al., 2004) selection to finite populations. The approach we have followed (Masel, 2005) focuses strictly on fixation probabilities. This captures the long-term evolutionary dynamics of the system under the simplifying assumptions that mutation is both symmetric and rare relative to the timescale of fixation. The alternative ESSN formulation attempts to follow more closely the spirit of an ESS by using both local stability (invasion) and global stability (fixation) criteria (Nowak et al., 2004) (see Lessard (2005) for the relationship between these criteria and a regular ESS). This represents a compromise between strategies that represent the dynamics in the very long-term and strategies that are difficult to disrupt once present.
But while resistance to the invasion of rare mutants may be a well-defined measure for frequency-dependent selection in a fixed environment as in Nowak et al. (2004), it is not obvious what its analogue should be in the case of fluctuating environments. Even with constant selection within each environment, the initial spread of a mutant depends on the environment at the time. Requiring resistance to the initial spread of a mutant in each environment would be one possible analogue, but this condition will not be satisfied by any strategies in settings for which different phenotypes are favored in different environments. (For an infinite population in an ergodic environment, the expected long term growth rate does not depend on the initial environment, but for a finite population the initial environment can be critical.) Our definition of optimality in a stochastic system, with its focus exclusively on replacement probabilities, is more broadly applicable than a definition that also considers invasion when rare. These definitions are not equivalent: for example we expect the existence of multiple ESSNs to be more common.
The approach to optimality we use is appropriate if the rules and frequencies specifying the range of environments stay constant and known over a long period of time. To apply it in its entirety by calculating the stationary probability distribution of states, it is necessary to have an estimate of the relative frequencies of mutations of different types, as discussed above. If all mutation rates are equal, then they can be neglected, and the state of the system that is more frequent than any other can be calculated as described in Section 4.1.
Our algebraic approximations to fixation probabilities complement prior work in which the risk of extinction is estimated by considering the variance of the growth-rate in an infinite population (Wolf et al., 2005), or in which stochastic simulations are used to estimate extinction probabilities of finite populations (Kussell et al., 2005; Menu et al., 2000; Wolf et al., 2005).
4.3 Autocorrelated environments
Both frequency-dependent and environment-dependent selection can provide an advantage for stochastic (mixed) strategies over fixed (pure) strategies. The phenotypic switching we consider is akin to a mixed strategy, where the pure strategies are phenotypes A and B. But here, in a fluctuating environment, we consider first-order Markov strategies, in which the probabilities of an offspring adopting a particular strategy depends on the strategy held by its parent, as opposed to the zeroth-order switching in which each individual makes an independent decision as to its strategy. This matches the first-order Markov dynamics of our model of environmental change, which produces what is sometimes referred to as an autocorrelated (Menu et al., 2000) or temporally patchy environment (Jablonka et al., 1995), as opposed to the completely random (zeroth-order) environment in, e.g., Cohen (1966).
The ability to sense the environment, even imperfectly, can allow for higher growth-rates (Jablonka et al., 1995; Kussell and Leibler, 2005; Wolf et al., 2005). But stochastic strategies may be preferred to sensing when to the environment changes very infrequently, due to the metabolic cost of sensing (Avery, 2006; Kussell et al., 2005; Kussell and Leibler, 2005; Stumpf et al., 2002; Thattai and van Oudenaarden, 2004; Wolf et al., 2005). Sensing may also offer little advantage when the environment changes very frequently and there is a lag between sensing and phenotypic switching (Jablonka et al., 1995). Note that an organism’s awareness of its own current phenotype provides it with indirect information about an autocorrelated environment, since selection in the current environment has sculpted the frequencies of the phenotypes. First-order phenotypic switching exploits this introspection implicitly, since the probability of an offspring adopting a particular phenotype depends on the phenotype of its parent.
4.4 Variable population size
The mathematical approach used here works only with constant population sizes, whereas changes in population size and resulting density-dependent dynamics may be critical in real populations. More realistic ecological scenarios such as this can be addressed using simulations (Benton and Grant, 2000; Menu et al., 2000). In such cases, our optimality criteria can still be applied by numerical estimation of fixation and counterfixation probabilities as an alternative to numerical estimation of the Lyapunov exponent (Benton and Grant, 2000) or short-term persistence (Menu et al., 2000).
Acknowledgments
We thank L. Venable and S. Lindquist for helpful discussions. J.M. was supported by the BIO5 Institute at the University of Arizona and National Institutes of Health grant GM076041. J.M. is a Pew Scholar in the Biomedical Sciences and an Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellow.
APPENDIX A: BAND DIAGONAL STRUCTURE OF FULL MARKOVIAN SYSTEM
The state space consists of all pentuples of nonnegative integers (e, i, j, k, l) with e = 1 or 2 and i + j + k + l = N --- e indexes the environment, and i, j, k, and l represent the number of individuals of type B1, A1, B2, and A2 respectively. There are two choices for e, and there are choices for (i, j, k, l) by the “stars and bars” trick for counting compositions --- see, e.g., Stanley (1997). The state space therefore has size ≈N3 / 3. The equations corresponding to states with i + k = 0 or j + l = 0 can be eliminated, since in these cases one modifier allele is already lost, but there are only 4(N + 1) such states.
In a fixed environment there are states for which i, j, k, l > 0. Each of these states can move to any of the others in fewer than N steps of the Moran model, in either direction. If the upper (resp. lower) bandwidth of the transition matrix of the Moran model were b, then at most bN states would be accessible within N forward (resp backwards) steps from each of these states. Thus we have bN ≥ ≈ N3/6, so b is of order at least N 2, even for a single environment. This bound is attainable: the state ordering defined by (i, j, k, l) > (i′, j′, k′, l′) if i(N+1)2 + j(N + 1) + k > i′(N + 1)2 + j′(N + 1) + k′ gives bandwidth of (N + 1)2 for a single environment. Interleaving states ordered this way for two environments doubles this bandwidth, so is still of order N2.
APPENDIX B: REDUCTION TO A SINGLE TRIDIAGONAL SYSTEM IN ENVIRONMENT E
Let q(i, j) be the probability that there are exactly j individuals of type A2 at the time of the next environmental change event, given there are initially i individuals of type A2. For fixed j, the N + 1 values q(i, j) are the solution to the following tridiagonal system of linear equations:
where r(i, j)=1−e−θ/N for i=j and 0 otherwise, and λi and μi are as defined in Section 2.4.
The only values of q(i, j) required for our purposes are q(1, j) for j = 1, …, N. As formulated above, we recover only one value q(1, j) from each tridiagonal system; this leads to a total computational time of order N2, which is potentially problematic for realistically large population sizes. Fortunately, the total computational cost can be reduced to order N, as described below.
The (N−1) × (N−1) matrix Q with i,j-th entry q(i, j) satisfies the matrix equation AQ=R, where A is the (N−1) × (N−1) tridiagonal matrix with a(i,i+1)= e−θ/N λi for i=1,..., N−2, a(i,i) = e−θ/N (1−λi−μi)−1 for i=1,..., N−1, and a(i−1,i) = e−θ/N μi for i = 2,..., N−1; and R is the (N−1) × (N−1) diagonal matrix with diagonal entries r(i,i) = 1− e−θ/N for i=1,..., N−1. The j-th tridiagonal system above solves for the j-th column of the matrix Q. But to compute pfix (m1 ,m2 , N, θ, s) we require only the N−1 entries q(1, j), i.e. the first row of Q. Note that R is just e−θ/N −1 times the identity matrix I, so Q=A−1 /( e−θ/N −1) . Since matrix inverses are two sided, Q and A commute and we have QA=R . Transposing both sides gives AtQt = (QA)t = Rt = R . Thus we can solve for the i-th row q of Q, which is the (transpose of the) i-th column of Qt, by solving the single tridiagonal system Atqt = r , where r is the i-th column of the matrix R. For i =1 this amounts to solving the following tridiagonal system:
We also require q(1, N) --- the probability that a single m2 fixes by drift before an environmental change. Consider the last time the system has N − 1 individuals of type A2, conditioned on either fixation of A2 or an environmental change while in state N − 1 taking place. The relative probabilities of these two outcomes are e−θ/N λN−1 (for fixation) to 1 − e−θ/N (for environmental change). Thus we have .
We can similarly compute the probability q(1,0) that a single A2 is lost by drift before an environmental change by , or by , but this is not needed for computing , since p(0) = 0.
APPENDIX C: APPROXIMATION THAT SUCCESSFUL SELECTIVE SWEEPS OCCUR INSTANTANEOUSLY
If at some initial time there are i type B individuals, with i > 1, y overestimates the probability that the entire population is ultimately descended from any particular one of these individuals. But in practice, the approximation 1−π(i)≈(1−y)i is quite good for small i (see, e.g., Orr and Betancourt (2001)) --- even though the probability that any given type B variant takes over is overestimated, by treating the failure of each type B variant to take over as independent, one arrives at approximately the correct probability that none of them takes over.
Our use of this approximation differs somewhat in that we are considering type B variants that appear by phenotypic switching, and not just from standing variation. The idea here is that the probability that the chain jumps directly to an absorbing state at some step before reaching an absorbing state by drift should be approximately correct, although the probability that this happens at any given point may be an overestimate. We would also like the relative probabilities of jumping to the absorbing states N and 0 to be accurate.
If the Markov chain is currently in state i, the probability of jumping directly to state N is m2yi/N, and the probability of jumping directly to state 0 is m1y(N−i) /N. The ratio of these probabilities, m2 i / (m1(N − i)) does not depend on y. But overestimating the probability of a jump from state i can introduce a bias if, during the sojourn that is being collapsed into the single jump step, the expected relative rates of appearance of new B2 and B1 variants changes from m2i/(m1(N−i)). As we do not consider back-switching from type B to type A, this can be an issue if the switching from A1 to B1 or from A2 to B2 begins to saturate. But this should have only a mild effect when the sojourn time τ is such that (1− (1− m2)τ)/(1 − (1 − m1)τ) ≈ m2 / m1 (or when m1 = 0); this is the case when (1− m2)τ and (1 − m1)τ are still approximately linear as functions of τ, say for τm1< 0.1 and τm2 < 0.1.
Ignoring subsequent phenotypic switching, when s = 0 the expected sojourn time τ̄ of a type B variant destined for fixation is N generations; this decreases for s > 0, and for sN > 2 or so it is approximately 2 log(sN + 0.577) / s generations (Hermisson and Pennings, 2005). But the conditions τ̄m1 < 0.1 and τ̄m2 < 0.1 are by themselves much too conservative, since the bias enters mainly through the jump moves, which happen rarely for small θ since then the probability of environment F being reached is small. (The probability of the chain being absorbed by a jump move to state N can be computed by changing the initial condition p(N) = 1 to p(N) = 0 in the triadiagonal system above.) Also, regardless of θ, when Ns is small enough so that y ≈1/N, the bias is again small, since y no longer overestimates the absolute probability that any particular type B variant eventually takes over the population.
Note that our values p(i) are exact in the case of y = 1; this corresponds to the limit as s approaches infinity, since y ≈ s/(s + 1) for large N. By setting y = 1 when evaluating Equation 1, we can compute bounds on fixation probabilities for finite s.
Because such bounds can be weak for smaller s, we also computed heuristic (i.e., not rigorously proven) bounds by modifying the algorithm for computing p̂fix (m1, m2) as follows. In environment F (but not E), we decrease the larger of m1 and m2: when m2 > m1 we replace m2 by m1 × (1 − (1 − m2)T)/(1 − (1 − m1)T), and when m1 > m2 we replace m1 by m2 × (1 − (1 − m1)T)/(1 − (1 − m2)T). Here T is half of the mean sojourn time τ̄. We computed τ̄ exactly, as in Eq. 2.159 of Ewens (2004) --- this amounts to solving two tridiagonal systems, and can be done in order N time --- but similar bounds are obtained using the approximations for τ̄ given above. The factor of one half in T = τ̄/2 is a conservative way to boost type B variants that appear earlier in the sojourn, since these should have an advantage over those that appear later.
APPENDIX D: ASSESSING ACCURACY WITH MONTE CARLO SIMULATIONS
We assessed the accuracy of our approximations for pfix(m1, m2 ), and the tightness of our heuristic bounds, using Monte Carlo simulations of the Moran model. In each run of the simulation, all four types A1, A2, B1, and B2 were tracked until either both A1 and B1 were lost, or both A2 and B2 were lost. The population began with a single individual of type A2 and with N − 1 individuals of type A1, and was in environment E. We also did Monte Carlo simulations using the alternate model for environment E, in which there are only two types, A1 and B1, with fitnesses 1 − m1 and 1 − m2 respectively; in environment F all four types were again explicitly tracked.
In Figure 4 we assess the accuracy of the values we compute for p̂(m1, m2, N, θ, s). Here we fix N = 1000 (small enough to allow for accurate Monte Carlo estimates), and compare p̂fix(m, θ, N, θ, s)to p̂fix(θ, m, N, θ, s) for various values of θ and s to see how the accuracy of depends on m, θ, s. Each Monte Carlo estimate used 106 trials, with the standard error estimated as , where f is the fraction of trials that ended in fixation of type B variants. Note that the discrepancy between p̂fix(m1, m2, N, θ, s) and the Monte Carlo estimate is usually very small, and is most noticeable when m is close to 1. Note also that when there is a noticeable discrepancy, to within the standard error the Monte Carlo estimates appear to be bracketed between p̂fix (m1, m2, N, θ, s) and our heuristic bound from section 2.5, which is a lower bound when m2 > m1 and an upper bound when m2 < m1.
We performed the Monte Carlo simulations using two models for environment E, as described in section 2.2. The results shown are for the model in which type B variants are replaced immediately in environment E, but aside from a slight difference when m > 0.1, the results were not noticeably different. This suggests that when type B variants in environment E are not immediately replaced, but have fitness 0, it is not critical to explicitly account for type B variants that preexist at the time of the environmental change. This is because they tend to reappear in approximately the right proportions in the first generation following the environmental change.
APPENDIX E: MINIMUM POPULATION SIZE FOR BET-HEDGING
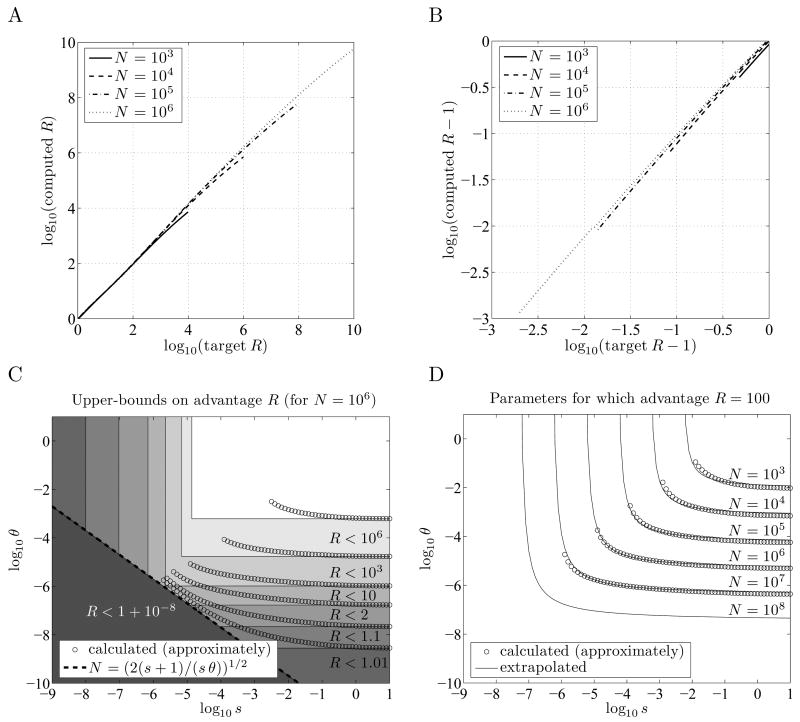
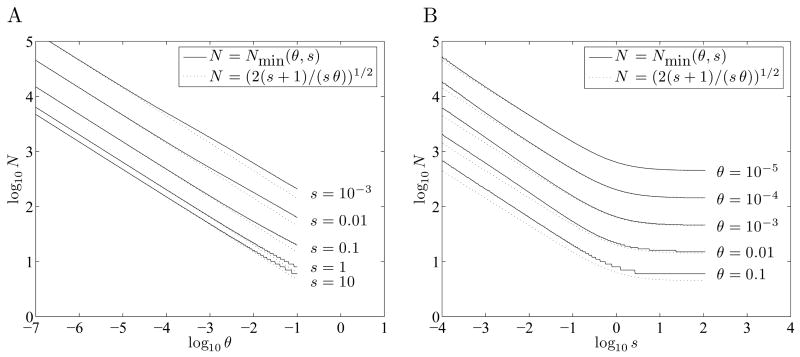
In Figures 5A and 5B we look at the minimum value of N as a function of θ and s, showing the smallest value of N for which m̄opt > 0. Since we are computing fixation probabilities numerically, we cannot distinguish between m̄opt being exactly zero, or just being very nearly zero. But clearly mopt is exactly zero when θ = 0 or when s ≤ 0, so by the continuity of fixation probabilities, for fixed N, m = 0 will be nearly optimal for sufficiently small positive θ and s. Figures 5A and 5B show the smallest value of N for which p̄fix(0, m̄opt, N, θ, s) / p̄fix (m̄opt, 0, N, θ, s) > 1 + 10−8; we refer to this value of N as Nmin.
Figure 5. Minimum population sizes for bet-hedging.
R = p̂fix (0, m̂opt, N, θ, s) / p̂fix(m̂opt, 0, N, θ, s) denotes the estimated advantage provided by using the optimal bet-hedging strategy over using no bet-hedging. A and B: Nmin the smallest N for which R > 1 + 10−8, is approximately .
Judging from Figures 5A and 5B, we have
| (8.) |
with this approximation underestimating Nmin somewhat for smaller s and θ. Note that Equation 8 is roughly the same as when s < 0.1, but stabilizes at as s goes to infinity. As our computations were limited to N ≤ 107, the precise choice of 1 + 10−8 in defining Nmin may mask some effects of order 1/N here.
Note that to have R > 1 + 10−8 we should have s > 10−8/N, and that this condition is not implied by Equation 8, which saturates for large s but not for largeθ. Thus Equation 8 may underestimate Nmin when s is extremely small, but the critical value s ≈ 10−8/N falls well below the range of parameters we are most interested in.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
LITERATURE CITED
- Abraham JM, Freitag CS, Clements JR, Eisenstein BI. An invertible element of DNA controls phase variation of type-1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985;82:5724–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreadis TG. Observations on installment egg hatching in the brown salt marsh mosquito, Aedes cantator. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1990;6:727–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery SV. Microbial cell individuality and the underlying sources of heterogeneity. Nat Rev Micro. 2006;4:577. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban NQ, Merrin J, Chait R, Kowalik L, Leibler S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science. 2004;305:1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.1099390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell JR, Bohan DA, Shaw EM, Weyman GS. Ballooning dispersal using silk: world fauna, phylogenies, genetics and models. Bull Entomol Res. 2005;95:69–114. doi: 10.1079/ber2004350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton TG, Grant A. Evolutionary fitness in ecology: Comparing measures of fitness in stochastic, density-dependent environments. Evol Ecol Res. 2000;2:769–789. [Google Scholar]
- Claussen JC, Traulsen A. Non-Gaussian fluctuations arising from finite populations: Exact results for the evolutionary Moran process. Phys Rev E. 2005;71:0251011–4. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.71.025101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. Optimizing reproduction in a randomly varying environment. J Theor Biol. 1966;12:119–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump ML. Variation in propagule size as a function of environmental uncertainty for tree frogs. Am Nat. 1981;117:724–737. [Google Scholar]
- Ewens WJ. Theoretical Introduction. Springer-Verlag; New York: 2004. Mathematical Population Genetics I. [Google Scholar]
- Fell PE. Deep diapause and the influence of low temperature on the hatching of the gemmules of Spongilla lacustris (L) and Eunapius fragilis (Leidy) Invertebr Biol. 1995;114:3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fogel GB, Andrews PC, Fogel DB. On the instability of evolutionary stable strategies in small populations. Ecol Model. 1998;109:283. doi: 10.1016/s0303-2647(97)00050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fudenberg D, Imhof LA. Imitation processes with small mutations. Journal of Economic Theory. 2006;131:251. [Google Scholar]
- Fudenberg D, Nowak MA, Taylor C, Imhof LA. Evolutionary game dynamics in finite populations with strong selection and weak mutation. Theor Popul Biol. 2006;70:352–363. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2006.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie JH. Some properties of finite populations experiencing strong selection and weak mutation. The American Naturalist. 1983;121:691–708. [Google Scholar]
- Golub GH, van Loan CF. Matrix Computations. John Hopkins University Press; Baltimore: 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hairston NG, Munns WR. The timing of copepod diapause as an evolutionarily stable strategy. Am Nat. 1984;123:733–751. [Google Scholar]
- Haldane JBS. The causes of evolution. Cornell University Press; Ithaca, N.Y: 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Hallet B. Playing Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde: combined mechanisms of phase variation in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2001;4:570–581. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton WD. Genetical evolution of social behaviour I. J Theor Biol. 1964;7:1–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(64)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson IR, Owen P, Nataro JP. Molecular switches - the ON and OFF of bacterial phase variation. Mol Microbiol. 1999;33:919–932. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermisson J, Pennings PS. Soft sweeps: molecular population genetics of adaptation from standing genetic variation. Genetics. 2005;169:2335–2352. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.036947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imhof LA, Fudenberg D, Nowak MA. Evolutionary cycles of cooperation and defection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:10797–10800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502589102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonka E, Oborny B, Molnar I, Kisdi E, Hofbauer J, Czaran T. The adaptive advantage of phenotypic memory in changing environments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B-Biol Sci. 1995;350:133–141. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1995.0147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kussell E, Kishony R, Balaban NQ, Leibler S. Bacterial persistence: A model of survival in changing environments. Genetics. 2005;169:1807–1814. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.035352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kussell E, Leibler S. Phenotypic diversity, population growth, and information in fluctuating environments. Science. 2005;309:2075–2078. doi: 10.1126/science.1114383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard S. Long-term stability from fixation probabilities in finite populations: New perspectives for ESS theory. Theor Popul Biol. 2005;68:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2005.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M, Conery JS. The origins of genome complexity. Science. 2003;302:1401–1404. doi: 10.1126/science.1089370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin KLM. Ready and waiting: Delayed hatching and extended incubation of anamniotic vertebrate terrestrial eggs. Am Zool. 1999;39:279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Masel J. Evolutionary capacitance may be favored by natural selection. Genetics. 2005;170:1359–1371. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.040493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masel J, Bergman A. The evolution of the evolvability properties of the yeast prion [PSI+] Evolution. 2003;57:1498–1512. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2003.tb00358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masel J, King OD, Maughan H. The loss of adaptive plasticity during long periods of environmental stasis. Am Nat. 2007;169:38–46. doi: 10.1086/510212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard Smith J. Evolution and the theory of games. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard Smith J, Price GR. Logic of animal conflict. Nature. 1973;246:15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Menu F, Roebuck JP, Viala M. Bet-hedging diapause strategies in stochastic environments. Am Nat. 2000;155:724–734. doi: 10.1086/303355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz JAJ, Nisbet RM, Geritz SAH. How should we define 'fitness' for general ecological scenarios? Trends Ecol Evol. 1992;7:198–202. doi: 10.1016/0169-5347(92)90073-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris JR. Markov Chains. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak MA, Sasaki A, Taylor C, Fudenberg D. Emergence of cooperation and evolutionary stability in finite populations. Nature. 2004;428:646–650. doi: 10.1038/nature02414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr HA, Betancourt AJ. Haldane's sieve and adaptation from the standing genetic variation. Genetics. 2001;157:875–884. doi: 10.1093/genetics/157.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippi T. Bet-hedging germination of desert annuals: beyond the first year. Am Nat. 1993;142:474–487. doi: 10.1086/285550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proulx SR, Day T. What can invasion analyses tell us about evolution under stochasticity in finite populations? Selection. 2001:1–2. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rand DA, Wilson HB, McGlade JM. Dynamics and evolution: evolutionarily stable attractors, invasion exponents and phenotype dynamics. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B-Biol Sci. 1994;343:261–283. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts HA, Feast PM. Fate of seeds of some annual weeds in different depths of cultivated and undisturbed soil. Weed Res. 1972;12:316–324. [Google Scholar]
- Robson AJ, Bergstrom CT, Pritchard JK. Risky business: sexual and asexual reproduction in variable environments. J Theor Biol. 1999;197:541–556. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1998.0894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger J, Brockman HJ. What is bet-hedging? In: Harvey PH, Partridge L, editors. Oxford Surveys in Evolutionary Biology. Oxford University Press; 1987. pp. 182–211. [Google Scholar]
- Sniegowski PD, Murphy HA. Evolvability. Curr Biol. 2006;16:R831–R834. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.08.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley RP. Enumerative Combinatorics. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf MPH, Laidlaw Z, Jansen VAA. Herpes viruses hedge their bets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:15234–15237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232546899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumby P, Smith MCM. Phase variation in the phage growth limitation system of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) J Bacteriol. 2003;185:4558–4563. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.15.4558-4563.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanton CJ, Weise SF. Integrated weed management - the rationale and approach. Weed Technol. 1991;5:657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Thattai M, van Oudenaarden A. Stochastic gene expression in fluctuating environments. Genetics. 2004;167:523–530. doi: 10.1534/genetics.167.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- True HL, Lindquist SL. A yeast prion provides a mechanism for genetic variation and phenotypic diversity. Nature. 2000;407:477–483. doi: 10.1038/35035005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuljapurkar S. Delayed reproduction and fitness in variable environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:1139–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuljapurkar SD. Population dynamics in variable environments. III Evolutionary dynamics of r-selection. Theor Popul Biol. 1982;21:141–165. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. Energy constraints on the evolution of gene expression. Mol Biol Evol. 2005;22:1365–1374. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msi126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf DM, Vazirani VV, Arkin AP. Diversity in times of adversity: probabilistic strategies in microbial survival games. J Theor Biol. 2005;234:227–253. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2004.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]