Abstract
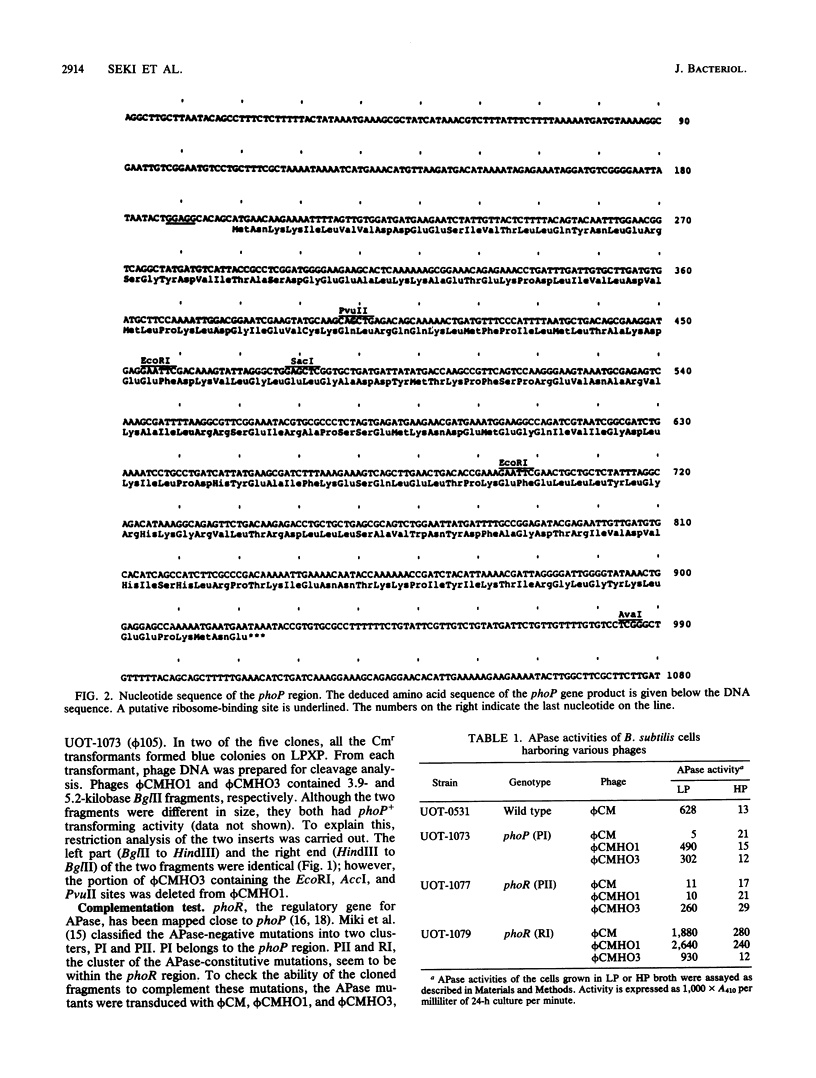
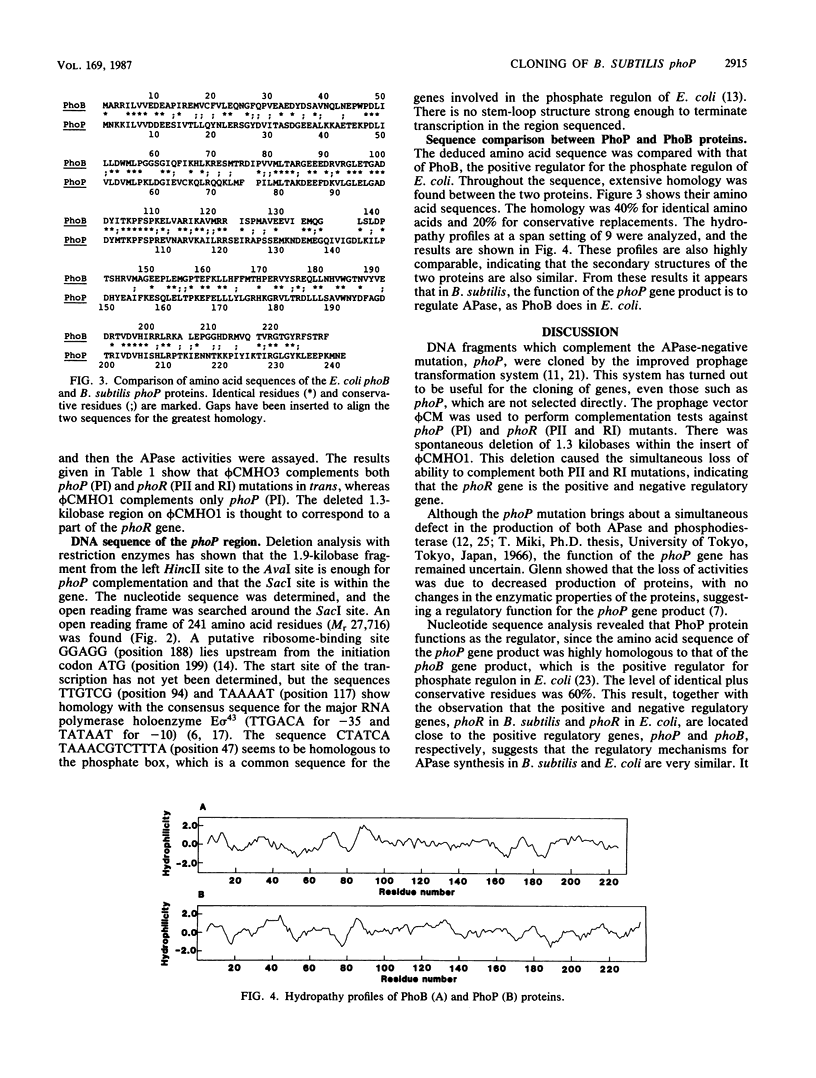
Two DNA fragments which complement the alkaline phosphatase-negative mutation phoP of Bacillus subtilis were cloned from a B. subtilis chromosome with the prophage vector phi CM (a derivative of phi 105). One of the fragments contained the regulatory gene phoR in addition to phoP. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the phoP region revealed that the phoP gene product consists of 241-amino-acid residues and that the sequence of these amino acids is extensively homologous with the sequence of the phoB gene product. This protein is the positive regulator for the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli. It therefore appears that phoP is a regulatory gene for alkaline phosphatase synthesis in B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang C. N., Kuang W. J., Chen E. Y. Nucleotide sequence of the alkaline phosphatase gene of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;44(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drury L. S., Buxton R. S. DNA sequence analysis of the dye gene of Escherichia coli reveals amino acid homology between the dye and OmpR proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4236–4242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., LeCoq D., Spence J., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the spo0A locus and its deduced product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J., Law M. F. Relationship between lysogeny, spontaneous induction, and transformation efficiencies in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1256–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1256-1259.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitt M. A., Wang L. F., Doi R. H. A strong sequence homology exists between the major RNA polymerase sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7178–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn A. R., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis 168. Comparison of alkaline phosphatase from sporulating and vegetative cells. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1230129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant W. D. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis 168. Control of synthesis of alkaline phosphatase. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):363–369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves H. Microbiological aspects of wood chip storage in tropical environments. Aust J Biol Sci. 1975 Jun;28(3):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi T., Kudoh J., Tsunasawa S. Amino-terminal structure of spoOA protein and sequence homology with spoOF and spoOB proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):371–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00422059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Saito H., Ikeda Y. A method for construction of specialized transducing phage rho 11 of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hégarat J. C., Anagnostopoulos C. Purification, subunit structure and properties of two repressible phosphohydrolases of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):525–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the phoB gene, the positive regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Minami Z., Ikeda Y. The genetics of alkaline phosphatase formation in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1965 Nov;52(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.5.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukushina J. I., Ikeda Y. Genetic analysis of the developmental processes during germination and outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis spores with temperature-sensitive mutants. Genetics. 1969 Sep;63(1):63–74. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L. Mapping of a temperate bacteriophage active on Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.38-44.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A., Koshland D. E., Jr, Stock J. Homologies between the Salmonella typhimurium CheY protein and proteins involved in the regulation of chemotaxis, membrane protein synthesis, and sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7989–7993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. PHO-regulon of Escherichia coli K12: a minireview. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtzel E. T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. Osmoregulation of gene expression. I. DNA sequence of the ompR gene of the ompB operon of Escherichia coli and characterization of its gene product. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13685–13691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Maruo B. Alkaline phosphatase possessing alkaline phosphodiesterase activity and other phosphodiesterases in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.108-114.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Kazami J., Yamashita S., Chibazakura T., Sone H., Kawamura F., Oda M., Isaka M., Kobayashi Y., Saito H. Revised assignment for the Bacillus subtilis spo0F gene and its homology with spo0A and with two Escherichia coli genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1063–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



