Abstract
Histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein (HPr) is common to all of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase systems (PTS) in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, except the fructose-specific PTS. Strains which lack HPr activity (ptsH) have been characterized in the past, and it has proved difficult to delineate between tight and leaky mutants. In this study four different parameters of ptsH strains were measured: in vitro sugar phosphorylation activity of the mutant HPr; detection of 32P-labeled P-HPr; ability of monoclonal antibodies to bind mutant HPr; and sensitivity of ptsH strains to fosfomycin. Tight ptsH strains could be defined; they were fosfomycin resistant and produced no HPr protein or completely inactive mutant HPr. All leaky ptsH strains were fosfomycin sensitive, usually produced normal amounts of mutant HPr protein, and had low but measurable activity, and HPr was detectable as a phosphoprotein. This indicates that the regulatory functions of the PTS require a very low level of HPr activity (about 1%). The antibodies used to detect mutant HPr in crude extracts were two monoclonal immunoglobulin G antibodies Jel42 and Jel44. Both antibodies, which have different pIs, inhibited PTS sugar phosphorylation assays, but the antibody-HPr complex could still be phosphorylated by enzyme I. Preliminary evidence suggests that the antibodies bind to two different epitopes which are in part located in a beta-sheet structure.
Full text
PDF
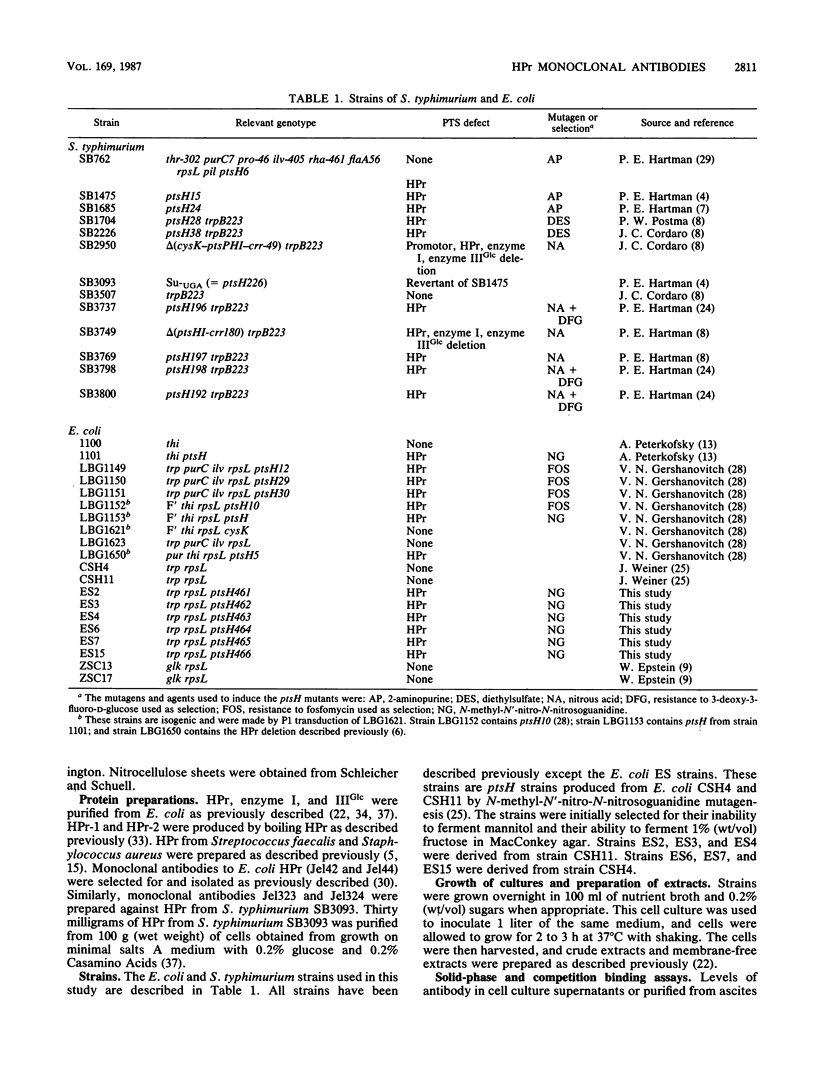







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Williamson A. R., Askonas B. A. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel and its application to immunoglobulins. Nature. 1968 Jul 6;219(5149):66–67. doi: 10.1038/219066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Williamson A. R., Askonas B. A. One cell-one immunoglobulin. Origin of limited heterogeneity of myeloma proteins. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj1160241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beneski D. A., Nakazawa A., Weigel N., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Isolation and characterization of a phosphocarrier protein HPr from wild type and mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14492–14498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyreuther K., Raufuss H., Schrecker O., Hengstenberg W. The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus. 1. Amino-acid sequence of the phosphocarrier protein HPr. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):275–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolshakova T. N., Dobrynina O. Y., Gershanovitch V. N. Isolation and investigation of the Escherichia coli mutant with the deletion in the ptsH gene. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80488-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro J. C., Melton T., Stratis J. P., Atagün M., Gladding C., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Fosfomycin resistance: selection method for internal and extended deletions of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase genes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;128(3):785–793. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.3.785-793.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordaro J. C., Roseman S. Deletion mapping of the genes coding for HPr and enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):17–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.17-29.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. J., Epstein W. Phosphorylation of D-glucose in Escherichia coli mutants defective in glucosephosphotransferase, mannosephosphotransferase, and glucokinase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1189–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1189-1199.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Reuse H., Roy A., Danchin A. Analysis of the ptsH-ptsI-crr region in Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence of the ptsH gene. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbaere L. T., Bruse L. M., Waygood E. B. Preliminary x-ray data for the HPr protein of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher J., Pevec B., Beyreuther K., Kiltz H. H., Hengstenberg W. Streptococcal phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase system: amino acid sequence and site of ATP-dependent phosphorylation of HPr. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6543–6551. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Wilson G. The role of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent kinase system in beta-glucoside catabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):988–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Cassidy P. J., Kropp H. The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):364–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalbitzer H. R., Hengstenberg W., Rösch P., Muss P., Bernsmann P., Engelmann R., Dörschug M., Deutscher J. HPr proteins of different microorganisms studied by hydrogen-1 high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance: similarities of structures and mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):2879–2885. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E., Drobny G. P., Waygood E. B. Two-dimensional 1H NMR studies of histidine-containing protein from Escherichia coli. 1. Sequential resonance assignments. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7760–7769. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E., Waygood E. B. Two-dimensional 1H NMR studies of histidine-containing protein from Escherichia coli. 3. Secondary and tertiary structure as determined by NMR. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7774–7781. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Lewis J. R., Morgan A. R., Mosmann T. R., Singh B. Monoclonal antibodies showing sequence specificity in their interaction with single-stranded DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1707–1721. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. G., Britton P., Parra F., Boronat A., Kornberg H. Expression of the ptsH+ gene of Escherichia coli cloned on plasmid pBR322. A convenient means for obtaining the histidine-containing carrier protein HPr. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 29;149(2):288–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo R. L., Khandelwal R. L., Waygood E. B. Isoelectrophoretic separation and the detection of soluble proteins containing acid-labile phosphate: use of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system as a model system for N1-P-histidine- and N3-P-histidine-containing proteins. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 15;139(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo R. L., Waygood E. B. An enzymatic method for [32P]phosphoenolpyruvate synthesis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo R. L., Waygood E. B. Determination of the levels of HPr and enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;61(1):29–37. doi: 10.1139/o83-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton T., Kundig W., Hartman P. E., Meadow N. 3-Deoxy-3-fluoro-D-glucose-resistant Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in the phosphoenolpyruvate:glycose phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;128(3):794–800. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.3.794-800.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):232–269. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.232-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers D. A., Roseman S. The primary structure of Salmonella typhimurium HPr, a phosphocarrier protein of the phosphoenolpyruvate:glycose phosphotransferase system. A correction. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15212–15214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusina O. Iu, Gershanovich V. N. Kartirovanie mutatsii vnutri genov, kodiruiushchikh ferment I i belok Hpr fosfoenolpiruvatzavisimoi fosfotransferaznoi sistemy u Escherichia coli K-12. Soobshchenie II. Kartirovanie mutatsii vnutri gena ptsH. Genetika. 1983 Mar;19(3):397–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Simoni R. D., Roseman S. The physiological behavior of enzyme I and heat-stable protein mutants of a bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5870–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandonselaar M., Lee J. S., Delbaere L. T. Preliminary crystallographic data for a monoclonal Fab fragment specific for HPr of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 5;177(2):369–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Erickson E., el Kabbani O. A., Delbaere L. T. Characterization of phosphorylated histidine-containing protein (HPr) of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6938–6945. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Mattoo R. L. A novel phosphoprotein dependent on the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase system. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Feb-Mar;61(2-3):150–153. doi: 10.1139/o83-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Mattoo R. L., Peri K. G. Phosphoproteins and the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: evidence for IIImannose, IIIfructose, IIIglucitol, and the phosphorylation of enzyme IImannitol and enzyme IIN-acetylglucosamine. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(3):139–159. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Modified assay procedures for the phosphotransferase system in enteric bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B. Resolution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: fructose phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli into two components: enzyme IIfructose and fructose-induced HPr-like protein (FPr). Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):1144–1146. doi: 10.1139/o80-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Steeves T. Enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system of Escherichia coli. Purification to homogeneity and some properties. Can J Biochem. 1980 Jan;58(1):40–48. doi: 10.1139/o80-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel N., Powers D. A., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Primary structure and active site of a general phosphocarrier protein (HPr) from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14499–14509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




