Abstract
In a cell-free system programmed with a plasmid bearing a malP'-'lacZ gene fusion under the control of malPp, beta-galactosidase synthesis was strictly dependent on the presence of both the MalT activator protein and the inducer of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon. We show that, among all maltodextrins tested (from maltose to maltoheptaose), only maltotriose was able to induce beta-galactosidase synthesis. Likewise, in an in vitro transcription system, initiation of transcription at malPp required the presence of the MalT protein and maltotriose along with the RNA polymerase holoenzyme; neither maltose nor maltotetraose could substitute for maltotriose.
Full text
PDF

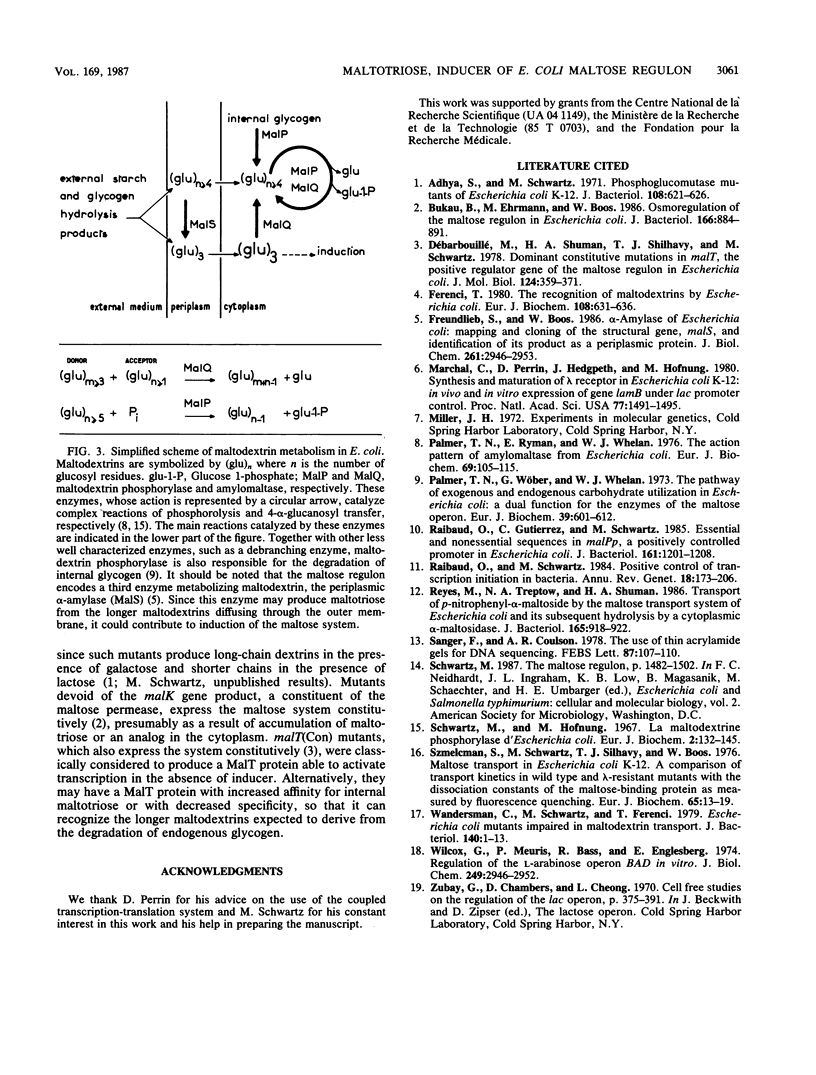
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Schwartz M. Phosphoglucomutase mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):621–626. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.621-626.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Ehrmann M., Boos W. Osmoregulation of the maltose regulon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):884–891. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.884-891.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Schwartz M. Dominant constitutive mutations in malT, the positive regulator gene of the maltose regulon in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T. The recognition of maltodextrins by Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):631–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlieb S., Boos W. Alpha-amylase of Escherichia coli, mapping and cloning of the structural gene, malS, and identification of its product as a periplasmic protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2946–2953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchal C., Perrin D., Hedgpeth J., Hofnung M. Synthesis and maturation of lambda receptor in Escherichia coli K-12: in vivo and in vitro expression of gene lamB under lac promoter control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1491–1495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer T. N., Ryman B. E., Whelan W. J. The action pattern of amylomaltase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):105–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer T. N., Wöber G., Whelan W. J. The pathway of exogenous and endogenous carbohydrate utilization in Escherichia coli: a dual function for the enzymes of the maltose operon. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):601–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Gutierrez C., Schwartz M. Essential and nonessential sequences in malPp, a positively controlled promoter in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1201–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1201-1208.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes M., Treptow N. A., Shuman H. A. Transport of p-nitrophenyl-alpha-maltoside by the maltose transport system of Escherichia coli and its subsequent hydrolysis by a cytoplasmic alpha-maltosidase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):918–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.918-922.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Hofnung M. La maltodextrine phosphorylase d'Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Sep;2(2):132–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Schwartz M., Silhavy T. J., Boos W. Maltose transport in Escherichia coli K12. A comparison of transport kinetics in wild-type and lambda-resistant mutants as measured by fluorescence quenching. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Schwartz M., Ferenci T. Escherichia coli mutants impaired in maltodextrin transport. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.1-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox G., Meuris P., Bass R., Englesberg E. Regulation of the L-arabinose operon BAD in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2946–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




