Abstract
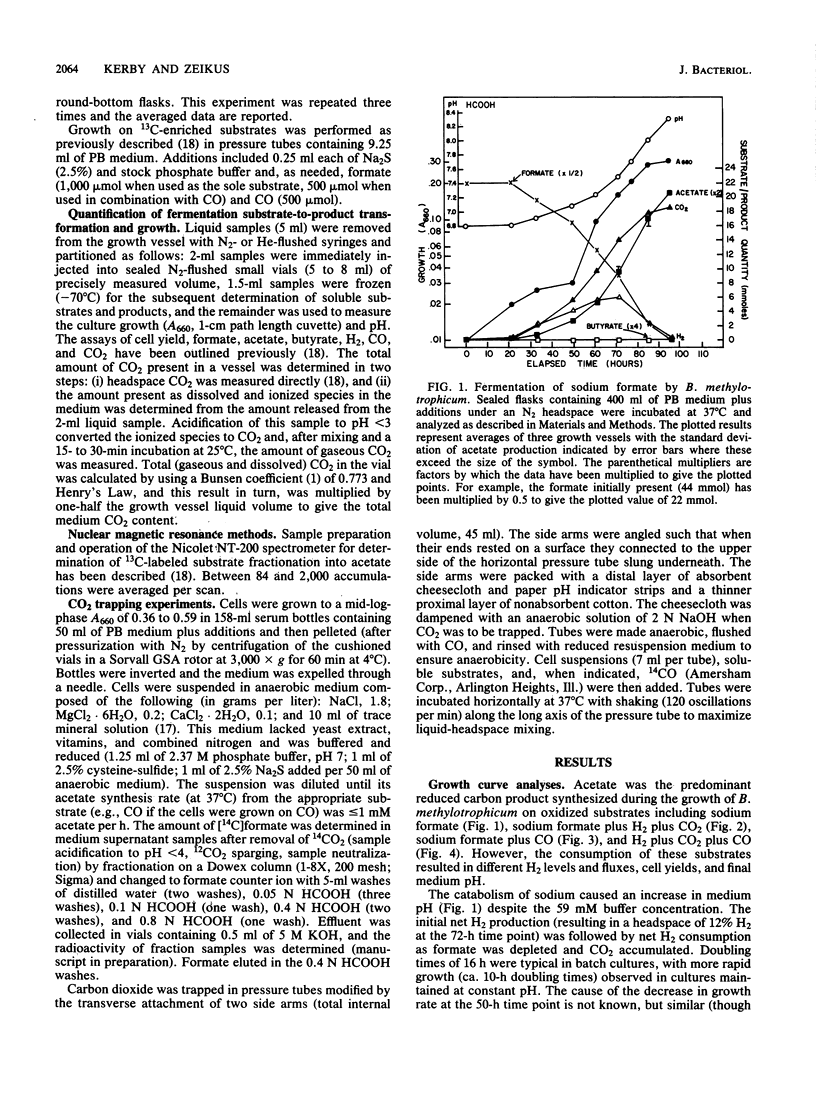
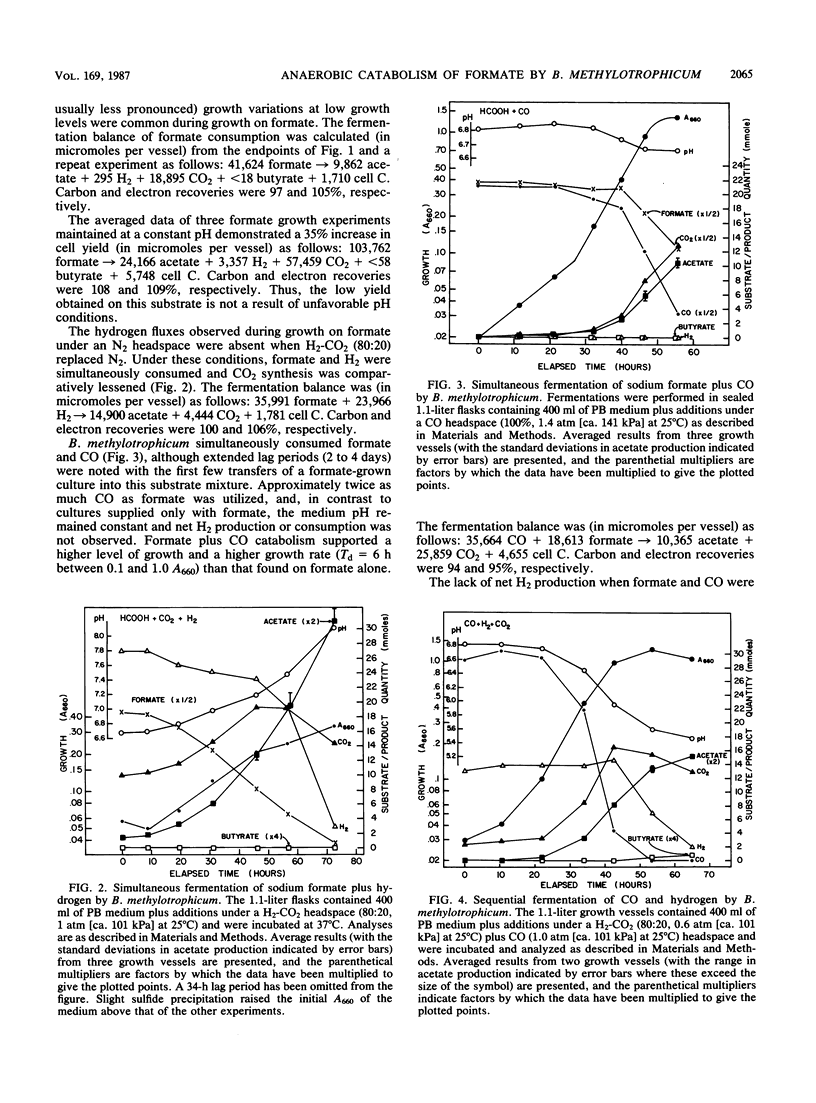
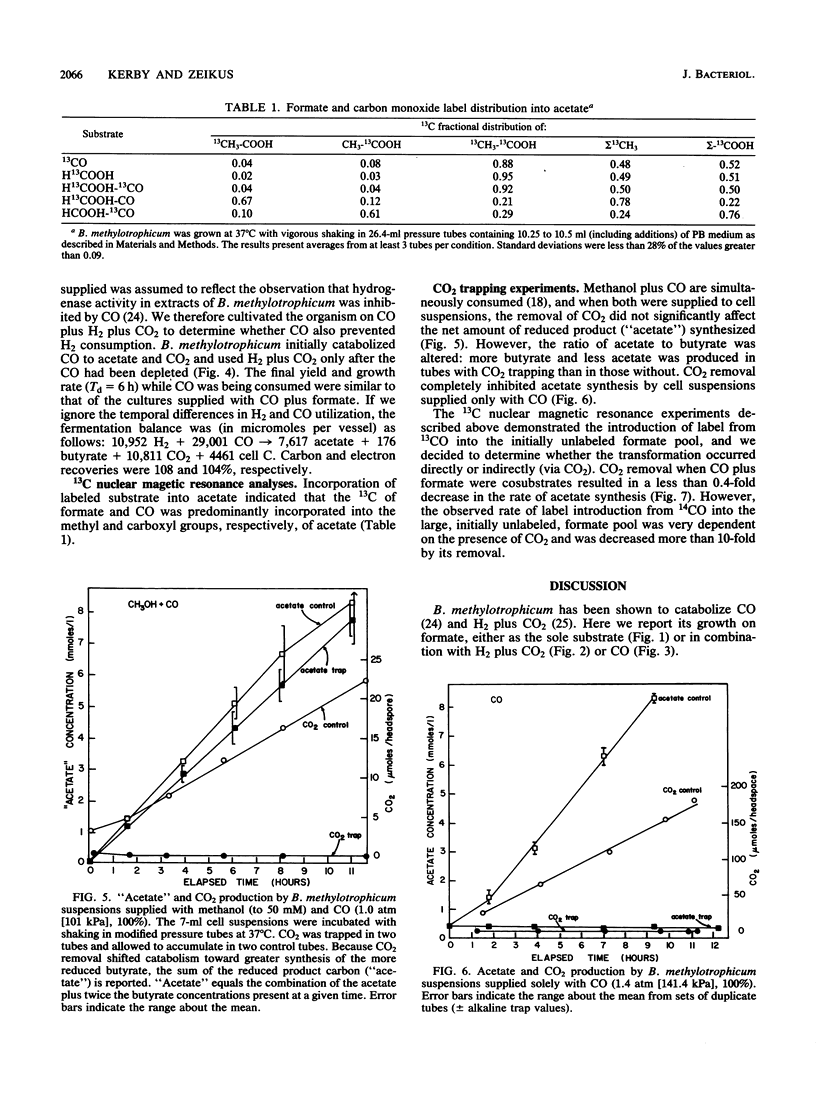
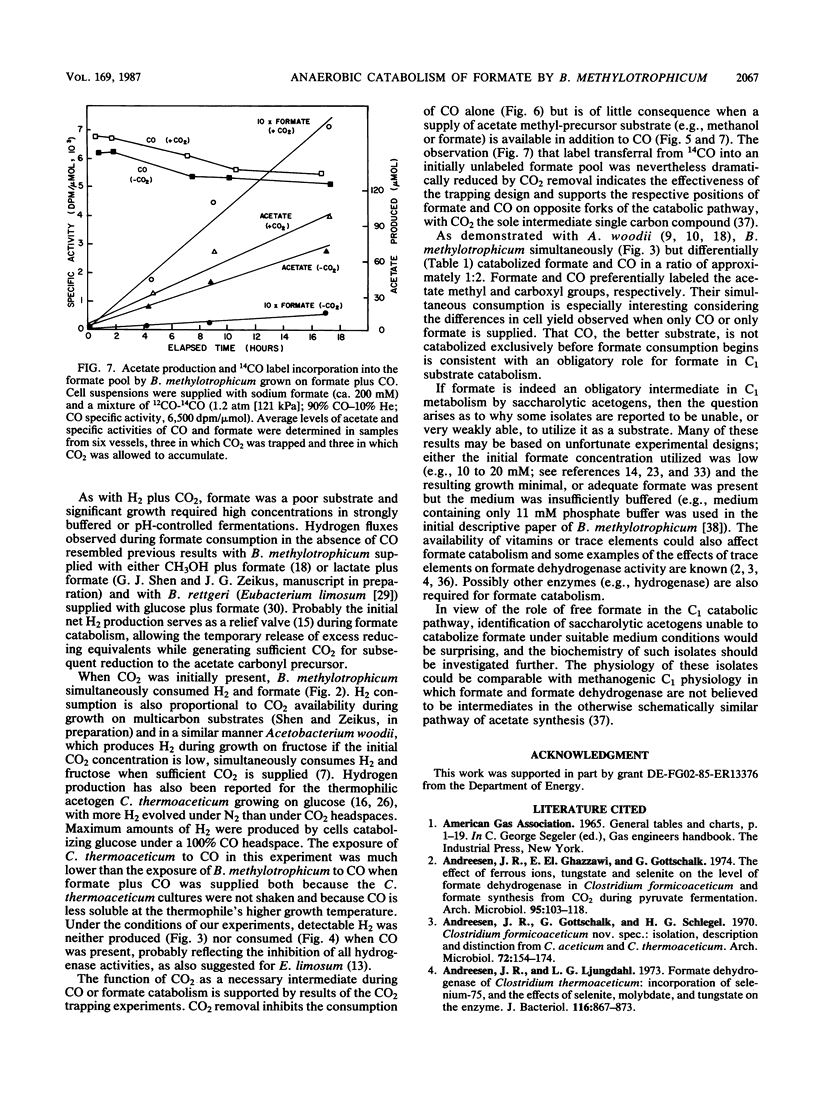
The catabolism of sodium formate to acetate and carbon dioxide by the anaerobic acetogen Butyribacterium methylotrophicum was analyzed by fermentation time course and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Significant hydrogen production and consumption fluxes were observed during formate catabolism but not during the catabolism of formate plus CO. In the latter case, formate and CO were simultaneously consumed and label distribution studies with mixtures of 13C-labeled CO and formate demonstrated their preferential incorporation into the acetate carboxyl and methyl groups, respectively. Hydrogen consumption was inhibited by CO when both were present, whereas hydrogen and formate were simultaneously consumed when CO2 was supplied. Carbon dioxide was required for the conversion of CO to acetate, but a similar need was not observed when methanol plus CO or formate plus CO was present. These analyses indicate a bifurcated single-carbon catabolic pathway in which CO2 is the sole single-carbon compound that directly supplies the carbonyl and methyl group synthesis pathways leading to the formation of acetyl coenzyme A, the primary reduced product. We discuss causes for the reported inability of B. methylotrophicum to use formate as a sole substrate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen J. R., El Ghazzawi E., Gottschalk G. The effect of ferrous ions, tungstate and selenite on the level of formate dehydrogenase in Clostridium formicoaceticum and formate synthesis from CO2 during pyruvate fermentation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 4;96(2):103–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00590167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen J. R., Gottschalk G., Schlegel H. G. Clostridium formicoaceticum nov. spec. isolation, description and distinction from C. aceticum and C. thermoaceticum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;72(2):154–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00409521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen J. R., Ljungdahl L. G. Formate dehydrogenase of Clostridium thermoaceticum: incorporation of selenium-75, and the effects of selenite, molybdate, and tungstate on the enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):867–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.867-873.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun K., Gottschalk G. Effect of molecular hydrogen and carbon dioxide on chemo-organotrophic growth of Acetobacterium woodii and Clostridium aceticum. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00422533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY C. T., GEST H. BIOLOGICAL FORMATION OF MOLECULAR HYDROGEN. Science. 1965 Apr 9;148(3667):186–192. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3667.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Bryant M. P. Growth of Eubacterium limosum with Carbon Monoxide as the Energy Source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):70–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.70-74.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Davis C. L., Bryant M. P. Features of rumen and sewage sludge strains of Eubacterium limosum, a methanol- and H2-CO2-utilizing species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):12–19. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.12-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Drake H. L. Effects of cultivation gas phase on hydrogenase of the acetogen Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):466–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.466-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W., Zeikus J. G. Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):133–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.133-140.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerby R., Niemczura W., Zeikus J. G. Single-carbon catabolism in acetogens: analysis of carbon flow in Acetobacterium woodii and Butyribacterium methylotrophicum by fermentation and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance measurement. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1208–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1208-1218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENTZ K., WOOD H. G. Synthesis of acetate from formate and carbon dioxide by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):645–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorowitz W. H., Bryant M. P. Peptostreptococcus productus strain that grows rapidly with CO as the energy source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):961–964. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.961-964.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynd L. H., Zeikus J. G. Metabolism of H2-CO2, methanol, and glucose by Butyribacterium methylotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1415-1423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynd L., Kerby R., Zeikus J. G. Carbon monoxide metabolism of the methylotrophic acidogen Butyribacterium methylotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):255–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.255-263.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L., BARKER H. A. Tracer experiments on the mechanism of acetate formation from carbon dioxide by Butyribacterium rettgeri. J Bacteriol. 1954 Aug;68(2):216–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.2.216-226.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Influence of pH on Terminal Carbon Metabolism in Anoxic Sediments from a Mildly Acidic Lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1088–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1088-1095.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale S. W., Wood H. G. Acetate biosynthesis by acetogenic bacteria. Evidence that carbon monoxide dehydrogenase is the condensing enzyme that catalyzes the final steps of the synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):3970–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Saiki T., Liu S. M., Ljungdahl L. G. Purification and properties of NADP-dependent formate dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum, a tungsten-selenium-iron protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1826–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Kerby R., Krzycki J. A. Single-carbon chemistry of acetogenic and methanogenic bacteria. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1167–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.3919443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


