Abstract
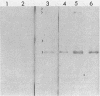
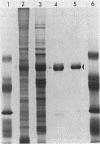
A characteristic of N2-fixing cyanobacteria in symbiotic associations appears to be release of N2-derived NH4+. The specific activity of the primary ammonium-assimilating enzyme, glutamine synthetase (GS), was found to be three- to fourfold lower in Nostoc sp. strain 7801 grown in symbiotic association with the bryophyte Anthoceros punctatus than in free-living Nostoc sp. strain 7801. Quantitative immunological assays with antisera against GS purified from Nostoc sp. strain 7801 and from Escherichia coli indicated that similar amounts of the GS protein were present in symbiotic (50 micrograms mg-1) and free-living (68 micrograms mg-1) cultures. The conclusion from these experiments is that GS is regulated by a posttranslational mechanism in Anthoceros-associated Nostoc sp. strain 7801. However, the results of comparative catalytic and immunological experiments between N2- and NH4+-grown free-living Nostoc sp. strain 7801 implied control of GS synthesis. A correlation was not observed between the level of GS expression and the extent of symbiotic heterocyst differentiation in Nostoc sp. strain 7801 associated with A. punctatus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. B., Arnon D. I. Studies on Nitrogen-Fixing Blue-Green Algae. I. Growth and Nitrogen Fixation by Anabaena Cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):366–372. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Lever J. Components of histidine transport: histidine-binding proteins and hisP protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1096–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann L., Baumann P. Studies of relationship among terrestrial Pseudomonas, Alcaligenes, and enterobacteria by an immunological comparison of glutamine synthetase. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00407923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Tuli R., Haselkorn R. A cloned cyanobacterial gene for glutamine synthetase functions in Escherichia coli, but the enzyme is not adenylylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3393–3397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E., Bancroft S., Rhee S. G., Kustu S. The product of a newly identified gene, gInF, is required for synthesis of glutamine synthetase in Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1662–1666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurn B. A., Chantler S. M. Production of reagent antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):104–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S. G., McKereghan K. Mutations affecting glutamine synthetase activity in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1006–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1006-1016.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Hirschman J., Burton D., Jelesko J., Meeks J. C. Covalent modification of bacterial glutamine synthetase: physiological significance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):309–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00330979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks J. C., Wolk C. P., Thomas J., Lockau W., Shaffer P. W., Austin S. M., Chien W. S., Galonsky A. The pathways of assimilation of 13NH4+ by the cyanobacterium, Anabaena cylindrica. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7894–7900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierzwicki-Bauer S. A., Haselkorn R. Differences in mRNA levels in Anabaena living freely or in symbiotic association with Azolla. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04173.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr J., Haselkorn R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase activity and synthesis in free-living and symbiotic Anabaena spp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):626–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.626-635.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr J., Keefer L. M., Keim P., Nguyen T. D., Wellems T., Heinrikson R. L., Haselkorn R. Purification, physical characterization, and NH2-terminal sequence of glutamine synthetase from the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13091–13098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. B., Peters G. A., Toia R. E., Mayne B. C. Azolla-Anabaena Relationships: VII. Distribution of Ammonia-assimilating Enzymes, Protein, and Chlorophyll between Host and Symbiont. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):463–467. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D., Rowell P. Effects of L-methionine-DL-sulphoximine on the assimilation of newly fixed NH3, acetylene reduction and heterocyst production in Anabaena cylindrica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):846–856. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]