Abstract
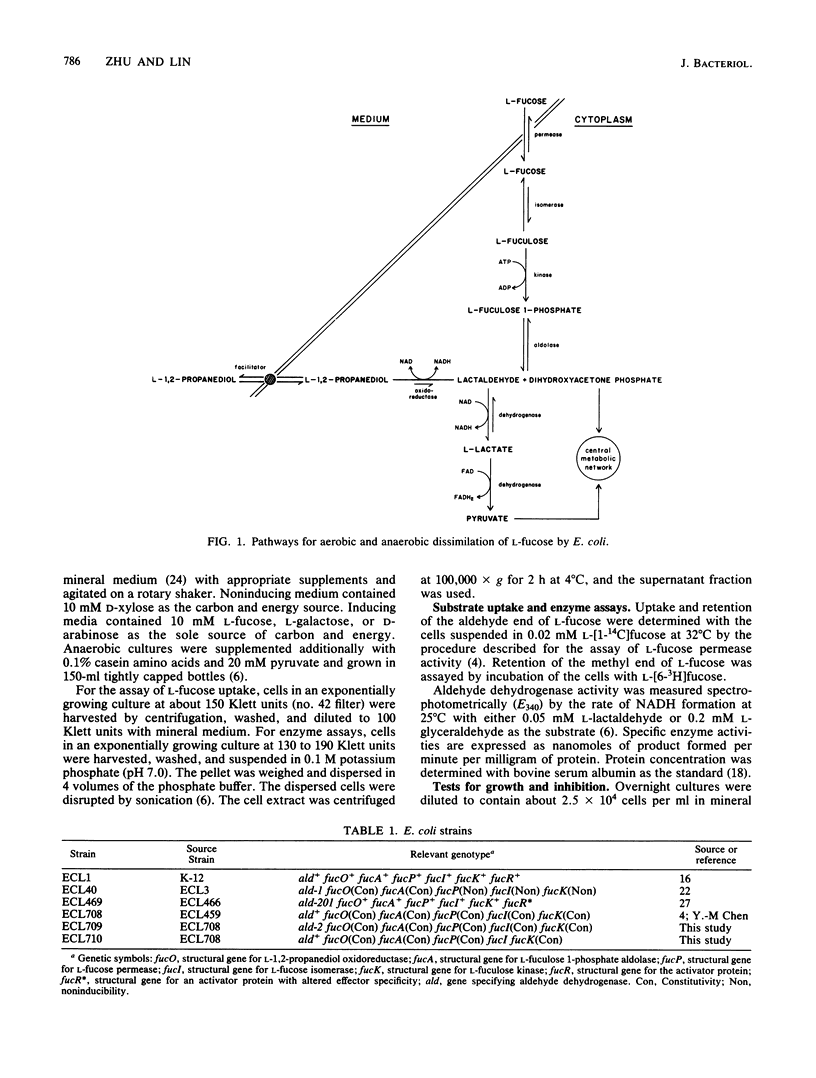
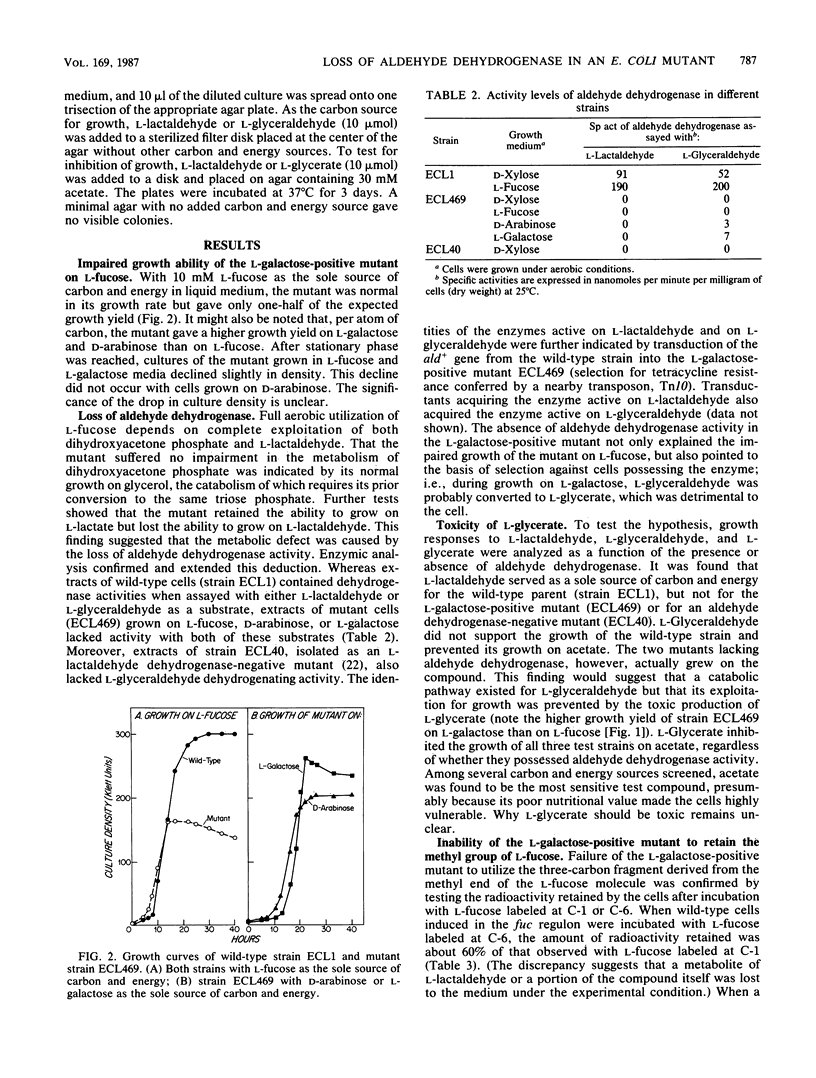
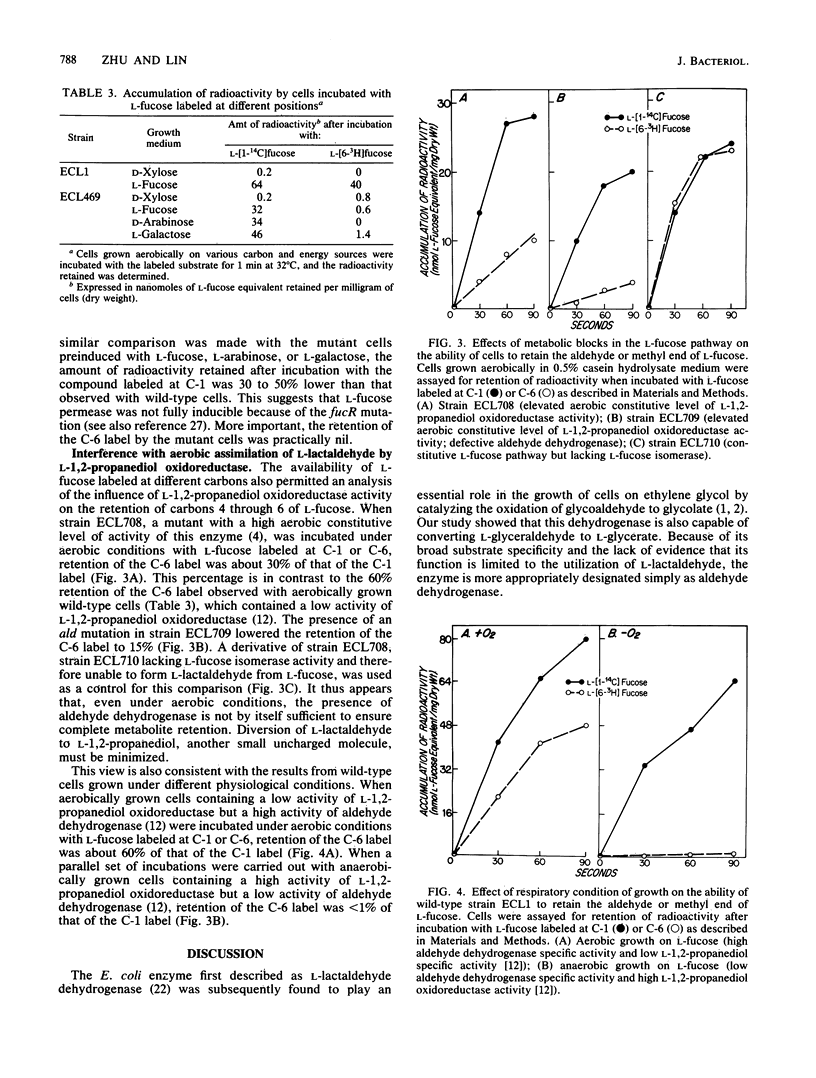
Escherichia coli K-12 converts L-fucose to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (C-1 to C-3) and L-lactaldehyde (C-4 to C-6) by a pathway specified by the fuc regulon. Aerobically, L-lactaldehyde serves as a carbon and energy source by the action of an aldehyde dehydrogenase of broad specificity; the product, L-lactate, is then converted to pyruvate. Anaerobically, L-lactaldehyde serves as an electron acceptor to regenerate NAD from NADH by the action of an oxidoreductase; the reduced product, L-12-propanediol, is excreted. A strain selected for growth on L-galactose (a structural analog of L-fucose) acquired a broadened inducer specificity because of an altered fucR gene encoding the activator protein for the fuc regulon (Y. Zhu and E. C. C. Lin, J. Mol. Evol. 23:259-266, 1986). In this study, a second mutation that abolished aldehyde dehydrogenase activity was discovered. The L-fucose pathway converts L-galactose to dihydroxyacetone phosphate and L-glyceraldehyde. Aldehyde dehydrogenase then converts L-glyceraldehyde to L-glycerate, which is toxic. Loss of the dehydrogenase averts the toxicity during growth on L-galactose, but reduces by one-half the aerobic growth yield on L-fucose. When mutant cells induced in the L-fucose system were incubated with radioactive L-fucose, accumulation of radioactivity occurred if the substrate was labeled at C-1 but not if it was labeled C-6. Complete aerobic utilization of carbons 4 through 6 of L-fucose depends not only on an adequate activity of aldehyde dehydrogenase to trap L-lactaldehyde as its anionic acid but also on the lack of L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase activity, which converts L-lactaldehyde to a readily excreted alcohol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boronat A., Caballero E., Aguilar J. Experimental evolution of a metabolic pathway for ethylene glycol utilization by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):134–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.134-139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caballero E., Baldomá L., Ros J., Boronat A., Aguilar J. Identification of lactaldehyde dehydrogenase and glycolaldehyde dehydrogenase as functions of the same protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7788–7792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti T., Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Clustering of genes for L-fucose dissimilation by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):984–986. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.984-986.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Chakrabarti T., Lin E. C. Constitutive activation of L-fucose genes by an unlinked mutation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):725–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.725-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Post-transcriptional control of L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase in the L-fucose pathway of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):341–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.341-344.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lin E. C., Ros J., Aguilar J. Use of operon fusions to examine the regulation of the L-1,2-propanediol oxidoreductase gene of the fucose system in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Nov;129(11):3355–3362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-11-3355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Aguilar T., Lin E. C. Evolution of L-1, 2-propanediol catabolism in Escherichia coli by recruitment of enzymes for L-fucose and L-lactate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.83-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D. On the importance of being ionized. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):497–509. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHALAMBOR M. A., HEATH E. C. The metabolism of L-fucose. II. The enzymatic cleavage of L-fuculose 1-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2427–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., COHEN S. S. Enzymatic conversion of L-fucose to L-fuculose. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):557–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH E. C., GHALAMBOR M. A. The metabolism of L-fucose. I. The purification and properties of L-fuculose kinase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2423–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking A. J., Aguilar J., Lin E. C. Evolution of propanediol utilization in Escherichia coli: mutant with improved substrate-scavenging power. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.522-530.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking A. J., Lin E. C. Disruption of the fucose pathway as a consequence of genetic adaptation to propanediol as a carbon source in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1166–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1166-1172.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacking A. J., Lin E. C. Regulatory changes in the fucose system associated with the evolution of a catabolic pathway for propanediol in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):832–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.832-838.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose: a new pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.90-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C. Glycerol dissimilation and its regulation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:535–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo J. W., Anderson R. L. Basis for the mutational acquisition of the ability of Aerobacter aerogenes to grow on L-mannose. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):948–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.948-955.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo J. W., Anderson R. L. Pathway of L-mannose degradation in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6330–6333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold A. C., Ezekiel D. H. Regulation of D-arabinose utilization in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):521–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.521-523.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhara S., Wu T. T., Chused T. M., Lin E. C. Ferrous-activated nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase from a mutant of Escherichia coli capable of growth on 1, 2-propanediol. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):87–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.87-95.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhara S., Wu T. T. Purification and properties of lactaldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5233–5238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. T., Engel R., Tropp B. E. L-Glyceraldehude 3-phosphate, a bactericidal agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):147–153. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagalak B., Frey P. A., Karabatsos G. L., Abeles R. H. The stereochemistry of the conversion of D and L 1,2-propanediols to propionaldehyde. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3028–3035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Lin E. C. An evolvant of Escherichia coli that employs the L-fucose pathway also for growth on L-galactose and D-arabinose. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(3):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF02115582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



