Abstract
The structural gene (appA) for the periplasmic acid phosphatase (optimum pH 2.5) of Escherichia coli was cloned into a plasmid by using a combination of in vivo and in vitro techniques. The position and orientation of the appA gene within the cloned DNA fragment were identified by using fusions to the alkaline phosphatase gene (phoA) generated by Tn5 IS50L::phoA (TnphoA) insertions. For TnphoA-generated hybrid proteins to have high enzymatic activity, it appears that the phoA gene must be fused to a target gene coding for a signal which promotes protein export. The approach used to identify the appA gene thus appears to provide a simple general means of selectively identifying genes encoding membrane and secreted proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassford P. J., Jr, Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Use of gene fusion to study secretion of maltose-binding protein into Escherichia coli periplasm. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.19-31.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
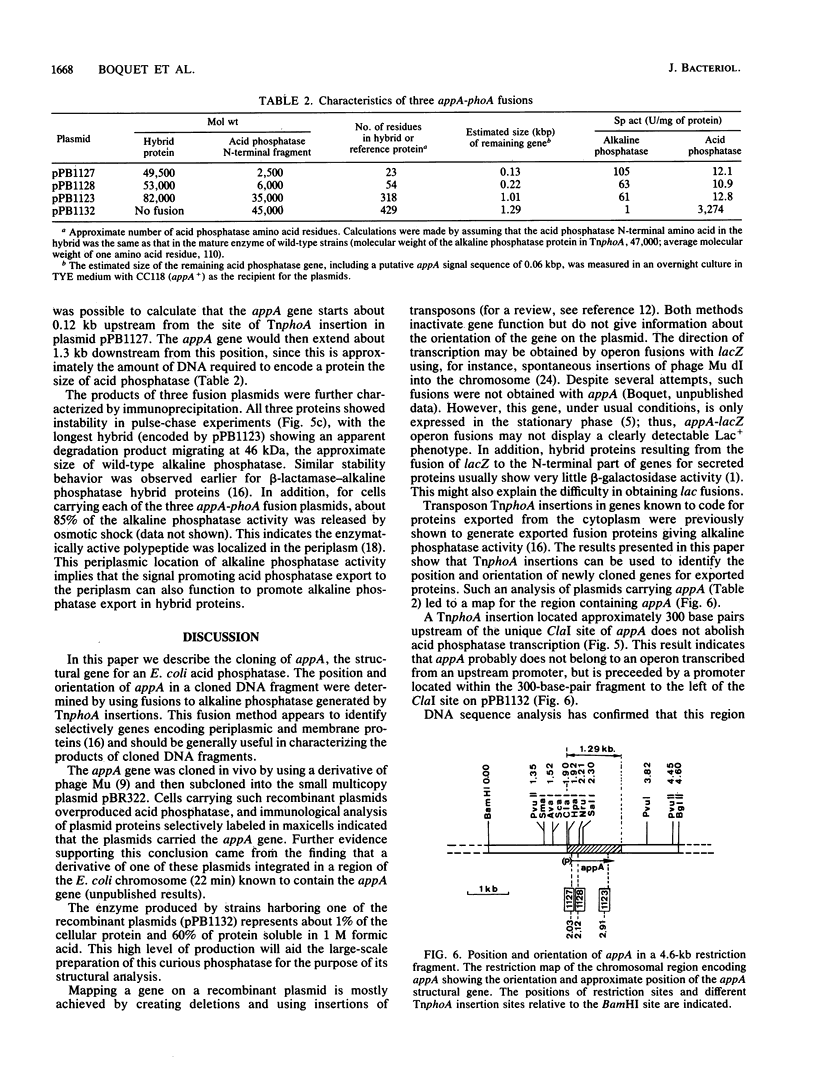
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Identification of the gene appA for the acid phosphatase (pH optimum 2.5) of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):68–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00383314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Is the acid phosphatase of Escherichia coli with pH optimum of 2.5 A polyphosphate depolymerase? FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Cahu M., Desjoyaux-Cherel B., Boquet P. L. The acid phosphatase with optimum pH of 2.5 of Escherichia coli. Physiological and Biochemical study. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6669–6676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Tetu C., Boquet P. L. Identification of the acid phosphatase (optimum pH 2.5) of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80608-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Brockman R. W., Heppel L. A. Purification and properties of two acid phosphatase fractions isolated from osmotic shock fluid of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1743–1751. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Castilho B. A., Casadaban M. J. In vivo DNA cloning and adjacent gene fusing with a mini-Mu-lac bacteriophage containing a plasmid replicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1480–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Roth J., Botstein D. Genetic engineering in vivo using translocatable drug-resistance elements. New methods in bacterial genetics. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):125–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS D., REITHEL F. J. Acid phosphatases of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Jul;89:97–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Wieder S., McSharry R. Use of bacteriophage transposon Mu d1 to determine the orientation for three proC-linked phosphate-starvation-inducible (psi) genes in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):93–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.93-101.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel B. K., Spicer S. S., Dvorak H. F., Heppel L. A. Cytochemical localization of certain phosphatases in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):529–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.529-542.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von HOFSTEN Acid phosphatase and the growth of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Mar 18;48:171–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90529-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von HOFSTEN, PORATH J. Purification and some properties of an acid phosphatase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;64:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90754-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]