Abstract
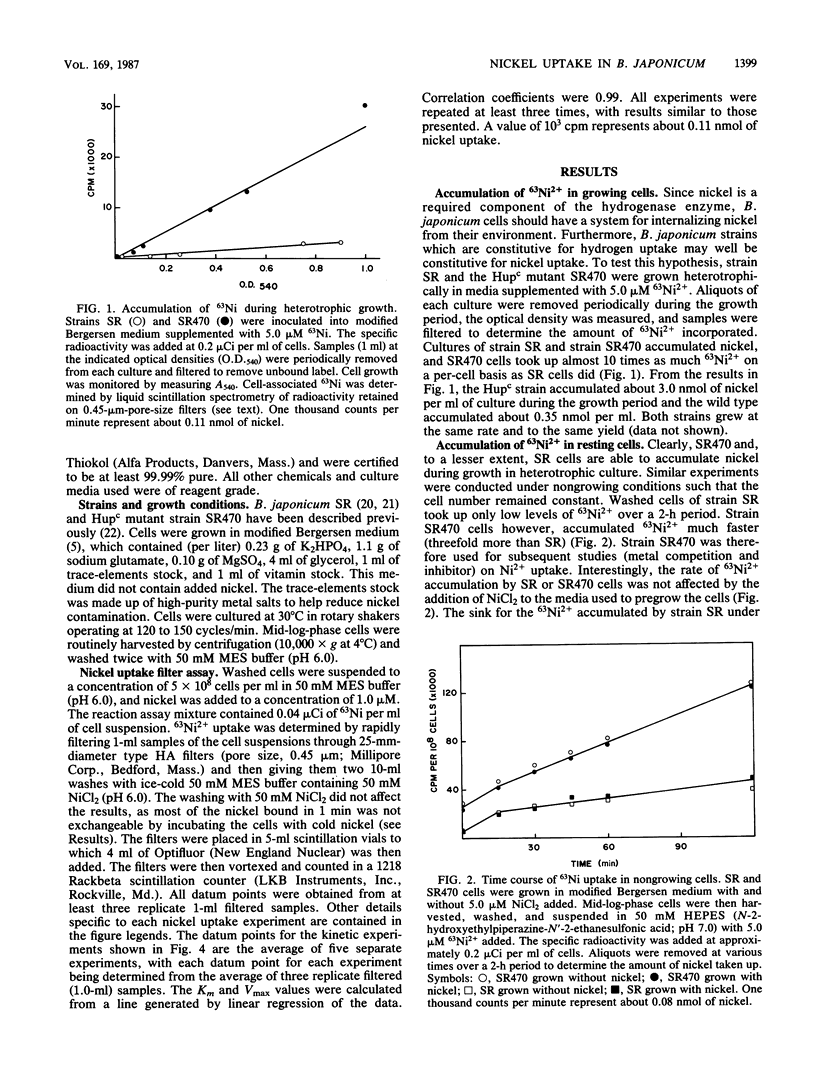
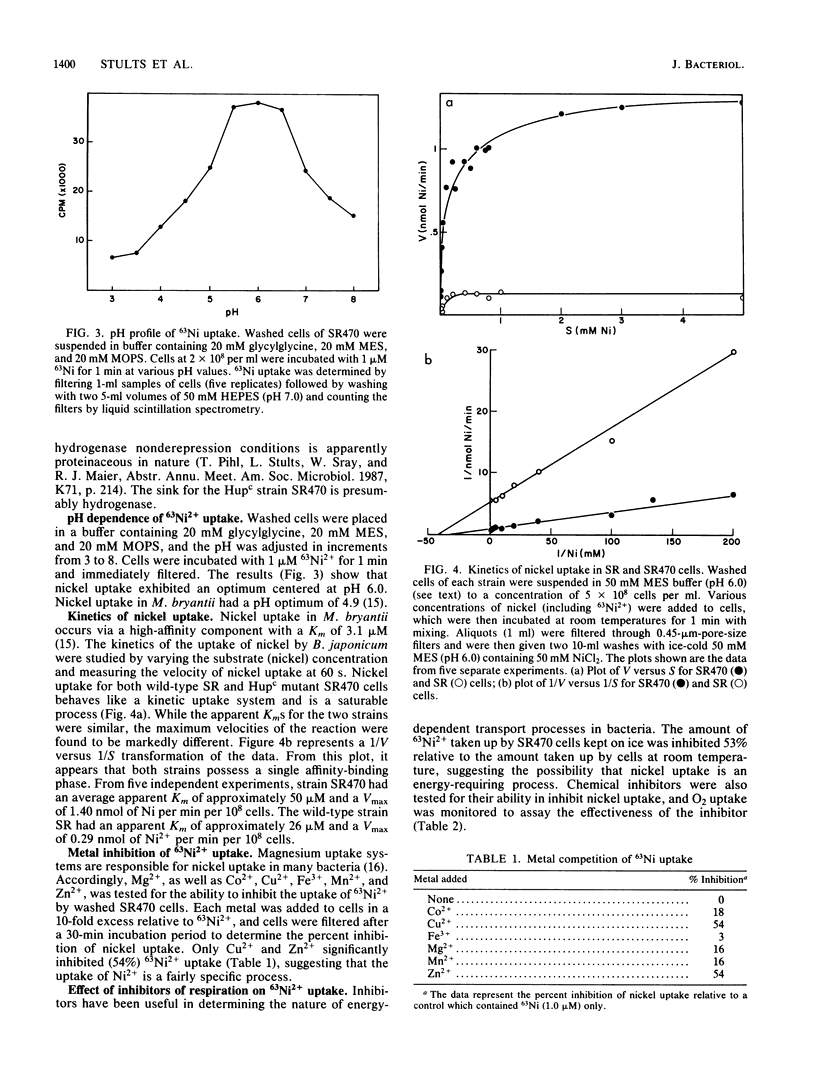
Free-living Bradyrhizobium japonicum grown heterotrophically with 1 microM 63Ni2+ accumulated label. Strain SR470, a Hupc mutant, accumulated almost 10-fold more 63Ni2+ on a per-cell basis than did strain SR, the wild type. Nongrowing cells were also able to accumulate nickel over a 2-h period, with the Hupc mutant strain SR470 again accumulating significantly more 63Ni2+ than strain SR. These results suggest that this mutant is constitutive for nickel uptake as well as for hydrogenase expression. The apparent Kms for nickel uptake in strain SR and strain SR470 were found to be similar, approximately 26 and 50 microM, respectively. The Vmax values, however, were significantly different, 0.29 nmol of Ni/min per 10(8) cells for SR and 1.40 nmol of Ni/min per 10(8) cells for SR470. The uptake process was relatively specific for nickel; only Cu2+ and Zn2+ (10 microM) were found to appreciably inhibit the uptake of 1 microM Ni, while a 10-fold excess of Mg2+, Co2+, Fe3+, or Mn2+ did not affect Ni2+ uptake. The lack of inhibition by Mg2+ indicates that nickel is not transported by a magnesium uptake system. Nickel uptake was also inhibited by cold (53% inhibition at 4 degrees C) and slightly by the ionophores nigericin and carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone. Other ionophores did not appreciably affect nickel uptake, even though they significantly stimulated O2 uptake. The cytochrome c oxidase inhibitors azide, cyanide, and hydroxylamine did not inhibit Ni2+ uptake, even at concentrations (of cyanide and hydroxylamine) that inhibited O2 uptake. The addition of oxidizable substrates such as succinate or gluconate did not increase nickel uptake, even though they increased respiratory activity. Nickel update showed a pH dependence with an optimum at 6.0. Most (approximately 85%) of the 63Ni2+ taken up in 1 min by strain SR470 was not exchangeable with cold nickel.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. W., Mortenson L. E. The physical and catalytic properties of hydrogenase II of Clostridium pasteurianum. A comparison with hydrogenase I. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7045–7055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arp D. J. Rhizobium japonicum hydrogenase: purification to homogeneity from soybean nodules, and molecular characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Mar;237(2):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Nickel-containing hydrogenase isoenzymes from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):454–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.454-459.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Guevara J. G., Engelke J. A., Evans H. J. Relation between Glutamine Synthetase and Nitrogenase Activities in the Symbiotic Association between Rhizobium japonicum and Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott B. B., Mortenson L. E. Transport of molybdate by Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1295–1301. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1295-1301.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Ruiz-Argüeso T., Ching T. M., Evans H. J. Hydrogen-dependent nitrogenase activity and ATP formation in Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.153-160.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich C. G., Schneider K., Friedrich B. Nickel in the catalytically active hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):42–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.42-48.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanus F. J., Maier R. J., Evans H. J. Autotrophic growth of H2-uptake-positive strains of Rhizobium japonicum in an atmosphere supplied with hydrogen gas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Xu L. S., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Some properties of the nickel-containing hydrogenase of chemolithotrophically grown Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):850–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.850-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh B. H., Czechowski M. H., Krüger H. J., DerVartanian D. V., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J. Desulfovibrio vulgaris hydrogenase: a nonheme iron enzyme lacking nickel that exhibits anomalous EPR and Mössbauer spectra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3728–3732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. F., Sprott G. D. Nickel transport in Methanobacterium bryantii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1195–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1195-1203.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucas R. V., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Nickel: A micronutrient element for hydrogen-dependent growth of Rhizobium japonicum and for expression of urease activity in soybean leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger H. J., Huynh B. H., Ljungdahl P. O., Xavier A. V., Der Vartanian D. V., Moura I., Peck H. D., Jr, Teixeira M., Moura J. J., LeGall J. Evidence for nickel and a three-iron center in the hydrogenase of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14620–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGall J., Ljungdahl P. O., Moura I., Peck H. D., Jr, Xavier A. V., Moura J. J., Teixera M., Huynh B. H., DerVartanian D. V. The presence of redox-sensitive nickel in the periplasmic hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):610–616. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Campbell N. E., Hanus F. J., Simpson F. B., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Expression of hydrogenase activity in free-living Rhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3258–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merberg D., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum: analysis of mutants altered in regulation by carbon substrates and oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1236–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1236-1242.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge C. D., Yates M. G. Effect of chelating agents on hydrogenase in Azotobacter chroococcum. Evidence that nickel is required for hydrogenase synthesis. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):339–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2040339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R., Cammack R., Hall D. O. Purification and properties of the soluble hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (strain Norway 4). Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):637–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Argüeso T., Emerich D. W., Evans H. J. Hydrogenase system in legume nodules: a mechanism of providing nitrogenase with energy and protection from oxygen damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 30;86(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90860-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., Moshiri F., Maier R. J. Aerobic purification of hydrogenase from Rhizobium japonicum by affinity chromatography. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):795–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.795-800.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Nickel is a component of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):153–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.153-158.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unden G., Böcher R., Knecht J., Kröger A. Hydrogenase from Vibrio succinogenes, a nickel protein. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 23;145(2):230–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zwaan J. W., Albracht S. P., Fontijn R. D., Slater E. C. Monovalent nickel in hydrogenase from Chromatium vinosum. Light sensitivity and evidence for direct interaction with hydrogen. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 7;179(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


