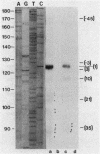
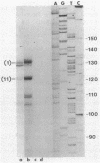
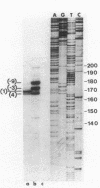
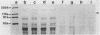Abstract
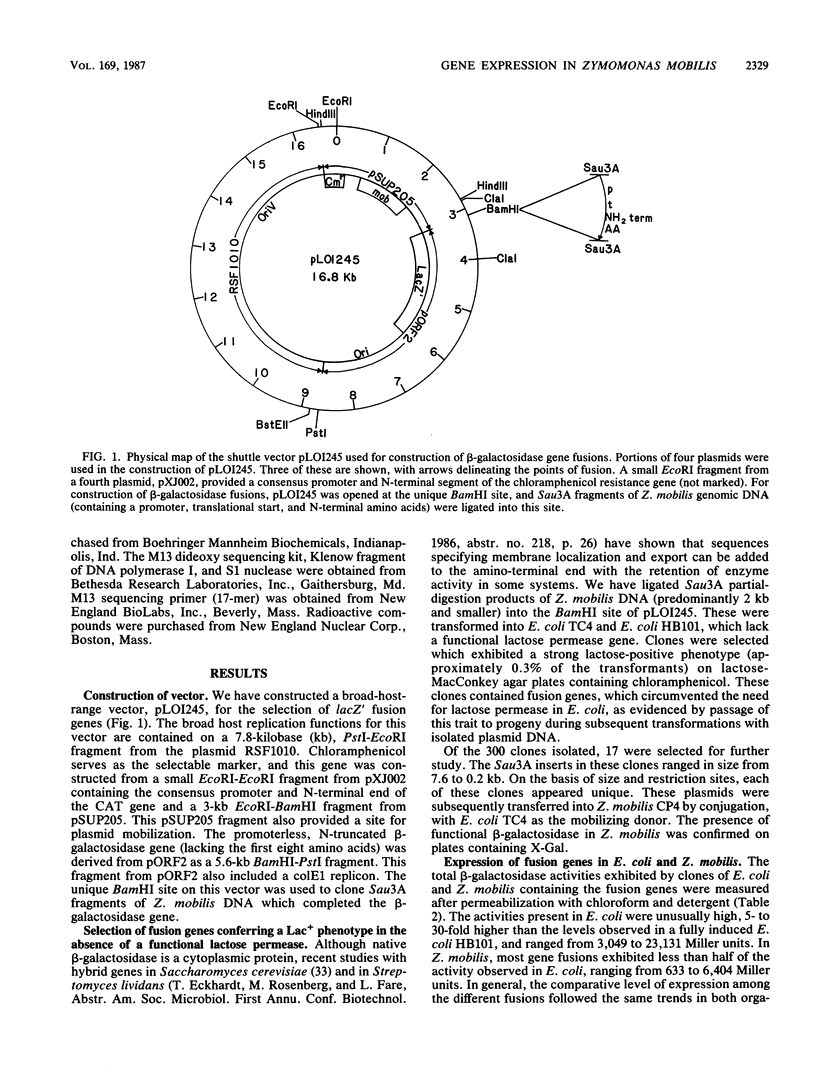
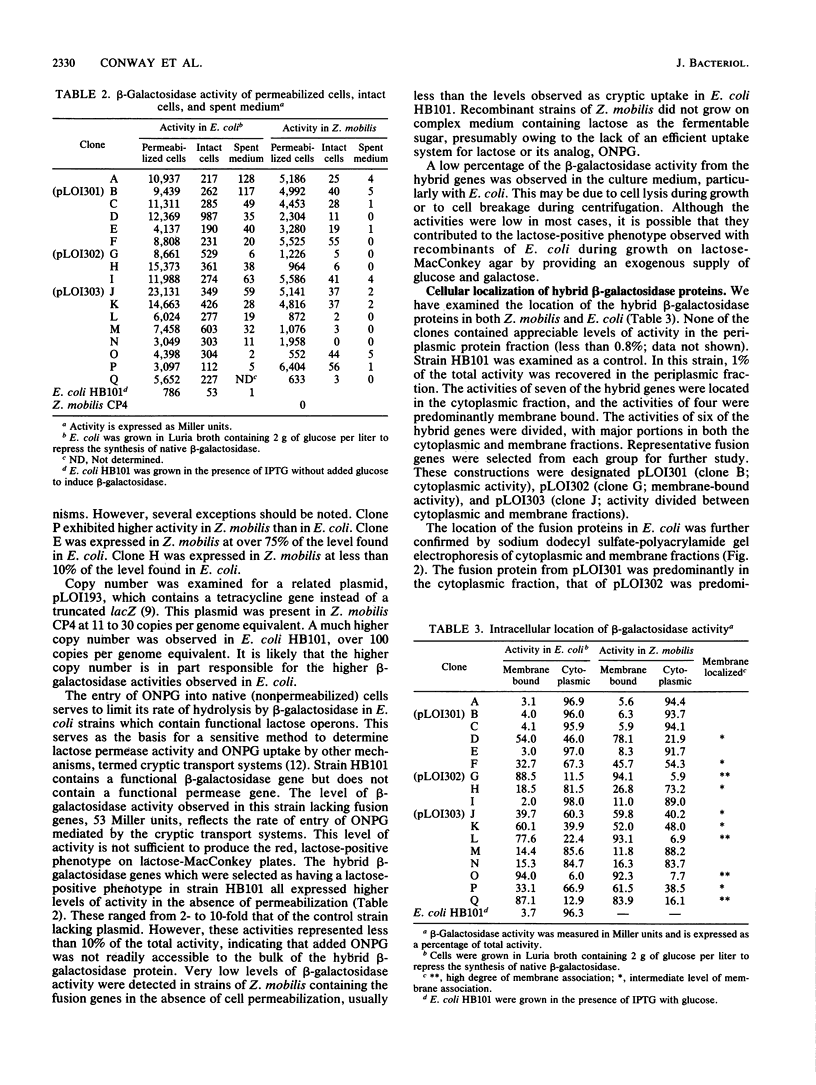
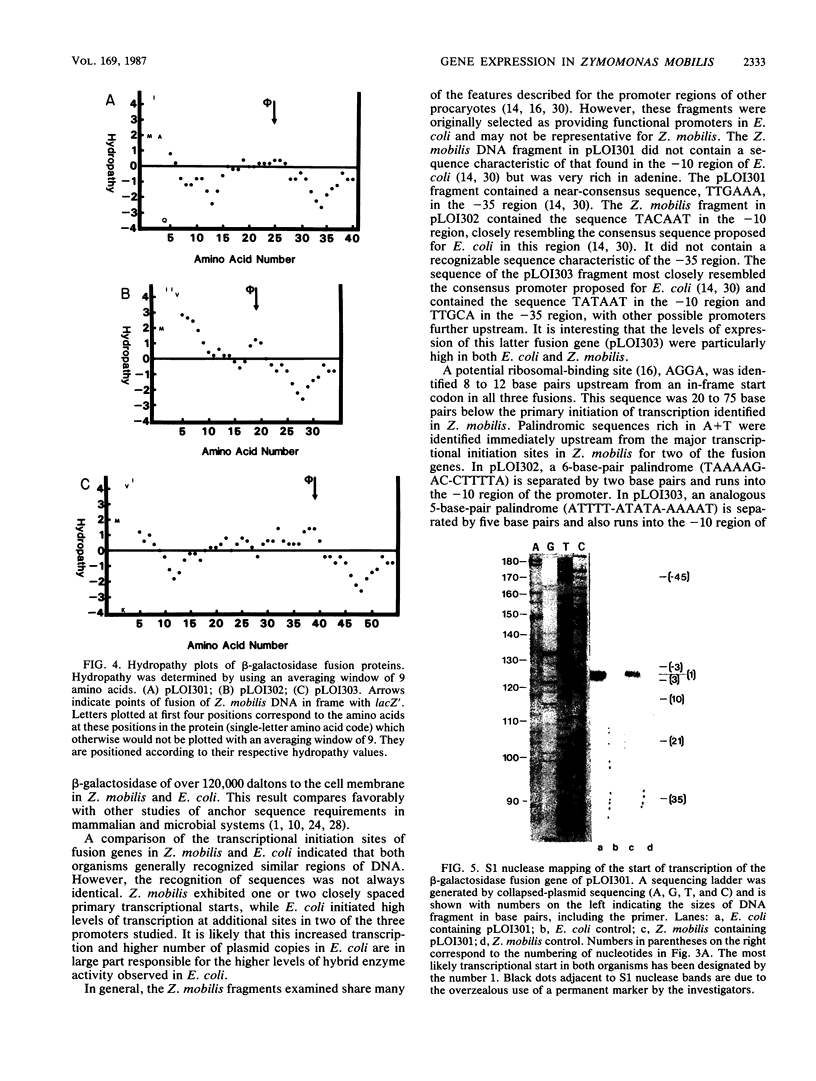
We have described a procedure for the isolation of lacZ' fusion genes which contain anchor sequences conferring membrane association. This method was used to isolate fragments of DNA from Zymomonas mobilis which contain promoter activity and amino-terminal sequences. The sequences and transcriptional initiation sites of three of these were compared. Both Escherichia coli and Z. mobilis recognized similar regions of DNA for transcriptional initiation. Five to eight consecutive hydrophobic amino acids in the amino terminus served to anchor these hybrid proteins to the membrane in both E. coli and Z. mobilis. General features observed in the Z. mobilis fragments included partial sequence homology with the -35 region sequence of E. coli, repetitive and palindromic A + T-rich regions preceding and adjoining the -10 region, a sequence resembling the consensus sequence of E. coli in the -10 region, and a potential ribosomal-binding site (AGGA) 8 to 12 bases upstream from an in-frame start codon. The level of expression of fusion proteins was generally higher in E. coli than in Z. mobilis. This higher level of expression in E. coli may result from multiple sites of transcriptional initiation and higher plasmid copy number.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Timmis K. N. Host: vector systems for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:47–67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. A., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli K12. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:101–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Gilchrist C. A., Denhardt D. T. Escherichia coli rep gene: identification of the promoter and N terminus of the rep protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1004-1010.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey V. C., Ingram L. O. Lipid composition of Zymomonas mobilis: effects of ethanol and glucose. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1291–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1291-1300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey V. C., Walia S. K., Ingram L. O. Expression of a Lactose Transposon (Tn951) in Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1163–1168. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1163-1168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Byun M. O., Ingram L. O. Expression Vector for Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):235–241. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.235-241.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Model P. An artificial anchor domain: hydrophobicity suffices to stop transfer. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried V. A., Novick A. Organic solvents as probes for the structure and function of the bacterial membrane: effects of ethanol on the wild type and an ethanol-resistant mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.239-248.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., van Embden J., Falkow S. Molecular nature of two nonconjugative plasmids carrying drug resistance genes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.619-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Buttke T. M. Effects of alcohols on micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1984;25:253–300. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):643–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Export of protein in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):290–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.290-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L. Translocation of domains of nascent periplasmic proteins across the cytoplasmic membrane is independent of elongation. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi J. J., Soberon X., Marumoto Y., McMahon J., Itakura K. Biological expression of an Escherichia coli consensus sequence promoter and some mutant derivatives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Uses of lac fusions for the study of biological problems. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):398–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.398-418.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skotnicki M. L., Lee K. J., Tribe D. E., Rogers P. L. Comparison of ethanol production by different zymomonas strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):889–893. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.889-893.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes H. W., Dally E. L., Yablonsky M. D., Eveleigh D. E. Comparison of plasmids in strains of Zymomonas mobilis. Plasmid. 1983 Mar;9(2):138–146. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swings J., De Ley J. The biology of Zymomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):1–46. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.1-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., ap Rhys C., Berman M. L., Hampar B., Jackson D., Silhavy T. J., Weisemann J., Zweig M. Open reading frame expression vectors: a general method for antigen production in Escherichia coli using protein fusions to beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4432–4436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]