Abstract
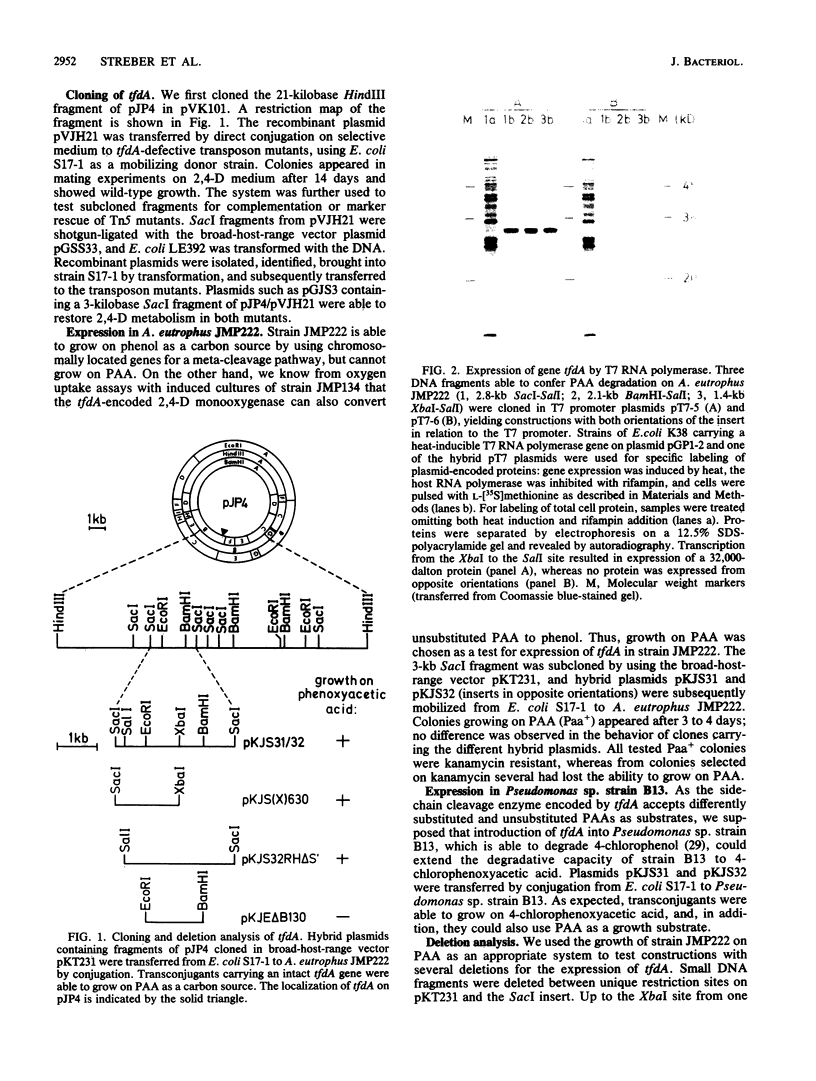
Plasmid pJP4 of Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134 contains all genes for the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Five of these genes, tfdB, tfdC, tfdD, tfdE, and tfdF, have recently been localized and cloned (R. H. Don, A. J. Weightman, H.-J. Knackmuss, and K. N. Timmis, J. Bacteriol. 161:85-90, 1985). Gene tfdA, which codes for the 2,4-D monooxygenase, has now been found by mutagenesis with transposon Tn5. A 3-kilobase fragment of pJP4 cloned in a broad-host-range vector could complement the 2,4-D-negative phenotype of two mutants which lacked 2,4-D monooxygenase activity. The cloned tfdA gene was also transferred to A. eutrophus JMP222, which is a cured derivative of JMP134. The recombinant strain could utilize phenoxyacetic acid as a sole source of carbon and energy. Pseudomonas sp. strain B13, containing the cloned tfdA, was able to degrade phenoxyacetic acid and 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid. Gene tfdA was subcloned and analyzed by deletions. Expression of 2,4-D monooxygenase in Escherichia coli containing a 1.4-kilobase subfragment was demonstrated by radioisotopic enzyme assay, and a protein of 32,000-dalton molecular mass was detected by labeling experiments. A 2-kilobase subfragment containing tfdA has been sequenced. Sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 861 bases which was identified as the coding region of tfdA by insertion mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy P. S., Schulke J. W., Frazier L. M., Seidler R. J. Characterization of aquatic bacteria and cloning of genes specifying partial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1237-1245.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL G. R. Some morphological and biochemical characteristics of a soil bacterium which decomposes 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Oct;3(6):821–840. doi: 10.1139/m57-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Timmis K. N. Host: vector systems for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:47–67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Genetic and physical map of the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degradative plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):466–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.466-468.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Weightman A. J., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Transposon mutagenesis and cloning analysis of the pathways for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 3-chlorobenzoate in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134(pJP4). J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.85-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Hellwig M., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00696222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. C., SMITH B. S. The photochemical inactivation and microbial metabolism of the chlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicides. Biochem J. 1954 May 15;57(329TH):xxx–xxx. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Fernley H. N., Davies J. I. Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1220543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. R., Appleton J., Pemberton J. M. Isolation and characterization of the pesticide-degrading plasmid pJP1 from Alcaligenes paradoxus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):798–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.798-804.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M., Bagdasarian M. M., Timmis K. N. Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWWO from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7458–7462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Krisch H. M. Omega mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria: a selectable interposon which is strongly polar in a wide range of bacterial species. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Meyer M., Schlegel H. G. Transfer and expression of the herbicide-degrading plasmid pJP4 in aerobic autotrophic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Feb;134(2):92–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00407938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Microbial degradation of halogenated compounds. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):135–142. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4696.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Leppik R. A., Rekik M., Mermod N., Lehrbach P. R., Reineke W., Timmis K. N. Gene order of the TOL catabolic plasmid upper pathway operon and oxidation of both toluene and benzyl alcohol by the xylA product. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.455-461.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P. New versatile cloning and sequencing vectors based on bacteriophage M13. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M. A. Indicator media for microorganisms degrading chlorinated pesticides. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):104–107. doi: 10.1139/m75-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEENSON T. I., WALKER N. The pathway of breakdown of 2:4-dichloro- and 4-chloro-2-methyl-phenoxyacetic acid by bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):146–155. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwien U., Schmidt E. Improved degradation of monochlorophenols by a constructed strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.33-39.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe G. S. Broad host range cloning vectors for gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
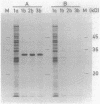
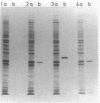
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. E., Finn R. K. Growth rates of a pseudomonad on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.181-184.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Plasmid gene organization: naphthalene/salicylate oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):874–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]