Abstract
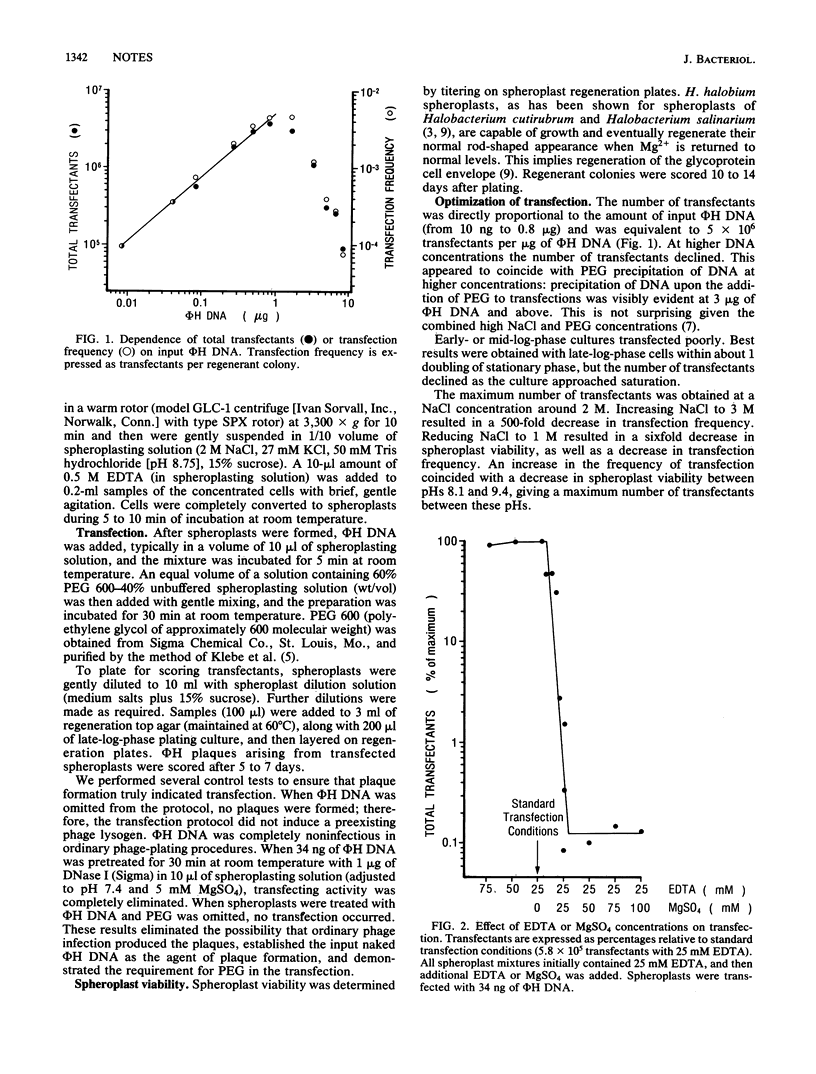
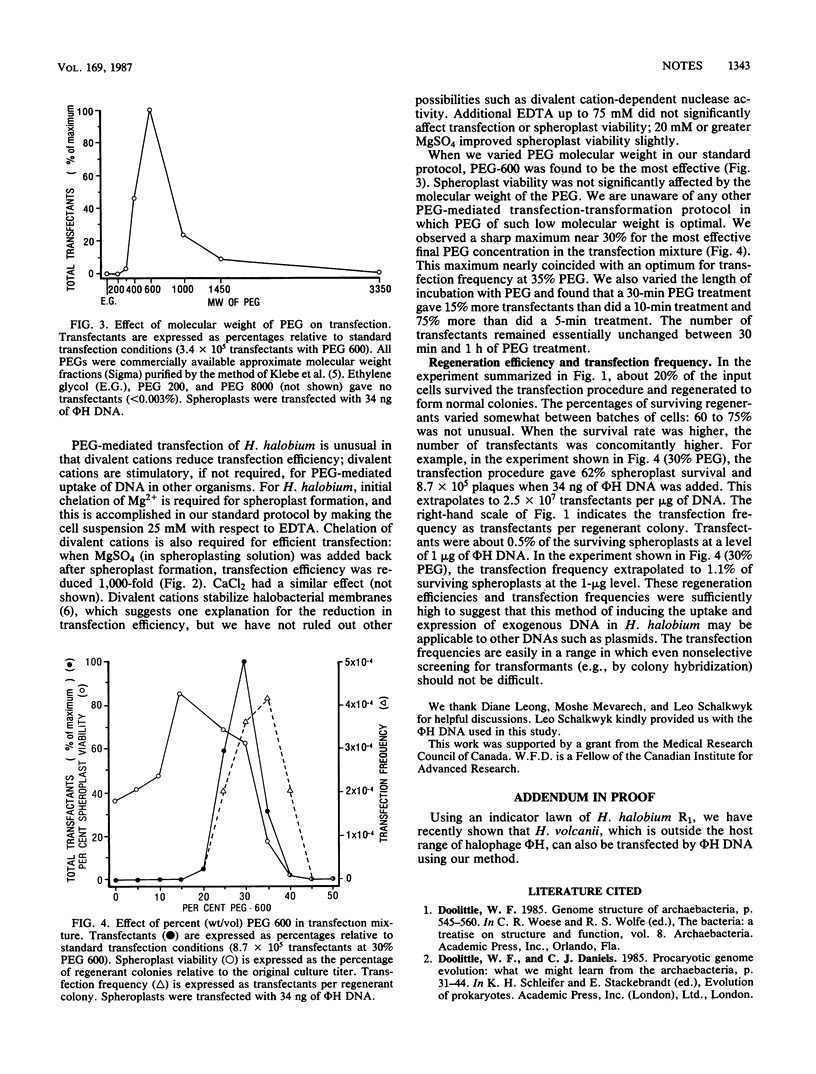
We developed an efficient polyethylene glycol-mediated spheroplast transfection method for the extremely halophilic archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. The 59-kilobase-pair linear phage phi H DNA molecule routinely produced between 5 X 10(6) and 2 X 10(7) transfectants per microgram of DNA. Between 0.5 and 1% of spheroplasts were transfected per microgram of luminal diameter H DNA. Under our conditions, survival and regeneration of H. halobium spheroplasts were also quite efficient, suggesting that this method will be useful for introducing other DNAs into these bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Klebe R. J., Harriss J. V., Sharp Z. D., Douglas M. G. A general method for polyethylene-glycol-induced genetic transformation of bacteria and yeast. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Plachy W. Z., Kates M. Lipid interactions in membranes of extremely halophilic bacteria. II. Modification of the bilayer structure by squalene. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):4914–4920. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T. Fractionation of DNA fragments by polyethylene glycol induced precipitation. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):347–353. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M. F., Strominger J. L. Structural (shape-maintaining) role of the cell surface glycoprotein of Halobacterium salinarium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Werczberger R. Genetic transfer in Halobacterium volcanii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):461–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.461-462.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel H., Zillig W., Pfäffle M., Schnabel R., Michel H., Delius H. Halobacterium halobium phage øH. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):87–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M., Herrmann G. Studies on the biosynthesis of bacterio-opsin. Demonstration of the existence of protein species structurally related to bacterio-opsin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):229–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


