Abstract
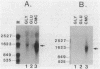
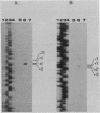
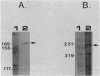
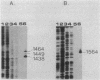
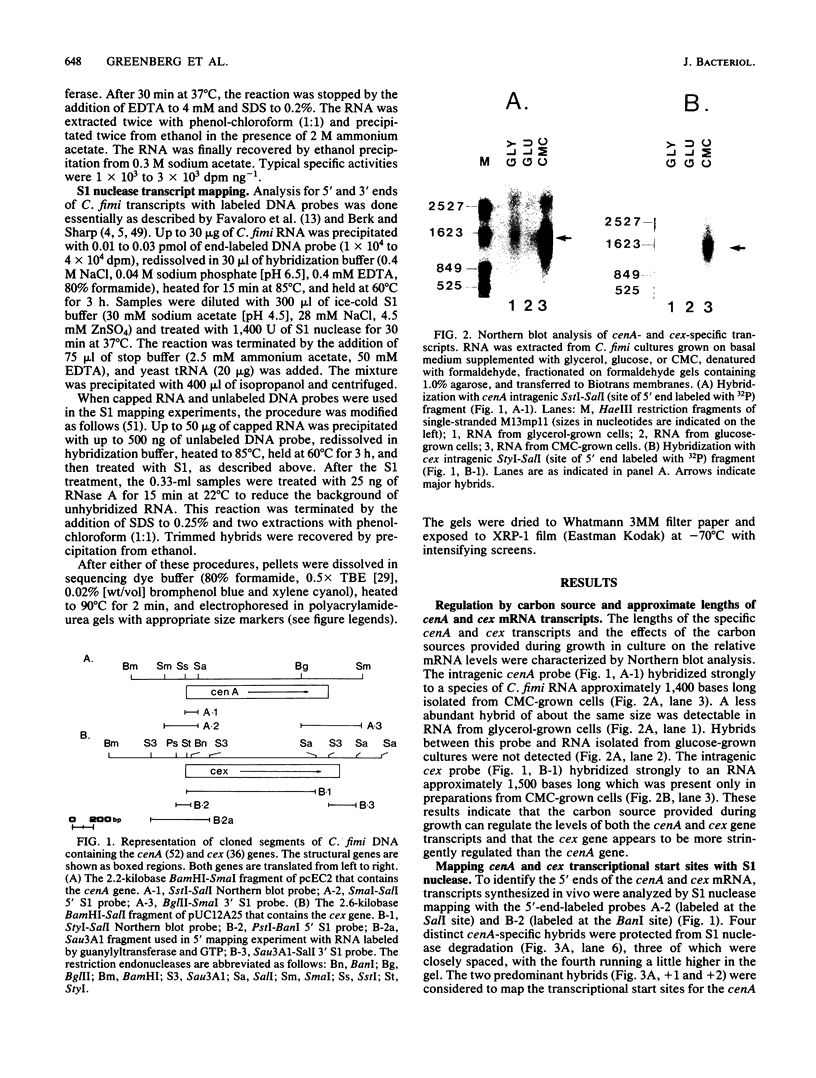
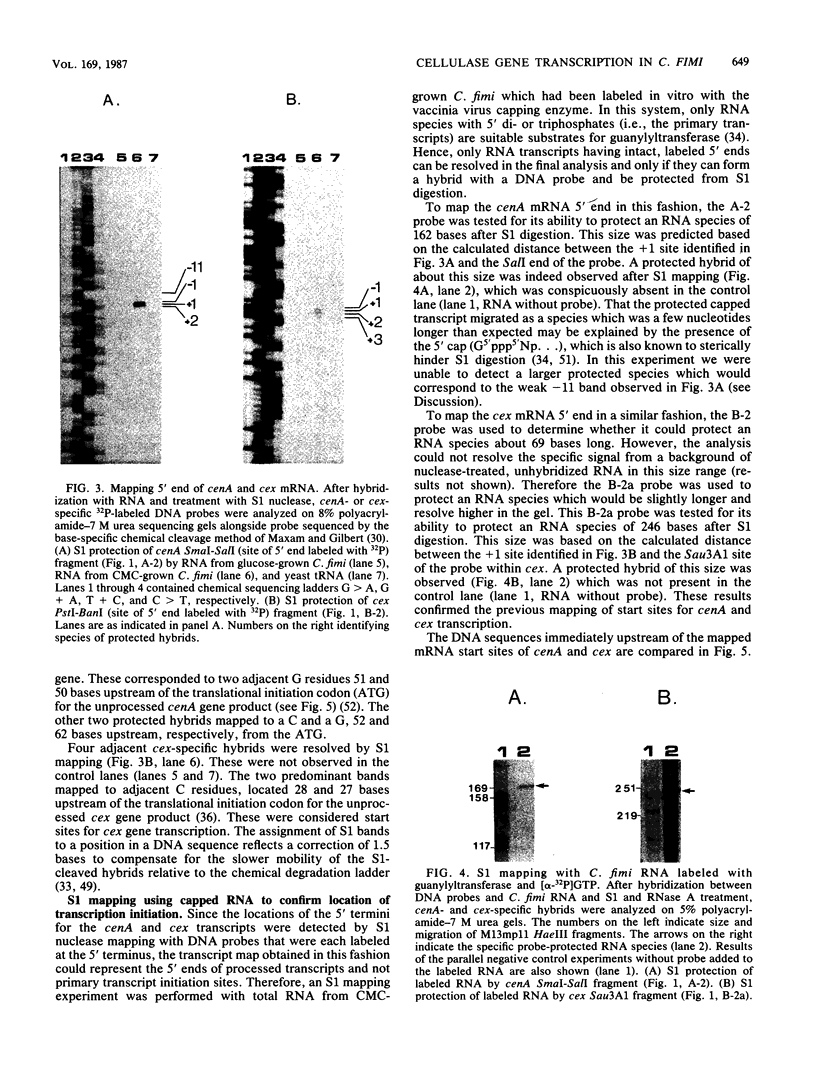
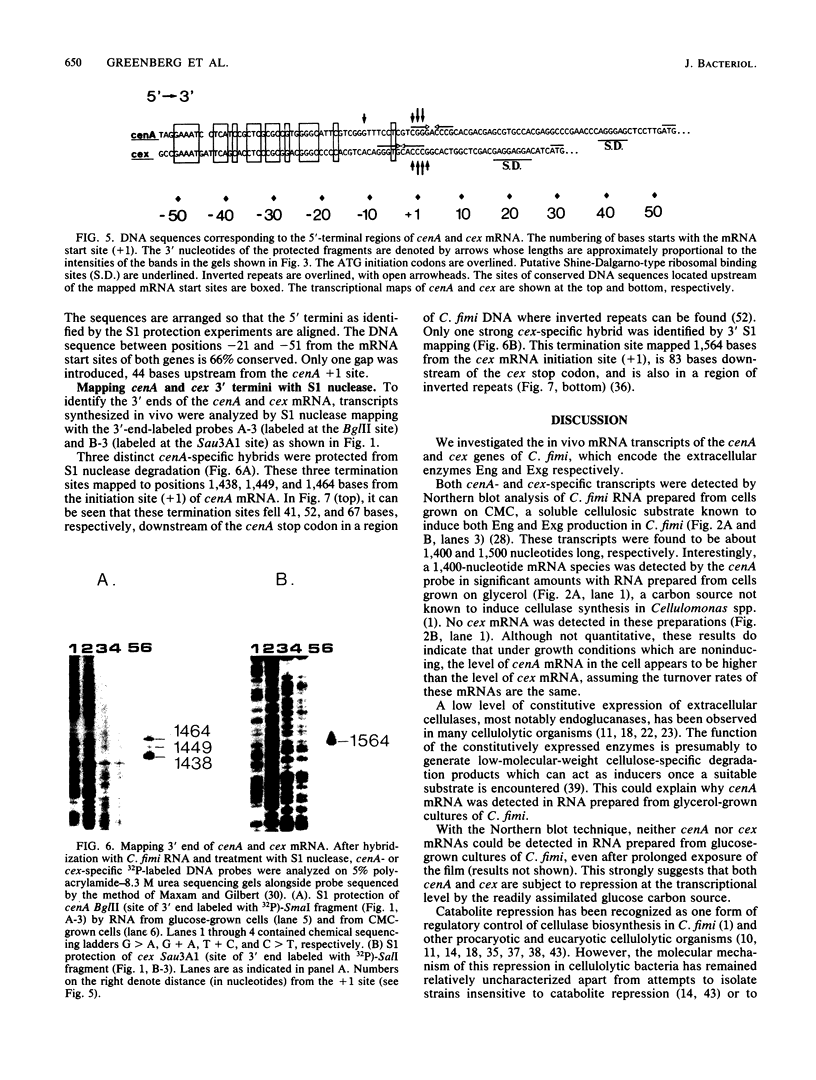
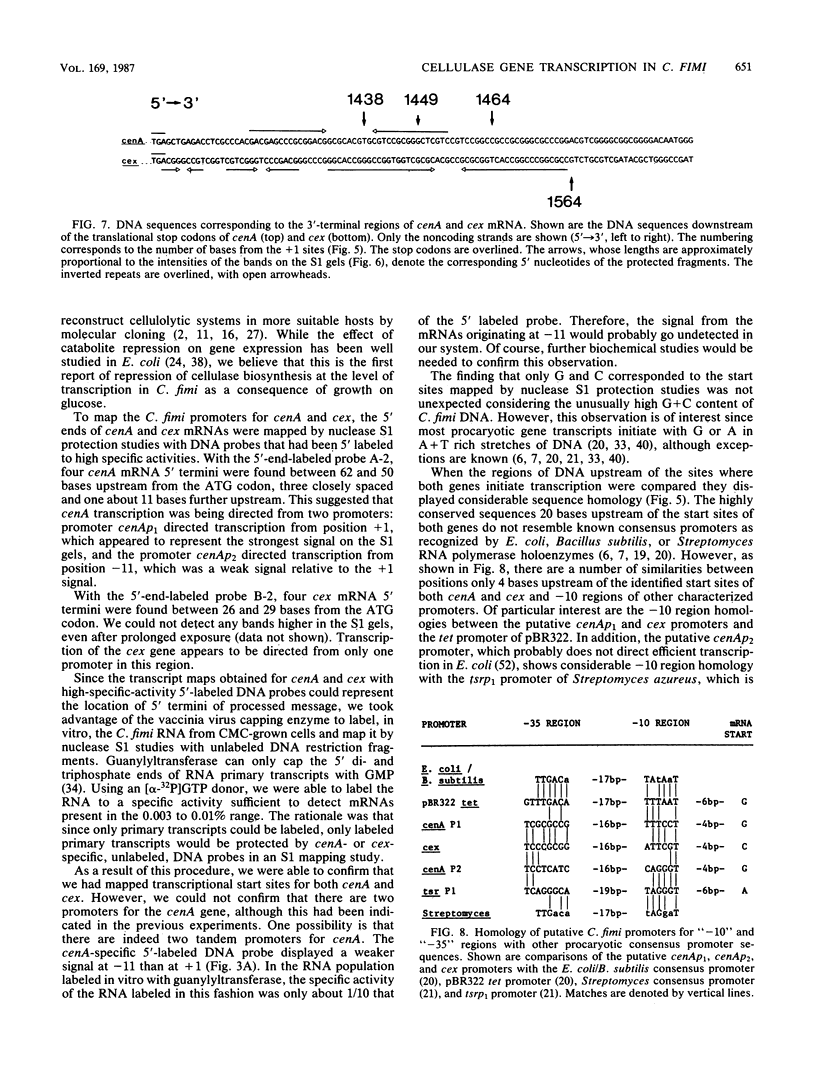
We characterized the in vivo transcripts of two Cellulomonas fimi genes, the cenA gene, which encodes an extracellular endo-beta-1,4-glucanase (EC 3.2.1.4) and the cex gene, which encodes an extracellular exo-beta-1,4-glucanase (EC 3.2.1.91). By Northern blot analysis, cenA mRNA was detected in C. fimi RNA preparations from glycerol- and carboxymethyl cellulose-grown cells but not from glucose-grown cells. In contrast, cex mRNA was detected only in the preparations from carboxymethyl cellulose-grown cells. Therefore, the transcription of these genes is subject to regulation by the carbon source provided to C. fimi. By nuclease S1 protection studies with unique 5'-labeled DNA probes and C. fimi RNA isolated in vivo, 5' termini were found 51 and 62 bases before the cenA translational initiation codon and 28 bases before the cex translational initiation codon. S1 mapping with unlabeled DNA probes and C. fimi RNA which had been isolated in vivo but which had been 5' labeled in vitro with guanylyltransferase and [alpha-32P]GTP confirmed that true transcription initiation sites for cenA and cex mRNA had been identified. Comparative analysis of the DNA sequences immediately upstream of the initiation sites of the cenA and cex mRNAs revealed a 30-base-pair region where these two sequences display at least 66% homology. S1 mapping was also used to locate the 3' termini of the cenA and cex transcripts. Three 3' termini were found for cenA messages, whereas only one 3' terminus was identified for cex mRNA. The transcripts of both genes terminate in regions where their corresponding DNA sequences contain inverted repeats.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Cohen S. N. Nucleotide sequences encoding and promoting expression of three antibiotic resistance genes indigenous to Streptomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):26–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00327505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Janssen G. R., Ward J. M. Cloning and analysis of the promoter region of the erythromycin resistance gene (ermE) of Streptomyces erythraeus. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béguin P., Rocancourt M., Chebrou M. C., Aubert J. P. Mapping of mRNA encoding endoglucanase A from Clostridium thermocellum. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):251–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00331645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg L., Fedorcsak I., Solymosy F. Diethyl pyrocarbonate in nucleic acid research. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;16:189–262. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60758-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennington G., Neubauer D., Stutzenberger F. Cellulase biosynthesis in a catabolite repression-resistant mutant of Thermomonospora curvata. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):201–204. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.201-204.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Langsford M. L., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Mode of action and substrate specificities of cellulases from cloned bacterial genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10455–10459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme M. A., Stranks D. W. Induction and the regulation of production of cellulase by fungi. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):469–470. doi: 10.1038/226469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme M. A., Stranks D. W. Regulation of cellulase production by Myrothecium verrucaria grown on non-cellulosic substrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):145–155. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D., Bicknell I. Decay of messenger ribonucleic acid from the lactose operon of Escherichia coli as a function of growth temperature. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. C., Jr, Young E. T., 2nd, Epstein R. H., Krisch H. M., Mattson T., Bolle A. Regulation of the synthesis of the T4 DNA polymerase (gene 43). Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. 5' end labeling of RNA with capping and methylating enzymes. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:253–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisizawa T., Suzuki H., Nisizawa K. Catabolite repression of cellulase formation in Trichoderma viride. J Biochem. 1972 Jun;71(6):999–1007. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G., Goh S. H., Warren R. A., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr Structure of the gene encoding the exoglucanase of Cellulomonas fimi. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart B. J., Leatherwood J. M. Derepressed synthesis of cellulase by Cellulomonas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):609–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.609-615.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle D. J., Kilburn D. G., Warren R. A., Miller R. C., Jr Molecular cloning of a Cellulomonas fimi cellulose gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Hummel H., Jarsch M., Bär U., Böck A. Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2459–2479. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W. K., Gerhard B., Guo Z. M., Kilburn D. G., Warren A. J., Miller R. C., Jr Characterization and structure of an endoglucanase gene cenA of Cellulomonas fimi. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C. Attenuation in the control of expression of bacterial operons. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):751–758. doi: 10.1038/289751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wezenbeek P. M., Hulsebos T. J., Schoenmakers J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the filamentous bacteriophage M13 DNA genome: comparison with phage fd. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):129–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]