Abstract
Halobacterium cutirubrum, a member of the archaebacteria, contains one superoxide dismutase (EC 1.15.1.1). This enzyme functions in the high-ionic-strength intracellular environment and protects the organism against the toxic effects of the superoxide anion. The enzyme has been purified to about 90% homogeneity by a four-step procedure which never removes it from conditions of high ionic strength. The subunits of the purified enzyme have a molecular weight of 25,000 and are possibly in tetrameric association. The enzyme shows anomalously high resistance to azide inhibition and sensitivity to inactivation by hydrogen peroxide. Metal analysis indicates 0.2 atom of Mn, less than 0.03 atom of Cu, and less than 0.001 atom of Fe per subunit. The low content of Mn may explain the low specific activity found for this enzyme compared with that of eubacterial enzymes. Optimum activity occurs in 2 M KCl; KCl gives about twice as much activity as NaCl over the range of 2 to 4 M. The enzyme appears to be related to those isolated from other archaebacteria but also exhibits several novel features.
Full text
PDF
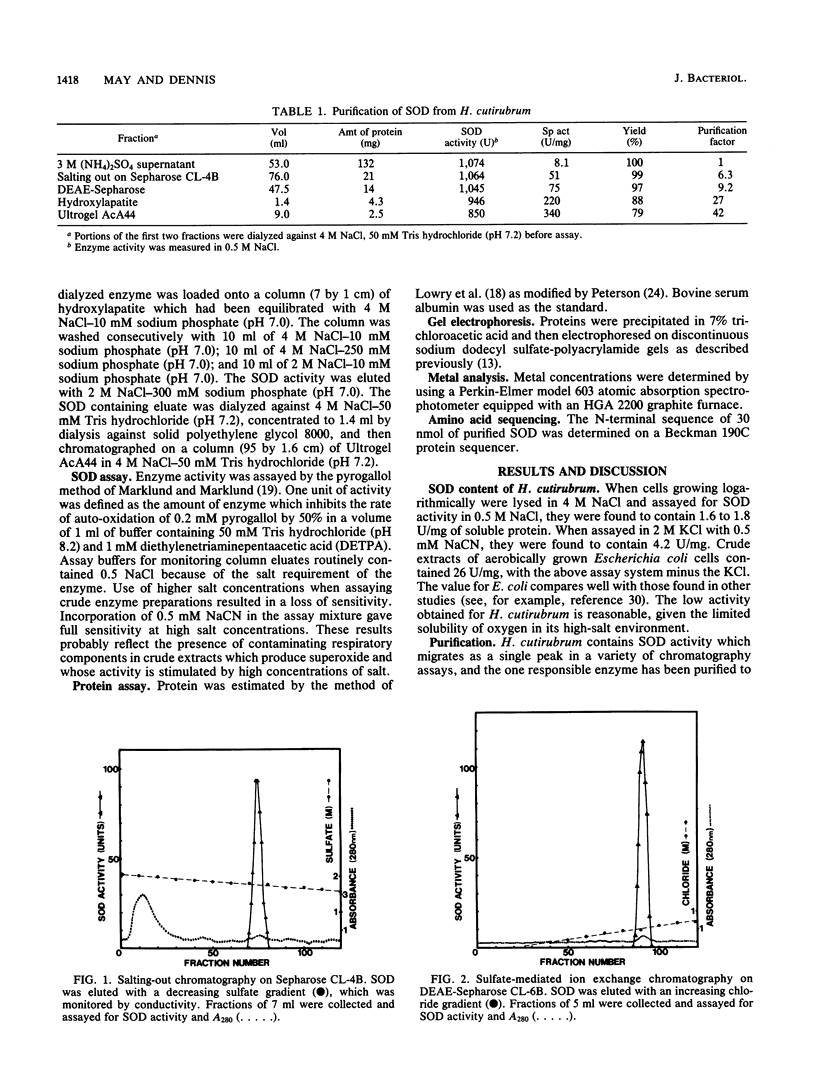
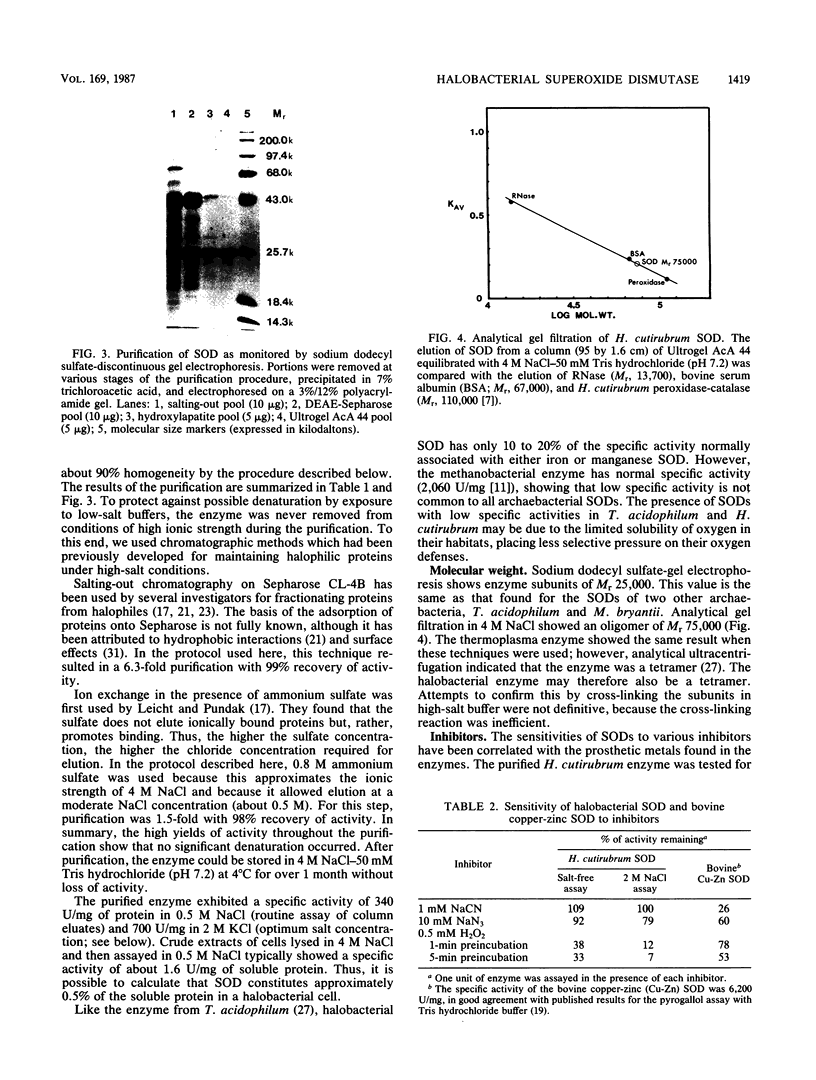
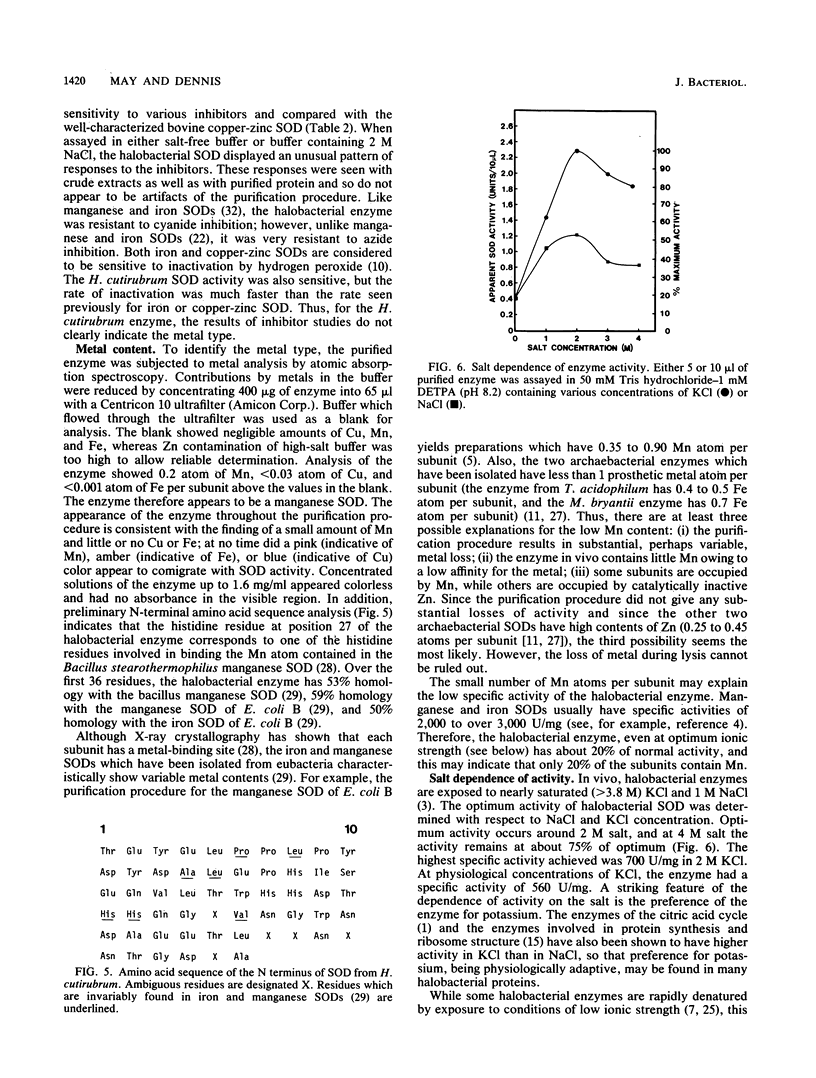


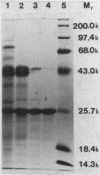
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken D. M., Brown A. D. Citrate and glyoxylate cycles in the halophil, Halobacterium salinarium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 1;177(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A., Shapiro E. R., Moss T. H. Direct evidence for manganese (III) binding to the manganosuperoxide dismutase of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):6157–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):35–97. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumori Y., Fujiwara T., Okada-Takahashi Y., Mukohata Y., Yamanaka T. Purification and properties of a peroxidase from Halobacterium halobium L-33. J Biochem. 1985 Oct;98(4):1055–1061. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson E. K., Fridovich I. The interaction of bovine erythrocyte superoxide dismutase with hydrogen peroxide: inactivation of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 2;14(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby T. W., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Fridovich I. Isolation and characterization of the iron-containing superoxide dismutase of Methanobacterium bryantii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):140–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz M. J., Ballou C. E. Analysis of Halobacterium halobium gas vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1058–1067. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1058-1067.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):272–290. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.272-290.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht W., Pundak S. Large-scale purification of halophilic enzymes by salting-out mediated chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):186–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S., Marklund G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):469–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Keele B. B., Jr, Fridovich I. An enzyme-based theory of obligate anaerobiosis: the physiological function of superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1024–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Leicht W., Werber M. M. Hydrophobic chromatography and fractionation of enzymes from extremely halophilic bacteria using decreasing concentration gradients of ammonium sulfate. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2383–2387. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P., Fridovich I. Inhibition of superoxide dismutases by azide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Aug;189(2):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pater A., Pater M. M. Simultaneous separation of halophilic proteins and nucleic acids after adsorption onto agarose gels. Can J Biochem. 1977 Aug;55(8):904–907. doi: 10.1139/o77-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pundak S., Aloni H., Eisenberg H. Structure and activity of malate dehydrogenase from the extreme halophilic bacteria of the Dead Sea. 2. Inactivation, dissociation and unfolding at NaCl concentrations below 2 M. Salt, salt concentration and temperature dependence of enzyme stability. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel R., Thomm M., Gerardy-Schahn R., Zillig W., Stetter K. O., Huet J. Structural homology between different archaebacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerases analyzed by immunological comparison of their components. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):751–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searcy K. B., Searcy D. G. Superoxide dismutase from the Archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 28;670(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallings W. C., Pattridge K. A., Strong R. K., Ludwig M. L. Manganese and iron superoxide dismutases are structural homologs. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10695–10699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. Cloning and mapping of the manganese superoxide dismutase gene (sodA) of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1078–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1078-1087.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. Organelle specificity. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3582–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Harr F. The ligand-induced solubility shift in salting out chromatography: a new affinity technique, demonstrated with phenylalanyl- and isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase from baker's yeast. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 15;94(2):371–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80980-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]