Abstract
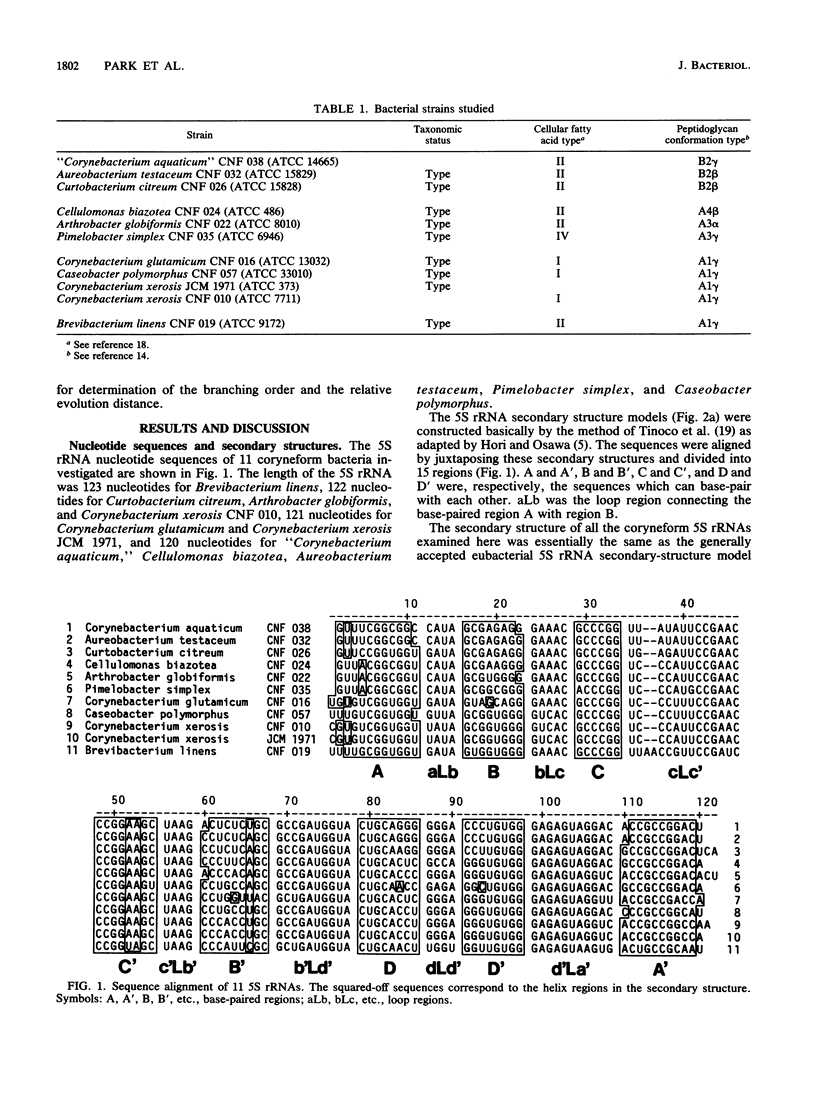
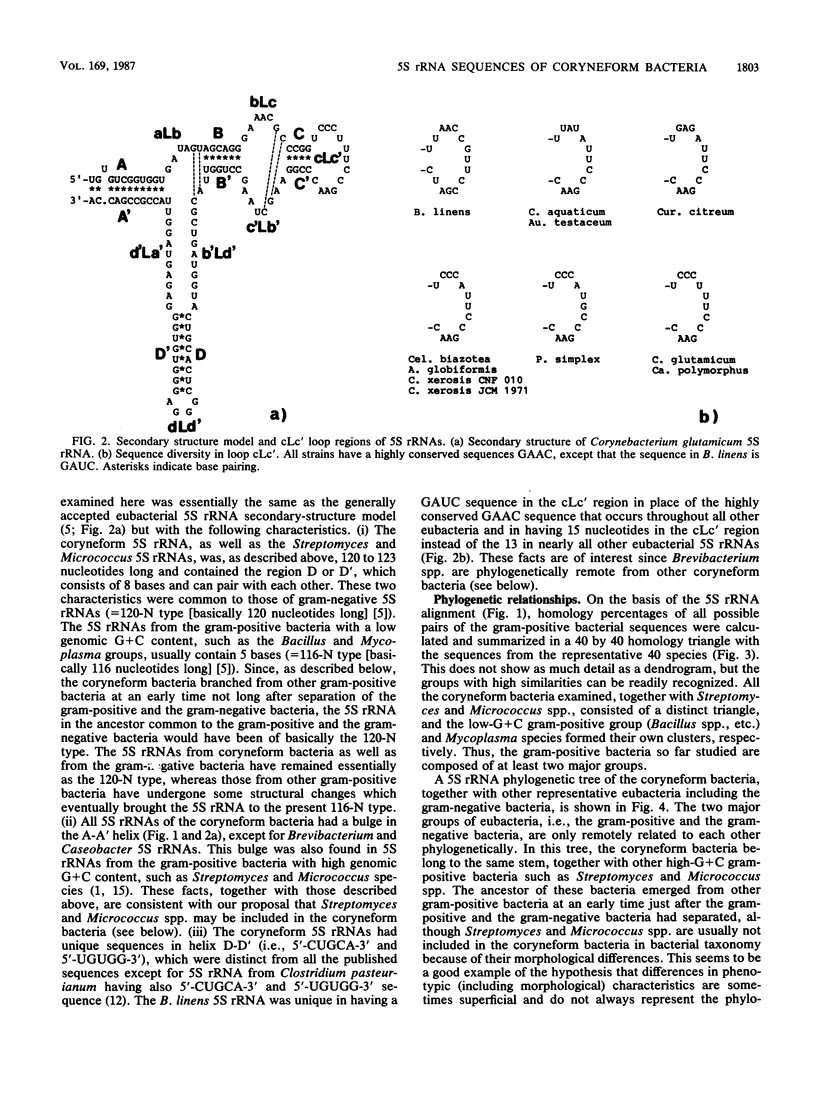
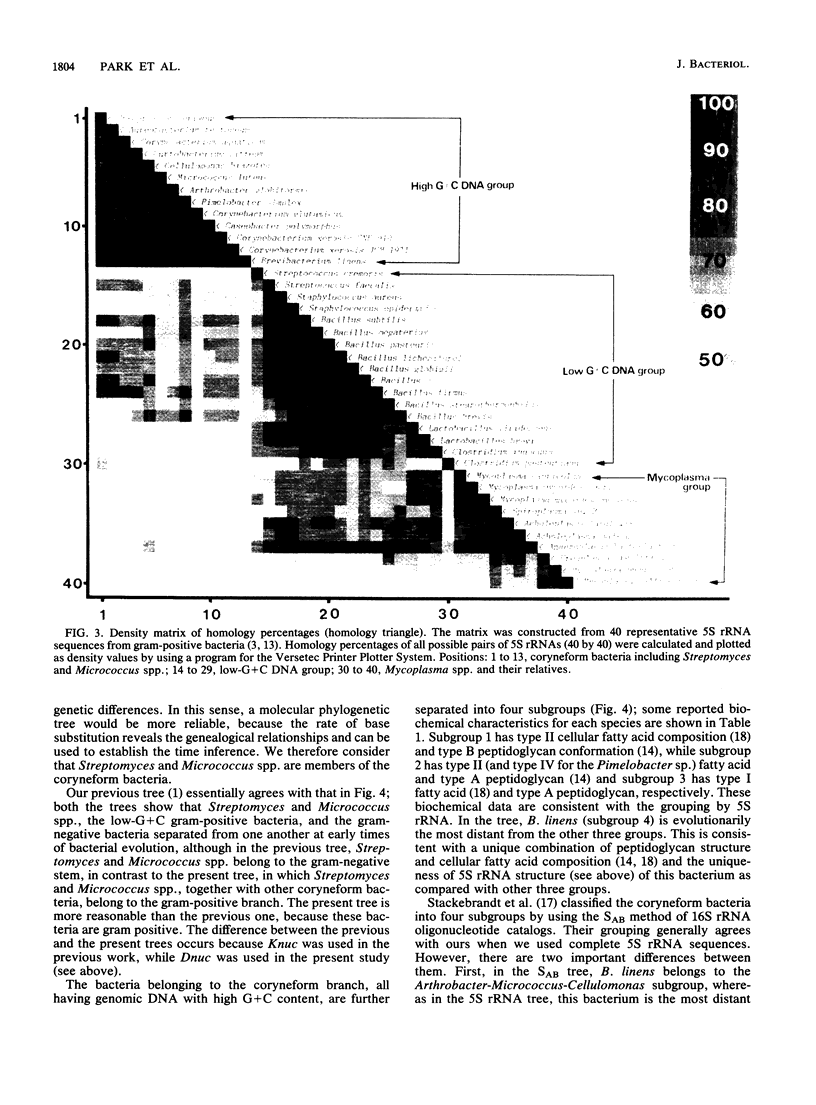
Nucleotide sequences of 5S rRNAs from 11 coryneform bacteria were determined. These were the type strains of Corynebacterium glutamicum, Corynebacterium xerosis, Brevibacterium linens, Arthrobacter globiformis, Cellulomonas biazotea, Aureobacterium testaceum, Curtobacterium citreum, Pimelobacter simplex, and Caseobacter polymorphus and representative strains of "Corynebacterium aquaticum" and Corynebacterium xerosis. A phylogenetic tree constructed from the sequences of these bacteria and published sequences indicated that the coryneform bacteria consist of a distinct eubacterial branch together with Streptomyces and Micrococcus spp. These bacteria could be further divided into four subgroups.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dekio S., Yamasaki R., Jidoi J., Hori H., Osawa S. Secondary structure and phylogeny of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus 5S rRNAs. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.233-237.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Wolters J. Collection of published 5S, 5.8S and 4.5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r1–59. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S. Evolutionary change in 5S rRNA secondary structure and a phylogenic tree of 352 5S rRNA species. Biosystems. 1986;19(3):163–172. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(86)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Stahl D. A., Olsen G. J., Heller D. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the genera Thiobacillus and Thiomicrospira by 5S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.75-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribula C. D., Fox G. E., Woese C. R. Nucleotide sequence of Clostridium pasteurianum 5S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1976 May 1;64(2):350–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Simmons J., Walker R. T., Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Tanner R. S., Robinson I. M., Stahl D. A., Olsen G., Leach R. H. Construction of the mycoplasma evolutionary tree from 5S rRNA sequence data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1160–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A. 3' Terminal labelling of RNA of RNA with beta-32P-pyrophosphate group and its application to the sequence analysis of 5S RNA from Streptomyces griseus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4111–4124. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C., Levine M. D. Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1971 Apr 9;230(5293):362–367. doi: 10.1038/230362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




