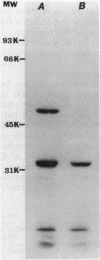
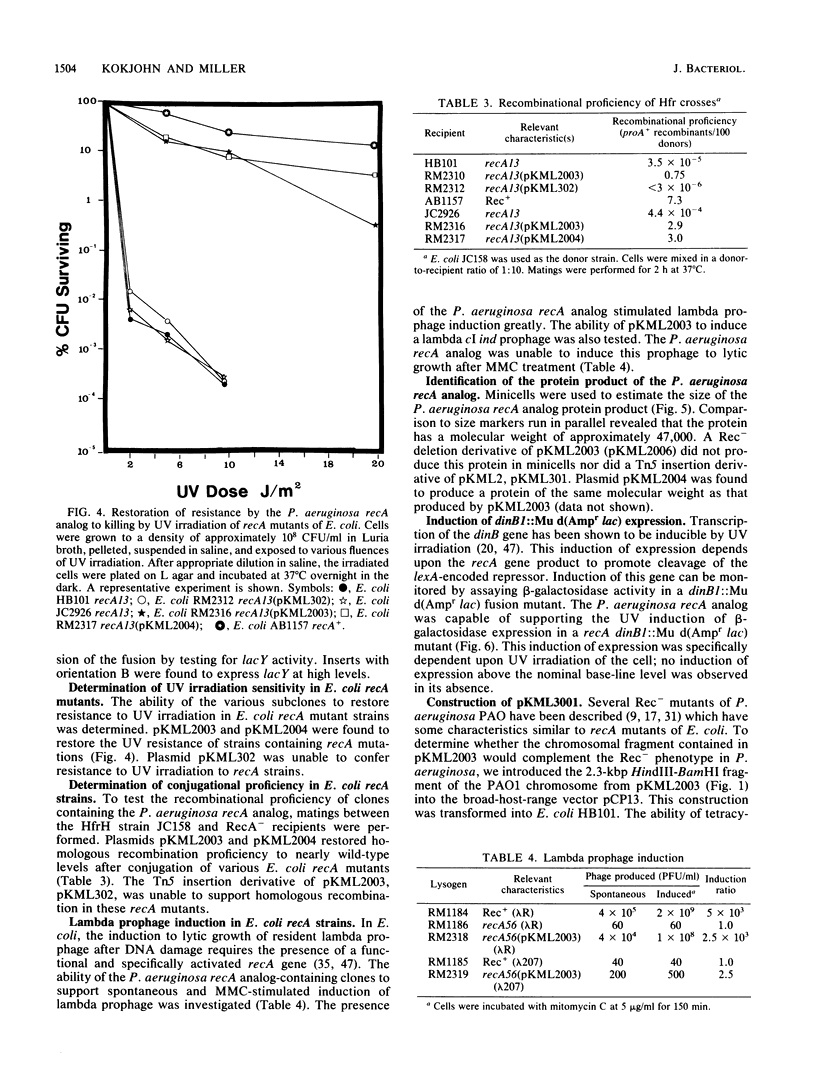
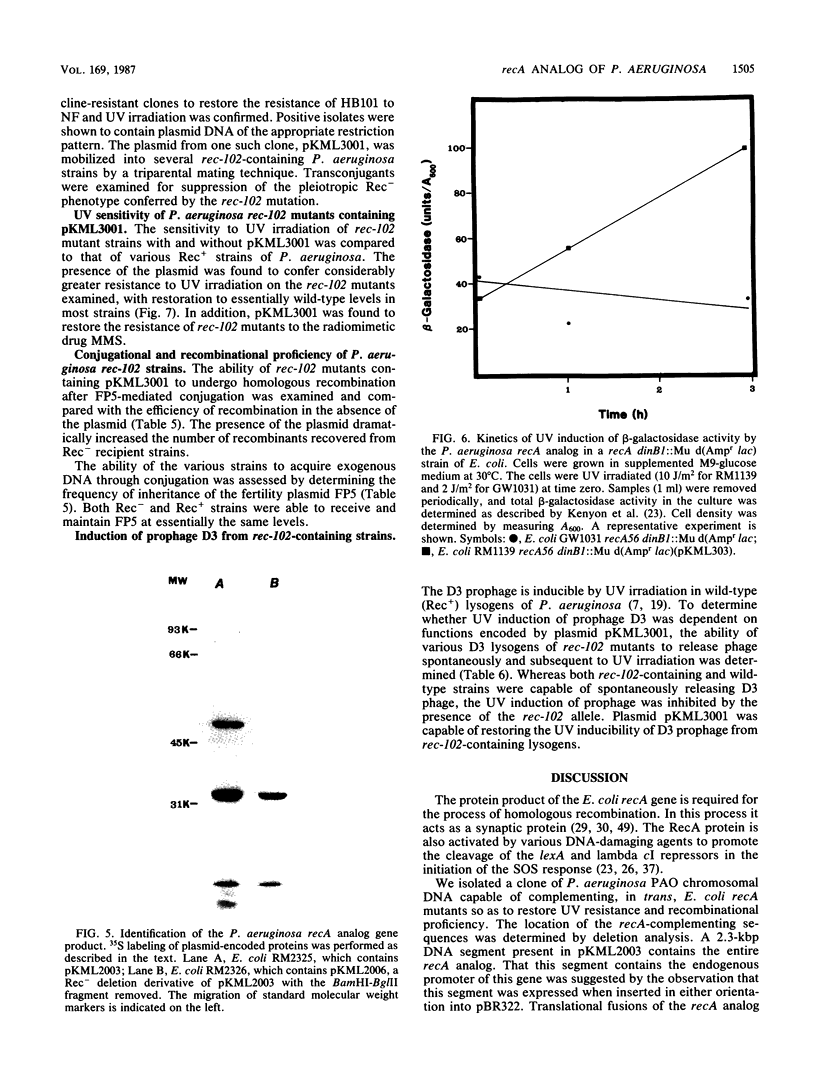
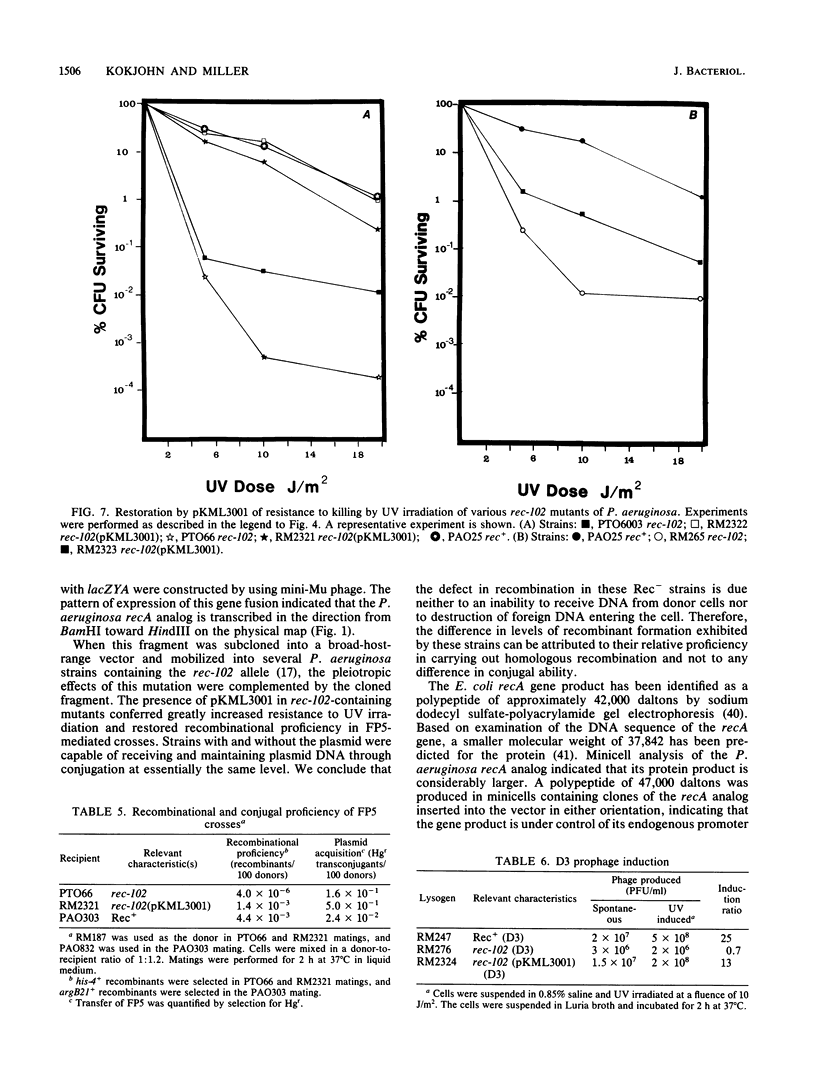
Abstract
We cloned a 2.3-kilobase-pair fragment of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome which is capable of complementing recA mutations of Escherichia coli. The recA-complementing activity was further localized to a 1.5-kilobase-pair PvuII-HindIII fragment. Southern blot analysis under conditions of high stringency indicated that DNA sequence homology is shared by the E. coli recA gene and the P. aeruginosa recA analog. The cloned recA analog was shown to restore resistance to methyl methanesulfonate, nitrofurantoin, and UV irradiation to E. coli recA mutants. Upon introduction of the cloned P. aeruginosa gene, these mutants regained recombination proficiency in HfrH-mediated conjugation and the ability to induce lambda prophages and SOS functions (din gene transcription) after exposure to DNA-damaging agents. Lambda prophage carrying a cI ind mutation was not inducible, suggesting that the mechanism of induction of these SOS functions by the P. aeruginosa RecA analog is similar to that by the activated E. coli RecA protein. The product of the recA analog was identified in minicells as a protein of approximately 47,000 daltons. Western blot analysis using anti-E. coli RecA antibody demonstrated that this protein is antigenically cross-reactive with the E. coli recA protein. The recA-containing fragment was cloned into the broad-host-range vector pCP13 and introduced into Rec- strains of P. aeruginosa containing the rec-102 allele. The plasmid was shown to restore recombination proficiency in FP5-mediated conjugations and to restore resistance to UV irradiation and methyl methanesulfonate to these Rec- mutants. It was shown that a wild-type allele of rec-102 is necessary for UV-mediated induction of D3 and F116 prophages. The cloned recA analog restored the UV inducibility of these prophages in rec-102 mutants. These data indicate that rec-102 is a mutant allele of the P. aeruginosa recA gene and suggest that there has been considerable conservation of the recA gene in the evolution of the gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF

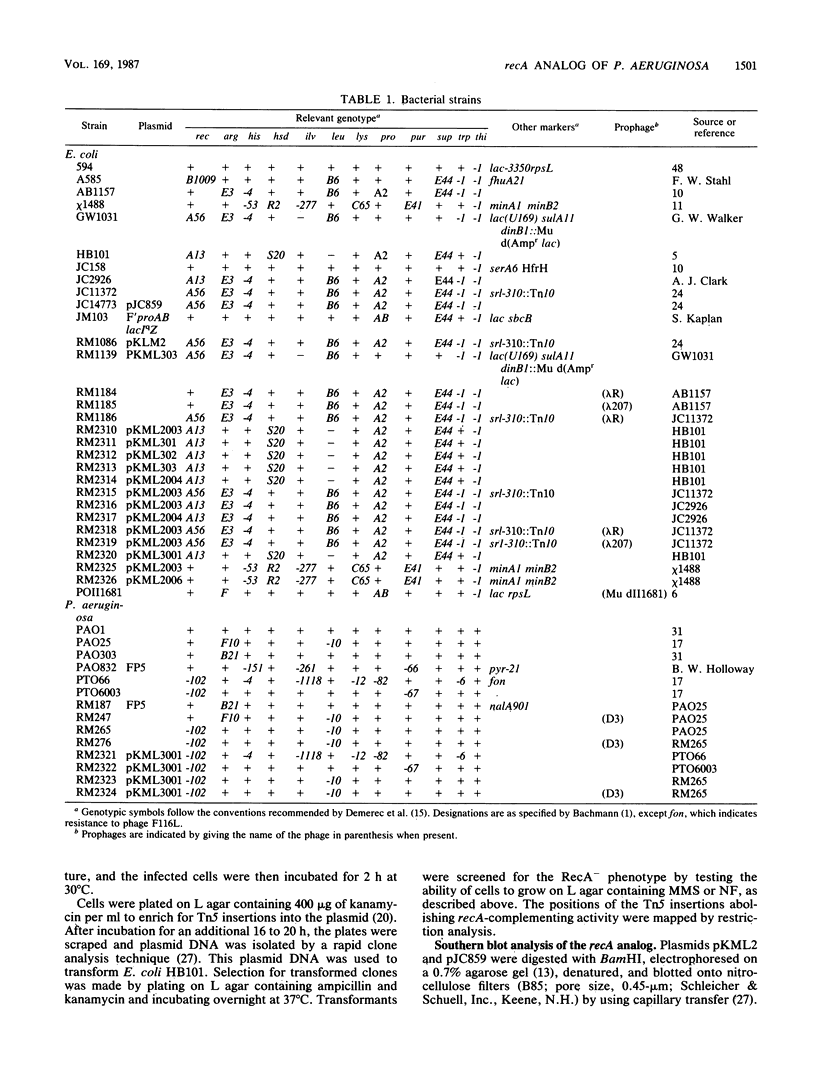
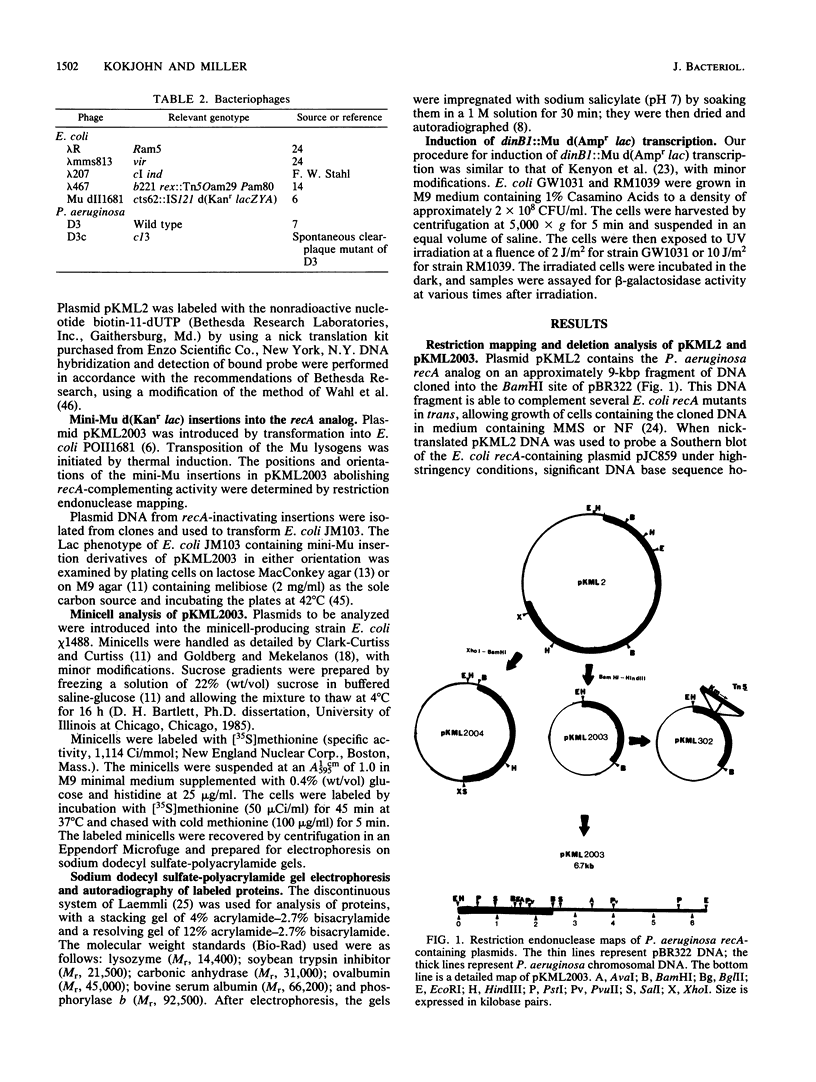
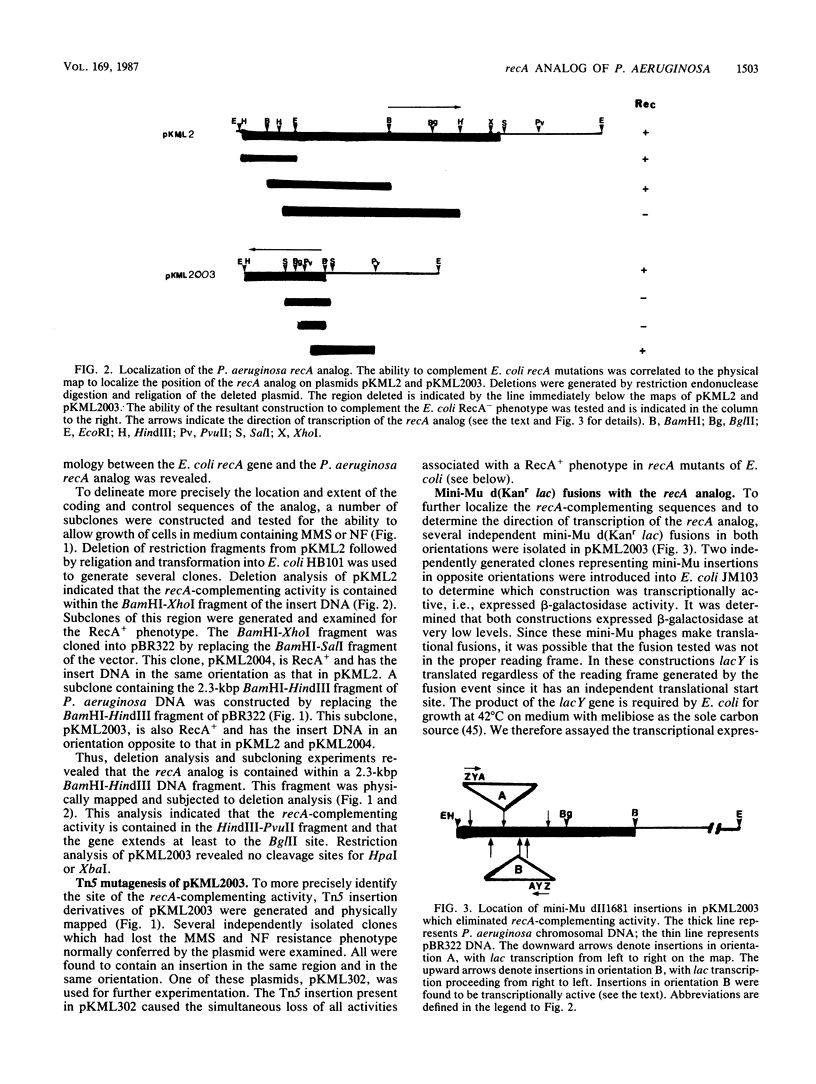


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett D. H., Matsumura P. Identification of Escherichia coli region III flagellar gene products and description of two new flagellar genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):577–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.577-585.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Miller R. V. Effects of norfloxacin on DNA metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Helinski D. R. Isolation and characterization of the recA gene of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.311-316.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenagh M. M., Miller R. V. Specialized transduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO by bacteriophage D3. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.448-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Krishnapillai V. Isolation and properties of recombination-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mutat Res. 1974 Apr;23(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Analysis of recombinant DNA using Escherichia coli minicells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:347–362. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. Genetics. 1966 Jul;54(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Früh R., Watson J. M., Haas D. Construction of recombination-deficient strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00334835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Mekalanos J. J. Cloning of the Vibrio cholerae recA gene and construction of a Vibrio cholerae recA mutant. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):715–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.715-722.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulett F. M. Cloning and characterization of the Bacillus licheniformis gene coding for alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):978–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.978-982.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeenes D. J., Soldati L., Baur H., Watson J. M., Mercenier A., Reimmann C., Leisinger T., Haas D. Expression of biosynthetic genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli in the heterologous host. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):421–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00422066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener S. L., McNamee K. P., McEntee K. Cloning and characterization of recA genes froM Proteus vulgaris, Erwinia carotovora, Shigella flexneri, and Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.153-160.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Brent R., Ptashne M., Walker G. C. Regulation of damage-inducible genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokjohn T. A., Miller R. V. Molecular cloning and characterization of the recA gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):568–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.568-572.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Edmiston S. H., Pacelli L. Z., Mount D. W. Cleavage of the Escherichia coli lexA protein by the recA protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Binding of the recA protein of Escherichia coli to single- and double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8835–8844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Initiation of general recombination catalyzed in vitro by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2615–2619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Ku C. M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants deficient in the establishment of lysogeny. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.875-883.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., West M. A., Flynn J. L., Goldberg J. B. Method for gene replacement in Pseudomonas aeruginosa used in construction of recA mutants: recA-independent instability of alginate production. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1068-1074.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okii M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mapping of the gene specifying aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase II on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):643–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.643-649.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quillardet P., Moreau P. L., Ginsburg H., Mount D. W., Devoret R. Cell survival, UV-reactivation and induction of prophage lambda in Escherichia coli K12 overproducing RecA protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(1):37–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00332993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Mount D. W. Inactivation and proteolytic cleavage of phage lambda repressor in vitro in an ATP-dependent reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W. Proteolytic cleavage of bacteriophage lambda repressor in induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe B., Holloway B. W. Alterations in host specificity of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid after an increase in growth temperature of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.43-48.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. Physical map of the recA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3144–3148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Stachelek C., Konigsberg W., Rupp W. D. Sequences of the recA gene and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker J. M., Gayda R. C., Markovitz A. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli: SOS induction and cellular location of the sulA protein, a key to lon-associated filamentation and death. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):551–561. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.551-561.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Goodwin P. A. Differences in mutagenic and recombinational DNA repair in enterobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4172–4176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle J. Assembly of phage lambda in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1462–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. ATP-dependent renaturation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):126–130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Cassuto E., Mursalim J., Howard-Flanders P. Recognition of duplex DNA containing single-stranded regions by recA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]